Abstract
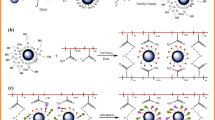
Lead and Cadmium, identified as toxic heavy metals, can cause a significant imbalance in the ecosystem due to their tendency to bioaccumulate. These metals can be seriously harmful to human health and the environment. In this work, a magnetic nanocomposite hydrogel was produced via grafting copolymerization of acrylic acid (AA) and acrylamide (AAm) in the presence of MnFe2O4@SiO2@Vinyltrimethylsilane (VTMS) as a cross-linking agent. To effectively adsorb Pb(II) and Cd(II) from an aqueous solution, the prepared magnetic nanocomposite hydrogel was applied. XRD, VSM, FT-IR, SEM–EDS, and TEM methods validated the structure of the prepared nanocomposite hydrogel. In addition, thermal characteristics was evaluated by TGA. The features that influence the adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions include pH, contact time, initial concentration of ions and dose of adsorbent experimented. The adsorption isotherm was investigated at various temperatures by employing Langmuir, Freundlich, Redlich-Peterson and Temkin. The adsorption data best fitted The Redlich-Peterson isotherm model. The adsorption kinetics models such as intraparticle, pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order and elovich in metal ion solutions of 25, 50, 100, and 150 mg/L were studied. The pseudo-first-order model well explained the adsorption results. The maximal adsorption capacities of magnetic nanocomposite hydrogel for Pb(II) and Cd(II) elimination from a 150 mg/L metal solution were 131 and 126 mg/g, respectively. The adsorption was employed effectively for four cycles of adsorption and desorption. Therefore, the nanocomposite hydrogel examined in this work may be used for various water filtration purposes, notably for eliminating toxic metals.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chunrong R, Xingeng D, Huiqin Fu, Li W, Huating W, Ya H (2017) Core–shell superparamagnetic monodisperse nanospheres based on amino-functionalized CoFe2O4@SiO2 for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 7:6911–6921. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA27728D
Kurdtabar M, Peyvand Kermani Z, Bagheri Marandi G (2015) Synthesis and characterization of collagen-based hydrogel nanocomposites for adsorption of Cd2+, Pb2+, methylene green and crystal violet. Iran Polym J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-015-0368-6
Sohrabi MR, Matbouie Z, Asgharinezhad AA, Dehghani A (2013) Solid phase extraction of Cd(II) and Pb(II) using a magnetic metal-organic framework, and their determination by FAAS. Microchim Acta 180:589–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-0952-4
Pâmela Becalli V, Dalalibera A, Costa Duminelli E, Becegato VA, Tadeu Paulino A (2017) Adsorption and removal of chromium (VI) contained in aqueous solutions using a chitosan-based hydrogel. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3208-3
Azimi A, Azari A, Rezakazemi M, Ansarpour M (2017) Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: a reviewion. ChemBioEng 4:37–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/cben.201600010
Gunatilake SK (2015) Methods of removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. J Multidiscip Eng Sci Stud 1:12–18
Burakov AE, Galunin EV, Irina V, Burakova AE, Kucherova SA, Tkachev AG, Gupta VK (2018) Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:702–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.034
Nematidil N, Nezami S, Sadeghi M, Sadeghi H (2019) Synthesis and characterization of Schiff-base based chitosan-g-glutaraldehyde/NaMMTNPs-APTES for removal Pb 2+ and Hg 2+ ions. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.114971
Chenxi Z, Liu G, Tan Q, Gao M, Chen Ge, Huang X, Xu X et al (2022) Polysaccharide-based biopolymer hydrogels for heavy metal detection and adsorption. J Adv Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2022.04.005
Liu Y, Wang W, Wang A (2010) Adsorption of lead ions from aqueous solution by using carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly (acrylic acid)/attapulgite hydrogel composites. Desalination -Amsterdam 259(1–3):258–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.03.039
Suguna P, Atchudan R, Thirukumaran P, Yoon DH, Lee YR, Cheong IW (2022) Simultaneous removal of heavy metal ions using carbon dots-doped hydrogel particles. Chemosphere 286:131760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131760
