Abstract
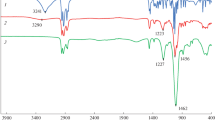
Two novel hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents (HDESs), composed of alkyl (=Hexyl, Nonan) ethylenediaminium and menthol (Men), namely Hexen/Men and Nonen/Men, were synthesized. Hexen and Nonen primarily act as hydrogen bond acceptors, with Men serving as the principal hydrogen bond donor. After the formation of HDES, the IR absorption peaks of Hexen, Nonen's–NH2, and Men–OH fused into a wider peak, the 1H-NMR spectra of Men–OH, shifted to a lower field. Furthermore, a significant redshift approximately 300 cm−1 was detected in the vibrational frequency of the Men–OH functional group when performing density functional theory (DFT) calculations for the HDESs. These results support the development of stronger O–H···N bonds between Hexen/Nonen–NH2 and Men–OH, and the calculated sum of hydrogen bonding energy was approximately 56 mol·kg–1, categorizing it as an intermediate-strength hydrogen bond. Both HDESs have ethylenediamine polar heads in their hydrogen bond acceptors, which have chelating characteristics that help them coordinate with transition metal ions. Metal ions such as Cu(II), Co(II), and Ni(II) were successfully extracted from aqueous solutions at a concentration of 10 mmol·L–1using HDESs. The Cu(II) and Ni(II) extraction efficiencies exceeded 90%, indicating their effectiveness. Notably, even at higher metal ion concentrations (100 mmol·L–1), the extraction efficiencies of all three metal ions remained consistently below 80%. This indicates that the HDESs can suitably collect trace metal ions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schaeffer, N., Martins, M., Seiça, Neves, C., Pinho, S.P., Coutinho, Joao, A.P.: Sustainable Hydrophobic Terpene-based Eutectic Solvents for The Extraction and Separation of Metals. Chem. Commun., 54, 8104–8107 (2018)
Vekariya, R.L.: A Review of Ionic Liquids: Applications Towards Catalytic Organic Transformations. J. Mol. Liq. 227, 44–60 (2017)
Zeng, S.J., Zhang, X.P., Bai, L., Zhang, X.C., Wang, H., Wang, J.J., Bao, D., Li, M.D., Liu, X.Y.: Ionic Liquid-Based CO2 Capture Systems: Structure. Interaction and Process. Chem. Rev. 117, 9625–9673 (2017)
Fan, M.J., Jin, Y.Y., Han, Y.Y., Ma, Lin, L., Wen, Q., Lu, Y., Zhou, F., Liu, W.M.: The Effect of Chemical Structure on The Tribological Performance of Perfluorosulfonate Ils as Lubricants for Ti-6Al-4V Tribopairs. J. Mol. Liq. 321, 114286 (2021)
Hua, E., Xu, Y., Zhao, H.: Properties of Mono-Protic Ionic Liquids Composed of Hexylammonium and Hexylethylenediaminium Cations with Trifluoroacetate and Bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) Imide Anions. J. Mol. Liq. 276, 379–384 (2019)
Álvaro, S.M., Ruth, R.R., Antonio, V.H., Bárbara, S.R., Miguel, Á.R.: Deep Eutectic Solvents. The New Generation of Green Solvents in Analytical Chemistry.Trac-Trend. Anal. Chem.134,116108 (2021)
Jeong, K.M., Lee, M.S., Nam, M.W., Zhao, J., Jin, Y., Lee, D.K., Kwon, S.W., Jeong, J.H., Lee, J.M.: Tailoring and Recycling of Deep Eutectic Solvents as Sustainable and Efficient Extraction Media. J. Chromatogr. A 1424, 7–10 (2015)
Chen, W.J., Xue, Z.M., Wang, J.F., Jiang, J.Y., Zhao, X.H., Mu, T.C.: Investigation on the Thermal Stability of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Acta. Phys-Chim. Sin. 34, 904–911 (2018)
Tang, B., Zhang, H., Row, K.H.: Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents in The Extraction and Separation of Target Compounds from Various Samples. J. Sep. Sci. 38, 1053–1064 (2015)
Zhang, M., Song, H., Zheng, C., Liu, S., Lin, Z., Liu, Y., Wu, W., Gao, X.: Highly Efficient Selective Extraction of Mo with Novel Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 71, 1492–1501 (2021)
