Abstract
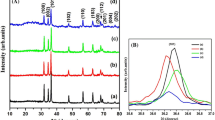
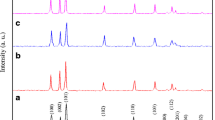
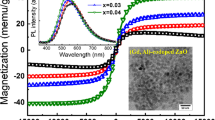
Strong room temperature superparamagnetic properties have been achieved in Zn0.94Li0.03Fe0.03O nanoparticles within a magnetic field of ± 20,000 Oe. High-purity ZnO, Zn0.97Li0.03O, Zn0.94Li0.03Mn0.03O, and Zn0.94Li0.03Fe0.03O nanostructures were synthesized by means of the coprecipitation method. The XRD crystallographic planes and HRTEM of the synthesized compositions showed that a single phase of a ZnO hexagonal wurtzite structure was obtained with the absence of any secondary phases or magnetic cluster. Pure ZnO powders show asymmetrical nanoparticles with a certain degree of agglomeration and approximately have an average particle size of 37 nm. The TEM image of Li-monodoped ZnO powders displays uniform spherical nanoparticles with less agglomeration, and the average particle size was reduced to 35 nm. The image of the (Li, Mn) codoped ZnO sample illustrates that the particles of ZnO are transformed to elongated shapes without agglomeration with an average particle size of 32 nm. In case of (Li, Fe) codoped ZnO powders, the image clearly shows a mixture of uniform nanospherical and elongated particles with a small average particle size of 27 nm. The absorption edge of ZnO is red shifted to more wavelength absorption due to (Li, Mn) and (Li, Fe) codoping, and it becomes sharper after Li monodoping which is a dynamic factor in the optoelectronic applications. Interestingly, the Zn0.94Li0.03Fe0.03O composition exhibits a superparamagnetic behavior at room temperature; it obviously shows a semi-saturation magnetization of 0.02 emu/g but has a nearly very small coercivity of 14 Oe. The instantaneous presence of both ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism in Zn0.94Li0.03Fe0.03O gives rise to the disordered state of superparamagnetism.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raizada, P., Sudhaik, A., Patial, S., Hasija, V., Khan, A.A.P., Singh, P., Gautam, S., Kaur, M., Nguyen, V.-H.: Engineering nanostructures of CuO-based photocatalysts for water treatment: Current progress and future challenges. Arab. J. Chem. 13, 8424–8457 (2020)
Bousslama, W., Elhouichet, H., Férid, M.: Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Fe doped ZnO nanocrystals under sunlight irradiation. Optik 134, 88–98 (2017)
Kazmi, J., Ooi, P.C., Goh, B.T., Lee, M.K., Wee, M.F.M.R., Karim, S.S.A., Razad, S.R.A., Mohamed, M.A.: Bi-doping improves the magnetic properties of zinc oxide nanowires. RSC Adv. 10, 23297–23311 (2020)
Punnoose, A., Reddy, K.M., Hays, J., Thurber, A., Engelhard, M.H.: Magnetic gas sensing using a dilute magnetic semiconductor, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 112509 (2006)
Kayani, Z.N., Bashir, H., Riaz, S., Naseem, S.: Optical properties and antibacterial activity of V doped ZnO used in solar cells and biomedical applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 115, 121–129 (2019)
Liu, H., Li, G.P., Xu, D.J.E.N.N., Lin, Q.L., Gao, X.D., Wang, C.L.: Room temperature ferromagnetism in D-D neutron irradiated ZnO single crystals. J Supercond Nov Magn. 33, 1535–1542 (2020)
Yaseen, M., Ambreen, H., Zia, M., Javed, H.M.A., Mahmood, A., Murtaza, A.: Study of half metallic ferromagnetism and optical properties of Mn-doped CdS. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 34, 135–141 (2021)
Sharma, K.R., Negi, N.S.: Doping effect of cobalt on various properties of nickel oxide prepared by solution combustion method. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 34, 633–645 (2021)
de Santana, W.M.O.S., Caetano, B.L., de Annunzio, S.R., Pulcinelli, S.H., Ménager, C., Fontana, C.R., Santilli, C.V.: Conjugation of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and curcumin photosensitizer to assist in photodynamic therapy. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 196, 111297 (2020)
Rosowska, J., Kaszewski, J., Witkowski, B., Wachnicki, Ł., Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I., Godlewski, M.: The effect of iron content on properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by microwave hydrothermal method. Optical Materials 109, 110089 (2020)
Look, D.C.: Recent advances in ZnO materials and devices. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 80, 383–387 (2001)
Kumar, S., Kumar, M., Kumar, A., Sharma, S., Shahi, P., Chatterjee, S., Ghosh, A.K.: Investigations on structural and optical properties of Al-modified ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 7715–7723 (2020)
Peter, I.J., Praveen, E., Vignesh, G., Nithiananthi, P.: ZnO nanostructures with different morphology for enhanced photocatalytic activity. Mater. Res. Express 4, 124003 (2017)
Yakout, S.M., El-Sayed, A.M.: Synthesis, structure, and room temperature ferromagnetism of Mn and/or Co doped ZnO nanocrystalline. J Supercond Nov Magn 29, 1593–1599 (2016)