Darban Z, Shahabuddin S, Gaur R, Ahmad I, Sridewi N (2022) Hydrogel-based adsorbent material for the effective removal of heavy metals from wastewater: a comprehensive review. Gels 8(5):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050263
Peppas NA (1991) Physiologically responsive hydrogels. J Bioact Compat Polym 6(3):241–246. https://doi.org/10.1021/la100294p
Kurdtabar M, Nourani Koutenaee R, Rezanejade Bardajee G (2018) Synthesis and characterization of a novel pH-responsive nanocomposite hydrogel based on chitosan for targeted drug release. J Polym Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1499-1
Chou F, Shih Ch, Tsai M, Chiu W, Lue ShJ (2012) Functional acrylic acid as stabilizer for synthesis of smart hydrogel particles containing a magnetic Fe3O4 core. Polymer 53(14):2839–2846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2012.05.010
Li Na, Fu F, Lu J, Ze D, Tang B, Pang J (2017) Facile preparation of magnetic mesoporous MnFe2O4@SiO2−CTAB composites for Cr(VI) adsorption and reduction. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.097
Ahmad F, Liu X, Zhou Y, Yao H (2015) An in vivo evaluation of acute toxicity of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles in larval-embryo Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 166:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.07.003
Reddy DHK, Lee SM (2013) Application of magnetic chitosan composites for the removal of toxic metal and dyes from aqueous solutions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 201–202:68–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2013.10.002
Tiwari A, Verma N, Singh A, Nandi CK, Randhawa JK (2018) Carbon coated core-shell multifunctional fluorescent SPIONs. Nanoscale 10(22):10389–10394. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR01941J
Jin H, Ji Zh, Li Y, Liu M, Yuan J, Xu Ch, Hou Sh (2014) The preparation of a core/shell structure with alumina coated spherical silica powder. Colloids Surf A 441:170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.09.004
Ding HL, Zhang YX, Wang S, Xu JM, Xu SC, Li GH (2012) Fe3O4@SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles: the silica coating regulations with a single core for different core sizes and shell thicknesses. Chem Mater 24(23):4572–4580. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm302828d
Kim Y, Kwon HJ, Kook HJ, Park JJ, Koh WG, Hwang Ki S, Lee JY (2021) Wetting properties and morphological behavior of core-shell polymer-based nanoparticle coatings Rho. Prog Organ Coat. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2021.106606
Rho WY, Kim HM, Kyeong S, Kang YL, Kim DK, Kang H, Jeong Ch, Kim DE, Lee YS, Jun BH (2014) Facile synthesis of monodispersed silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles. J Ind Eng Chem 20(5):2646–2649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.12.014
Sajadi S, Sajadi S (2022) 4 - Covalent functionalized silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles: classification, synthetic methods and their applications. In: Fundamentals and industrial applications of magnetic nanoparticles, pp 117–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-822819-7.00016-8
Lakshmi K, Rangasamy R (2021) Synthetic modification of silica coated magnetite cored PAMAM dendrimer to enrich branched Amine groups and peripheral carboxyl groups for environmental remediation. J Mol Struct 1224:2021–2101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129081
Kuzminska M, Carlier BN, Rénal B, Gaigneaux EM (2015) Magnetic nanoparticles: improving chemical stability via silica coating and organic grafting with silanes for acidic media catalytic reactions. Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2015.08.005
Paulino AT, Belfiore LA, Kubota LT, Muniz EC, Almeida VC, Tambourgi EB (2011) Effect of magnetite on the adsorption behavior of Pb (II), Cd (II), and Cu (II) in chitosan-based hydrogels. Desalination 275(1–3):187–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.02.056
Mahmoud GA (2013) Adsorption of copper (II), lead (II), and cadmium (II) ions from aqueous solution by using hydrogel with magnetic properties. Monatsh Chem 144(8):1097–1106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-013-0957-z
