Abstract
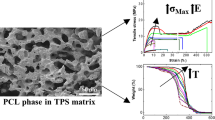
Thermoplastic starch (TPS) as a renewable filler and biodegradable polyester polylactic acid (PLA) blending is a cost-effective and feasible method. To improve the performance and compatibility of PLA/TPS blends, an epoxy-terminated hyperbranched polymer (EHBP) was designed and synthesized. The end epoxide group of EHBP formed chemical micro-crosslinking with the carboxyl group and hydroxyl group of PLA and TPS, thus improving the compatibility between PLA and TPS. The formation of chemical micro-crosslinks and improved compatibility of PLA/TPS blends were demonstrated. The tensile strength, elongation at break, impact strength, composite viscosity and energy storage modulus of the blends were significantly improved. When the EHBP content reached 5phr, the tensile strength, elongation at break and impact strength of the sample increased by 115.01%, 341.11% and 205.51%, respectively. However, the addition of EHBP resulted in a lower crystallinity and a slight decrease in biodegradability due to the occurrence of chemical micro-crosslinking. Nevertheless, the use of EHBP has great potential in PLA/TPS biodegradable packaging materials.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors will supply the relevant data in response to reasonable requests.
References
Jin Y, Sun X, Song C, Cai F, Liu G, Chen C (2023) Understanding the mechanism of enhanced anaerobic biodegradation of biodegradable plastics after alkaline pretreatment. Sci Total Environ 873:162324
Mahani H, Karevan M, Safavi M (2023) Comparative performance of fused deposit modeling 3D-printed and injection molded polylactic acid/thermoplastic starch/nanoclay bio-based nanocomposites. Polym Adv Technol 34:1901–1917
Wang J, Euring M, Ostendorf K, Zhang K (2022) Biobased materials for food packaging. J Bioresour Bioprod 7:1–13
Deeksha B, Sadanand V, Hariram N, Rajulu AV (2021) Preparation and properties of cellulose nanocomposite fabrics with in situ generated silver nanoparticles by bioreduction method. J Bioresour Bioprod 6:75–81
Balanon DAG, Sane A, Jariyasakoolroj P, Leelaphiwat P (2023) Application of biodegradable film as modified atmosphere packaging for red chili (Capsicum annuumcv. Jinda). Packag Technol Sci 36:379–388
Dmitruk A, Ludwiczak J, Skwarski M, Makuła P, Kaczyński P (2023) Influence of PBS, PBAT and TPS content on tensile and processing properties of PLA-based polymeric blends at different temperatures. J Mater Sci 58:1991–2004
Noivoil N, Yoksan R (2020) Oligo(lactic acid)-grafted starch: a compatibilizer for poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic starch blend. Int J Biol Macromol 160:506–517
Zhong J, Xin Y (2023) Preparation, compatibility and barrier properties of attapulgite/poly (lactic acid)/thermoplastic starch composites. Int J Biol Macromol 24:124727
Zhang J, Liu C, Cheng J, Miao M, Zhang D (2018) Simultaneous toughening and strengthening of diglycidyl ether of bisphenol-a using epoxy-ended hyperbranched polymers obtained from thiol-ene click reaction. Polym Eng Sci 58:1703–1709
Han XL, Han Y, Jin YJ, Tian HF, Wang Z, Huang JW, Men S, Kumar R (2022) Tailoring compatibility and toughness of microbial poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/bio-based polyester elastomer blends by epoxy-terminated hyperbranched polyester. Int J Biol Macromol 220:1163–1176
Guo M, Jin Y, Han X, Sun J, Yuan J, Tian H (2023) Biodegradable poly (Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) and thermoplastic starch sustainable blends modified by epoxy-terminated hyperbranched polyester with excellent mechanical properties and high transparency. Starch - Stärke 75:2200169
Xiaolong H, Yi H, Yujuan J, Huafeng T, Zhao W, Jiawei H, Shuang M, Rakesh K (2022) Tailoring compatibility and toughness of microbial poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) /bio-based polyester elastomer blends by epoxy-terminated hyperbranched polyester. Int J Biol Macromol 220:1163–1176
Kodal M, Wis AA, Ozkoc G (2018) The mechanical, thermal and morphological properties of γ-irradiated PLA/TAIC and PLA/OvPOSS. Radiat Phys Chem 153:214–225
Camacho-Munoz R, Villada-Castillo HS, Solanilla-Duque JF (2020) Anaerobic biodegradation under slurry thermophilic conditions of poly(lactic acid)/starch blend compatibilized by maleic anhydride. Int J Biol Macromol 163:1859–1865
Wei X-F, Bao R-Y, Cao Z-Q, Yang W, Xie B-H, Yang M-B (2014) Stereocomplex crystallite network in asymmetric PLLA/PDLA blends: formation, structure, and confining effect on the crystallization rate of homocrystallites. Macromolecules 47:1439–1448
Wadaugsorn K, Panrong T, Wongphan P, Harnkarnsujarit N (2022) Plasticized hydroxypropyl cassava starch blended PBAT for improved clarity blown films: morphology and properties. Ind Crops Prod 176:114311