Wang, J., Wan, J., Chen, K.: Facile synthesis of superparamagnetic Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles in liquid polyols. Mater. Lett. 64, 2373–2375 (2010)
Mukherjee, S., Liang, L., Veiseh, O.: Recent advancements of magnetic nanomaterials in cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 12, 147 (2020)
Vettumperumal, R., Kalyanaraman, S., Santoshkumar, B., Thangavel, R.: Magnetic properties of high Li doped ZnO sol–gel thin films. Mater. Res. Bull. 50, 7–11 (2014)
Ahmed, S.A.: Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO samples. Results in Physics 7, 604–610 (2017)
Beltrán, J.J., Barrero, C.A., Punnoose, A.: Understanding the role of iron in the magnetism of Fe doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 15284–15296 (2015)
Duan, J., Wang, H., Wang, H., Zhang, J., Wu, S., Wang, Y.: Mn-doped ZnO nanotubes: from facile solution synthesis to room temperature ferromagnetism. Cryst Eng Comm 14, 1330–1336 (2012)
Djerdj, I., Garnweitner, G., Arcon, D., Pregelj, M., Jaglicicef, Z., Niederberger, M.: Diluted magnetic semiconductors: Mn/Co-doped ZnO nanorods as case study. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 5208–5217 (2008)
Zulfiqar, M., Zubair, A., Khan, T., Hua, N., Ilyas, S., Fashu, A.M., Afzal, M.A., Safeen, R., Khan. Oxygen vacancies induced room temperature ferromagnetism and enhanced dielectric properties in Co and Mn co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 9463–9474 (2021)
Tariq, M., Li, Y., Li, W., Yu, Z., Li, J., Hu, Y., Zhu, M., Jin, H., Li, Y., Skotnicova, K.: Enhancement of ferromagnetic properties in (Fe, Ni) co-doped ZnO flowers by pulsed magnetic field processing. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 8226–8232 (2019)
Shawuti, S., Sherwani, A.R., Can, M.M., Gülgün, M.A.: Complex impedance analyses of Li doped ZnO electrolyte materials. Sci. Rep. 10, 8228 (2020)
Elilarassi, R., Chandrasekaran, G.: Optical, electrical and ferromagnetic studies of ZnO: Fe diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles for spintronic applications. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 186, 120–131 (2017)
Akbarian, M., Mahjoub, S., Elahi, S.M., Zabihi, E., Tashakkorian, H.: Urtica dioica L. extracts as a green catalyst for the biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: characterization and cytotoxic effects on fibroblast and MCF-7 cell lines. New J. Chem. 42, 5822–5833 (2018)
Sandeep, K.M., Bhat, S., Serrao, F.J., Dharmaprakash, S.M.: Li doped ZnO thin films for optoelectronic applications. AIP Conference Proceedings 1731, 080055 (2016)
Uddin, M.T., Hoque, M.E., Bhoumick, M.C.: Facile one-pot synthesis of heterostructure SnO2/ ZnO photocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of organic dye. RSC Adv. 10, 23554–23565 (2020)
Bhatt, A.S., Ranjitha, R., Santosh, M.S., Ravikumar, C.R., Prashantha, S.C., Maphanga, R.R., Lenz e Silva, G.F.B.: Optical and electrochemical applications of Li-doped NiO nanostructures synthesized via facile microwave technique. Materials 13, 2961 (2020)
López-Suárez, A., Acosta, D., Magaña, C., Hernández, F.: Optical, structural and electrical properties of ZnO thin films doped with Mn. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 7389–7397 (2020)
Srinivasulu, T., Saritha, K., Reddy, K.T.R.: Synthesis and characterization of Fe-doped ZnO thin films deposited by chemical spray pyrolysis. Modern Electronic Materials 3, 76–85 (2017)
Rezende, C.P., da Silva, J.B., Mohallem, N.D.S.: Influence of drying on the characteristics of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Braz. J. Phys. 39, 248–251 (2009)
Thi, T.U.D., Nguyen, T.T., Thi, Y.D., Thi, K.H.T., Phan, B.T., Pham, K.N.: Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using orange fruit peel extract for antibacterial activities. RSC Adv. 10, 23899–23907 (2020)
Shamhari, N.M., Wee, B.S., Chin, S.F., Kok, K.Y.: Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles with small particle size distribution. Acta Chim. Slov. 65, 578–585 (2018)
Largani, S.H., Pasha, M.A.: The effect of concentration ratio and type of functional group on synthesis of CNT–ZnO hybrid nanomaterial by an in situ sol–gel process. Int Nano Lett 7, 25–33 (2017)
Yakout, S.M.: Pure and Gd-based Li, Na, Mn or Fe codoped ZnO nanoparticles: Insights into the magnetic and photocatalytic properties. Solid State Sci. 83, 207–217 (2018)
Mohapatra, J., Mishra, D.K., Singh, S.K.: Superparamagnetic behavior in chemically synthesized nanocrystalline Zn0.99Ni0.01O powders. Materials Letters 75, 91–94 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youssef, A.M., Yakout, S.M. Robust Room Temperature Superparamagnetic Properties of ZnO Nanostructures: Li-Based Fe Dual Dopants. J Supercond Nov Magn 34, 3011–3017 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05972-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05972-1