Pourjavadi A, Tehrani ZM, Salimi H, Banazadeh A, Abedini N (2015) Hydrogel nanocomposite based on chitosan-g-acrylic acid and modified nanosilica with high adsorption capacity for heavy metal ion removal. Iran Polym J 24(9):725–734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-015-0360-1
Areal MP, Arciniegas ML, Horst F, Lassalle V, Sánchez FH, Alvarez VA, Gonzalez JS (2018) Water remediation: PVA-based magnetic gels as efficient devices to heavy metal removal. J Polym Environ 26(8):3129–3138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-018-1197-4
Yari M, Derakhshi P, Tahvildari K, Nozari M (2021) Preparation and characterization of magnetic iron nanoparticles on alginate/bentonite substrate for the adsorptive removal of Pb2+ ions to protect the environment. J Polym Environ 29(7):2185–2199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-02028-8
Aijun H, Juanjuan L, Mingquan Y, Yan L, Xinhua P (2011) Preparation of nano-MnFe2O4 and its catalytic performance of thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Chin J Chem Eng 19(6):1047–1051. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1004-9541(11)60090-6
Rashid Z, Naeimi H, Zarnani AH, Zarnani AH et al (2016) Fast and highly efficient purification of 6×histidine-tagged recombinant proteins by Ni-decorated MnFe2O4@SiO2@NH2@2AB as novel and efficient affinity adsorbent magnetic nanoparticles. RSC Adv 6(43):36840–36848. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA25949E
Rashid Z, Soleimani M, Ghahremanzadeh R, Vossoughi M, Esmaeili E (2017) Effective surface modification of MnFe2O4@SiO2@PMIDA magnetic nanoparticles for rapid and high-density antibody immobilization. Appl Surf Sci 426:1023–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.246
Sheng C, Wang X, Zhang X, Xia W, Tang X, Lin B, Wu Q, Shen X (2017) Preparation of magnetic MnFe2O4-Cellulose aerogel composite and its kinetics and thermodynamics of Cu(II) adsorption. Cellulose. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1598-x
Zhang B, Cui Y, Yin G, Li X (2012) Adsorption of copper (II) and lead (II) ions onto cottonseed protein-PAA hydrogel composite. Polym Plast Technol Eng 51(6):612–619. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2012.659311
Ren C, Ding X, Fu H, Li W, Wu H, Yang H (2017) Core-shell superparamagnetic monodisperse nanospheres based on amino-functionalized CoFe2O4@SiO2 for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 7(12):6911–6921. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA27728D
Ahadi N, Bodaghifard MA, Mobinikhaledi A (2019) Cu (II)-β-cyclodextrin complex stabilized on magnetic nanoparticles: a retrievable hybrid promoter for green synthesis of spiropyrans. Appl Organometall Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4738
Ertürk AS, Elmacı G, Ulvi Gürbüz’s M (2021) Reductant free green synthesis of magnetically recyclable MnFe2O4@SiO2-Ag core- shell nanocatalyst for the direct reduction of organic dye pollutants. Turkish J Chem. https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-2108-2
Ertürkr AS, Elmaci G, Ulvi GÜRBÜZM (2021) Eductant free green synthesis of magnetically recyclable MnFe2O4@SiO2-Ag coreshell nanocatalyst for the direct reduction of organic dye pollutants. Turkish J Chem 45:1968–1979. https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-2108-2
Gemeay AH, Keshta BE, El-Sharkawy RG, Zaki AB (2020) Chemical insight into the adsorption of reactive wool dyes onto amine-functionalized magnetite/silica core-shell from industrial wastewaters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(26):32341–32358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06530-y
Zhang Y, Wang F, Zhao R, Wang Y, Dai J (2019) Preparation of SiO2-MnFe2O4 composites via one-pot hydrothermal synthesis method and microwave absorption investigation in S-Band. Molecules 24(14):2605. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142605
Javaheri F, Hassanajili Sh (2016) Synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2@MPS@P4VP nanoparticles for nitrate removal from aqueous solutions. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44330
Lin T, Ye C, Yang G, Liu Y, Zeng G, Zhou Y, Si Li et al (2014) Cobalt nanoparticles-embedded magnetic ordered mesoporous carbon for highly effective adsorption of rhodamine B. Appl Surf Sci 314:746–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.07.060
