Abstract
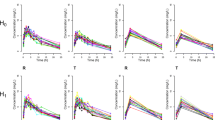
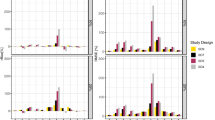
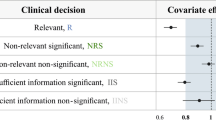
Key elements of pharmacokinetics (PK) studies include both, the number of sampling points (NSP) as well as the spacing between the sampling points (SSP). Optimization of the SSP is discussed in guidelines of all key regulatory agencies (RA). Those however, provide only very general rules on how to properly distribute the NSPs in proposed PK studies. Here we demonstrate that the six sigma (SX) method can be effectively used to assess the quality of SSPs. We have tested a modified SX method analyzing 466 PK profiles from 16 studies including a total of 368 healthy volunteers. Non-compartmental modeling was used to estimate PK parameters. The arithmetic means of minimum and maximum values of SX obtained for each subject in all studies were 1.97 and 3.83, respectively. The method described here allows comparing quality of studies performed at different centers, even if they cover different chemical entities. We propose that the SX values can be used to assess quality of PK studies, what is consistent with recommendations of the RAs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
EMA (2010) Guideline on the investigation of bioequivalence. 1–27
FDA (2003a) Guidance for industry bioavailability and bioequivalence studies for orally administered drug products-general considerations. 1–26
HC (2012) Conduct and analysis of comparative bioavailability studies. 1–46
Bioequivalence Studies-Part B: oral modified release formulations. 1–136
FDA (2000) Guidance for industry and other stakeholders toxicological principles for the safety assessment of food ingredients. Redbook, pp 1–286
Sokovic M, Pavletic D, Fakin S (2005) Application of Six Sigma methodology for process design. J Mat Proces Tech 162–163:777–783
Elder BL (2008) Six Sigma in the Microbiology Laboratory. Clin Microb Newsl 30:143–147
De Vore D (2008) A six-sigma approach to stability testing. J Pharm Biomed Anal 47:413–421
Christian DR, Drilling S (2009) Implementing quality in laboratory policies and processes: using templates, project management, and six sigma, CRC Press, 1 edn. 1–1432
Llopis MA, Trujillo G, Llovet MI, Tarrés E, Ibarz M, Biosca C, Ruiz R, Kirchner MJ, Alvarez V, Busquets G, Doménech MV, Figueres C, Minchinela J, Pastor RM, Perich C, Ricós C, Sansalvador M, Palmada MS (2011) Quality indicators and specifications for key analytical-extranalytical processes in the clinical laboratory, Five years’ experience using the Six Sigma concept. Clin Chem Lab Med 49:463–470
Johnstone C, Pairaudeau G, Pettersson JA (2011) Creativity, innovation and lean sigma: a controversial combination? Drug Discov Today 16:50–57
Junker B, Maheshwari G, Ranheim T, Altaras N, Stankevicz M, Harmon L, Rios S, D’anjou M (2011) Design-for-Six-Sigma To Develop a Bioprocess Knowledge Management Framework. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol 65:140–165
Chopra V, Bairagi M, Trivedi P, Nagar M (2012) A case study: application of statistical process control tool for determining process capability and sigma level. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol 66:98–115
Egan S, Murphy PG, Fennell JP, Kelly S, Hickey M, McLean C, Pate M, Kirke C, Whiriskey A, Wall N, McCullagh E, Murphy J, Delaney T (2012) Using Six Sigma to improve once daily gentamicin dosing and therapeutic drug monitoring performance. BMJ Qual Saf 21:1042–1051
Nevalainen D, Berte L, Kraft C, Leigh E, Picaso L, Morgan T (2000) Evaluating laboratory performance on quality indicators with the six sigma scale. Arch Pathol Lab Med 124:516–519
Taghizadegan S (2006) Essentials of lean six sigma, Butterworth-Heinemann, 1st edn. pp 7–304
Henderson GR (2011) Six Sigma Quality Improvement with Minitab, 2nd edn. Willey, pp 1–528
HC (1996) Guidance for industry: conduct and analysis of bioavailability and bioequivalence studies-part B: oral modified release formulations. pp 1–136
Grabowski T, Jaroszewski JJ, Sasinowska-Motyl M, Bujalska-Zadrożny M (2013) Sampling Intervals Verification in Pharmacokinetics Studies. Drug Res (Stuttg). doi:10.1055/s-0033-1361143
WHO (2006) Annex 7 Multisource (generic) pharmaceutical products: guidelines on registration requirements to establish interchangeability, WHO Technical report series, No. 937. 347–390
FDA (2003b) Guidance for industry source animal, product, preclinical, and clinical issues concerning the use of xenotransplantation products in humans. pp 1–63
FDA (2005) guidance for industry nonclinical studies for the safety evaluation of pharmaceutical excipients. pp 1–12
EMA (2006) Guideline on the role of pharmacokinetics in the development of medicinal products in the paediatric population. pp 1–8
EMA (2011) Guideline on the role of pharmacokinetics in the development of medicinal products in the paediatric population. pp 1–30
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Terry O’Reilly for valuable comments and the critical reading of the manuscript. Authors thank Ms. Karolina Flejszman for correcting grammar and language of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grabowski, T., Raczyńska-Pawelec, A., Starościak, M. et al. Evaluation of sampling spacing in pharmacokinetic studies using six sigma method. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 41, 251–260 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-014-9361-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-014-9361-5