Li F, Yu H-Y, Li Y, Hussain Abdalkarim SY, Zhu J, Zhou Y (2021) “Soft-rigid” synergistic reinforcement of PHBV composites with functionalized cellulose nanocrystals and amorphous recycled polycarbonate. Compos B Eng 206:108542
Palai B, Mohanty S, Nayak SK (2021) A comparison on biodegradation behaviour of polylactic Acid (PLA) based blown films by Incorporating Thermoplasticized Starch (TPS) and Poly (Butylene Succinate-co-Adipate) (PBSA) biopolymer in soil. J Polym Environ 29:2772–2788
Nazrin A, Sapuan SM, Zuhri MYM, Tawakkal ISMA, Ilyas RA (2021) Flammability and physical stability of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/poly(lactic acid) blend bionanocomposites. Nanotechnol Rev 11(1):86–95
Fonseca-Garcia A, Osorio BH, Aguirre-Loredo RY, Calambas HL, Caicedo C (2022) Miscibility study of thermoplastic starch/polylactic acid blends: thermal and superficial properties. Carbohydr Polym 293:119744
Zhai X, Wang W, Zhang H, Dai Y, Dong H, Hou H (2020) Effects of high starch content on the physicochemical properties of starch/PBAT nanocomposite films prepared by extrusion blowing. Carbohydr Polym 239:116231
Quynh TM, Mitomo H, Nagasawa N, Wada Y, Yoshii F, Tamada M (2007) Properties of crosslinked polylactides (PLLA & PDLA) by radiation and its biodegradability. Eur Polym J 43:1779–1785
Camani PH, Souza AG, Barbosa RFS, Zanini NC, Mulinari DR, Rosa DS (2021) Comprehensive insight into surfactant modified-PBAT physico-chemical and biodegradability properties. Chemosphere 269:128708
Tian J, Xu T, Tan Y, Zhang Z, Tang B, Sun Z (2019) Effects of non-covalent functionalized graphene oxide with hyperbranched polyesters on mechanical properties and mechanism of epoxy composites. Materials (Basel) 12:3103
Kervran M, Vagner C, Cochez M, Ponçot M, Saeb MR, Vahabi H (2022) Thermal degradation of polylactic acid (PLA)/polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) blends: a systematic review. Polym Degrad Stab 201:109995
Dang KM, Yoksan R, Pollet E, Averous L (2020) Morphology and properties of thermoplastic starch blended with biodegradable polyester and filled with halloysite nanoclay. Carbohydr Polym 242:116392
Yoksan R, Boontanimitr A, Klompong N, Phothongsurakun T (2022) Poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic cassava starch blends filled with duckweed biomass. Int J Biol Macromol 203:369–378
Zhang X, Zhang Y (2016) Reinforcement effect of poly(butylene succinate) (PBS)-grafted cellulose nanocrystal on toughened PBS/polylactic acid blends. Carbohydr Polym 140:374–382
Chotiprayon P, Chaisawad B, Yoksan R (2020) Thermoplastic cassava starch/poly(lactic acid) blend reinforced with coir fibres. Int J Biol Macromol 156:960–968
Jullanun P, Yoksan R (2020) Morphological characteristics and properties of TPS/PLA/cassava pulp biocomposites. Polym Test 88:106522
Abdelwahab MA, Flynn A, Chiou B-S, Imam S, Orts W, Chiellini E (2012) Thermal, mechanical and morphological characterization of plasticized PLA–PHB blends. Polym Degrad Stab 97:1822–1828
Sikhosana ST, Gumede TP, Malebo NJ, Ogundeji AO, Motloung B (2023) The influence of cellulose content on the morphology, thermal, and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid)/ Eucomis autumnalis cellulose biocomposites. Polym Eng Sci 63:1411–1422
Akhir MAM, Zubir SA, Mariatti J (2022) Effect of different starch contents on physical, morphological, mechanical, barrier, and biodegradation properties of tapioca starch and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blend film. Polym Adv Technol 34:717–730
Ruggero F, Onderwater RCA, Carretti E, Roosa S, Benali S, Raquez J-M, Gori R, Lubello C, Wattiez R (2021) Degradation of film and rigid bioplastics during the thermophilic phase and the maturation phase of simulated composting. J Polym Environ 29:3015–3028
Salomez M, George M, Fabre P, Touchaleaume F, Cesar G, Lajarrige A, Gastaldi E (2019) A comparative study of degradation mechanisms of PHBV and PBSA under laboratory-scale composting conditions. Polym Degrad Stab 167:102–113
Funding
The authors are grateful to the financial support of Beijing Young Top-notch Personnel Foundation (CIT&TCD201804030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MG, YJ, HT and JH: The experimental idea was proposed. GM: The method design and data analysis were conducted. XH and JS: The preparation of experimental materials was completed. Maolin Guo wrote the main manuscript text and prepared all the figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, M., Jin, Y., Han, X. et al. Simultaneously Strengthening and Toughening Biodegradable Polylactic Acid/Thermoplastic Starch Blends by Compatibilizing with Epoxy-Terminated Hyperbranched Polyester. J Polym Environ (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-03113-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-03113-4