Abukhadra MR, Mostafa M, Jumah MNB, Al-Khalawi N, Alruhaimi RS, Salama YF, Allam AA (2022) Insight into the adsorption properties of chitosan/zeolite-A hybrid structure for effective decontamination of toxic Cd (II) and As (V) ions from the aqueous environments. J Polym Environ 30(1):295–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02197-0
Ge F, Li MM, Ye H, Zhao BX (2012) Effective removal of heavy metal ions Cd2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Cu2+ from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 211–212:366–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.12.013
Liu Z, Chen G, Hu F, Li X (2020) Synthesis of mesoporous magnetic MnFe2O4@CS-SiO2 microsphere and its adsorption performance of Zn2+ and MB studies. J Environ Manag 263:2020–2106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110377
Khodabakhshi MJ, Ahmad Panahi H, Konoz E, Alireza Feizbakhsh A, Kimiagar S (2021) Synthesis of pH and thermo-sensitive dendrimers based on MoS2 and magnetic nanoparticles for cisplatin drug delivery system by the near-infrared laser. Polym Adv Technol 32(4):1626–1635. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5199
Nakhjiri MT, Marandi GB, Kurdtabar M (2018) Poly (AA-co-VPA) hydrogel cross-linked with N-maleyl chitosan as dye adsorbent: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic investigation. Int J Biol Macromol 117:152–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.140
Facchi DP, Cazetta AL, Canesin EA, Almeida VC, Bonafé EG, Kipper MJ, Martins AF (2018) New magnetic chitosan/alginate/Fe3O4@SiO2 hydrogel composites applied for removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous systems. Chem Eng J 337:595–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.142
Aflaki Jalali M, Dadvand Koohi A, Sheykhan M (2016) Experimental study of the removal of copper ions using hydrogels of xanthan, 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propane sulfonic acid, montmorillonite: kinetic and equilibrium study. Carbohyd Polym 142:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.01.033
Chen Y, Xu F, Li H, Li Y, Liu Y, Chen Y, Li M, Li L, Jiang H, Chen L (2021) Simple hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic MnFe2O4-sludge biochar composites for removal of aqueous Pb2+. J Anal Appl Pyrol 156:105173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105173
Mahdavinia GR, Massoudi A, Baghban A, Shokri E (2014) Study of adsorption of cationic dye on magnetic kappa-carrageenan/PVA nanocomposite hydrogels. J Environ Chem Eng 2(3):1578–1587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.05.020
Pang Li HuJ, Zhang M, Yang Ch, Wu G (2018) An efficient and reusable quaternary ammonium fabric adsorbent prepared by radiation grafting for removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(11):11045–11053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1355-1
Saberi A, Alipour E, Sadeghi M (2019) Superabsorbent magnetic Fe3O4-based starch-poly (acrylic acid) nanocomposite hydrogel for efficient removal of dyes and heavy metal ions from water. J Polym Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1917-z
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Cui W, Xi Z, Wang S (2020) Removing Copper and Cadmium from water and sediment by magnetic microspheres—MnFe2O4/chitosan prepared by waste shrimp shells. J Environ Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104647
Sekhavat Pour Z, Ghaemy M (2015) Removal of dyes and heavy metal ions from water by magnetic hydrogel beads based on poly (vinyl alcohol)/carboxymethyl starch-g-poly (vinyl imidazole). RSC Adv. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra08025h
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely appreciate the instrumental supports of this work by Islamic Azad University Karaj Branch.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by VG, GBM and MK. The first draft of the manuscript was written by VG and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghobadifar, V., Marandi, G.B., Kurdtabar, M. et al. Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) by MnFe2O4@SiO2@VTMS Nanocomposite Hydrogel from Aqueous Solutions. J Polym Environ 31, 2686–2704 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02670-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02670-4