Clarke, C.J., Tu, W.C., Levers, O., Bröhl, A., Hallett, J.P.: Green and Sustainable Solvents in Chemical Processes. Chem. Rev. 118, 747–800 (2018)
Zhang, Q.H., De-Oliveira, Vigier, K., Royer, S. Jérôme, F.: Deep Eutectic Solvents: Syntheses, Properties and Applications [J]. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 7108–7146 (2012)
Samarov, A.A., Smirnov, M.A., Sokolova, M.P., Popova, E.N., Toikka, A.M.: Choline Chloride Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Extraction Media for Separation Of N-Hexane–Ethanol Mixture. Fluid. Phase. Equilibr. 448, 123–127 (2017)
Li, X., Row, K.H.: Development of Deep Eutectic Solvents Applied in Extraction and Separation. J. Sep. Sci. 39, 3505–3520 (2016)
Altamash, T., Atilhan, M., Aliyan, A., Ullah, R., García, G., Aparicio, S., García, G., Aparicio, S.: Insights into Choline Chloride-Phenylacetic Acid Deep Eutectic Solvent for CO2 Absorption [J]. RSC Adv. 6, 109201–109210 (2016)
Bai, C., Wei, Q., Ren, X.: Selective Extraction of Collagen Peptides with High Purity from Cod Skins by Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5, 7220–7227 (2017)
Cheng, H.M., Huang, Y., Lv, H.Q., Li, L.G., Meng, Q.G., Yuan, M.Z., Ling, Y.X., Jin, M.L.: Insights into The Liquid Extraction Mechanism of Actual High-Strength Phenolic Waste Water by Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 368, 120609 (2022)
Kollau, L., Vis, M., Van, Den, Bruinhorst, A., Esteves, A., Catarina, C., Tuinier, R.: Quantification of The Liquid Window of Deep Eutectic Solvents [J]. Chem. Commun. 54, 13351–13354 (2018)
Martins, M.A.R., Pinho, S.P., Coutinho, J.A.P.: Insights into The Nature of Eutectic and Deep Eutectic Mixtures. J. Solution Chem. 48, 962–982 (2018)
Smith, E.L., Abbott, A.P., Ryder, K.S.: Deep Eutectic Solvents (Dess) And Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 114, 11060–11082 (2014)
Hua, E., Liu, J., Naren, G.: Studies on Amino Acid Type Protic Ionic Liquid Comprising N-2-Ethylhexylethylenediaminium Cation Coupled with The DL-Hexanoylalaninate Anion. J. Solution Chem. 50, 941–953 (2021)
Nakayama, C., Harada, M., Iida, M.: Properties of Protic Ionic Liquids Comprised of N-Alkyldiethylenetriamine and Their Complexation of Copper (II) Ions. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 31, 3744–3754 (2017)
Hua, E., Wang, H.: Properties of Protic Ionic Liquids Composed of N-Alkyl (=Hexyl, Octyl And 2-Ethylhexyl) Ethylhexylethylenediamine Cations with Trifluoromethanesulfonate and Trifluoroacetate Anion. J. Mol. Liq. 220, 649–656 (2016)
Robert, G.: Density-Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules, Oxford Science (1989)
Zhao, Y., Truhlar, D.G.: The M06 Suite of Density Functionals for Main Group Thermochemistry, Thermochemical Kinetics, Noncovalent Interactions, Excited States, And Transition Elements: Two New Functionals and Systematic Testing of Four M06-Class Functionals And 12 Other Functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 120, 215–241 (2017)
Hunt, P.A., Ashworth, C.R., Matthews, R.P.: Hydrogen Bonding in Ionic Liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 1257–1288 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Foundation of Ningxia Higher Education (Project Number: NGY2020063). We are also grateful to Prof. Masafumi Harada of Nara Women's University for helping in the discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CW conducted the experiments and wrote the manuscript. EH designed the experiment, performed the analysis, and edited the English text of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Hua, E. Extraction of Metal Ions Using Novel Deep Eutectic Solvents with Chelating Amine. J Solution Chem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-024-01378-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-024-01378-4