Abstract
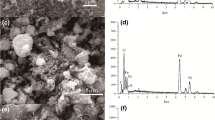
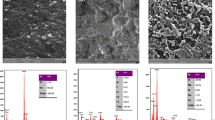
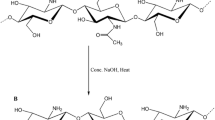
The effluent release containing heavy metals as Ni2+ ions has drastic risks to both the natural environment and human health. In this research, the nano Fe3O4/chitosan-acrylamide hydrogel was prepared as a novel nano sorbent for dispersive solid-phase extraction of Ni2+ ions and applied to the water sample solution. The pH, amount and type of elution solvent, the extraction time, etc. were optimized to improve the efficiency of the proposed method. Analytical parameters such as concentration factor and relative standard deviation (%) were achieved as 33.3 and 1.8%, respectively. The capacity in equilibrium sorption was calculated at 22.54 mg g−1. Furthermore, to estimate the adsorption mode, Freundlich, Langmuir, and Temkin models were fitted with experimental isotherm data. Besides, to check the basic process of the metal adsorption mechanism, pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and Roginsky-Zeldovich models were investigated and the results were fitted with the pseudo-second-order model. The value of change in entropy (⊿S) obtained is −65.24 (J(mol K)−1). Negative values of change in enthalpy, ⊿H in (kJ mol−1) is −24.45 (kJ mol−1) which indicates both physical and chemical adsorptions involved in the process of adsorption. Finally, the nano Fe3O4/chitosan-acrylamide hydrogel exhibited high performance to remove the Ni2+ ions from water sample solution.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All of the data and material are owned by the authors and/or no permissions are required. All authors (Morteza Parsayi Arvand, Ali Moghimi, and Narges Salehi) have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to authorship once the paper is submitted.
References
Al-Karawi, A. J. M., Al-Qaisi, Z. H. J., Abdullah, H. I., & Al-Mokaram, A. M. A. (2011). Al-Heetimi, D.T.A. Synthesis, characterization of acrylamide grafted chitosan and its use in removal of copper(II) ions from water. Carbohydrate Polymers, 83, 495–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2010.08.017
Anthemidis, A. N., Zachariadis, G. A., & Stratis, J. A. (2003). Development of an on-line solvent extraction system for electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry utilizing a new gravitational phase separator. Determination of cadmium in natural waters and urine samples. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 18, 1400–1403. https://doi.org/10.1039/b308325j
Arvand, M. P., Moghimi, A., & Abniki, M. (2022). Extraction of alprazolam in biological samples using the dispersive solid-phase method with nanographene oxide grafted with α-pyridylamine. IET Nanobiotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1049/nbt2.12105
Ashrafzadeh, T., & Qomi, M. (2016). Preconcentration and determination of solifenacin using hollow fiber microextraction coupled with HPLC. Current Analytical Chemistry, 12, 594–601. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573411012666160606170219
Atsumi, K., Minami, T., & Ueda, J. (2005). Determination of cadmium in spring water by graphite-furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after coprecipitation with ytterbium hydroxide. Analytical Sciences, 21, 647–649. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.21.647
Bagheri, H., Zandi, O., & Aghakhani, A. (2011). Extraction of fluoxetine from aquatic and urine samples using sodium dodecyl sulfate-coated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles followed by spectrofluorimetric determination. Analytica Chimica Acta, 692, 80–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.02.060
Boudreau, S. P., & Cooper, W. T. (1989). Analysis of thermally and chemically modified silica gels by heterogeneous gas-solid chromatography and infrared spectroscopy. Analytical Chemistry, 61, 41–47. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00176a010
Chen, Y., He, M., Wang, C., & Wei, Y. (2014). A novel polyvinyltetrazole-grafted resin with high capacity for adsorption of Pb (II), Cu (II) and Cr (III) ions from aqueous solutions. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2, 10444–10453. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta01512f
Duran, A., Soylak, M., & Tuncel, S. A. (2008). Poly (vinyl pyridine-poly ethylene glycol methacrylate-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) beads for heavy metal removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 155, 114–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.037
Duru, İ., Ege, D., & Kamali, A. R. (2016). Graphene oxides for removal of heavy and precious metals from wastewater. Journal of Materials Science, 51, 6097–6116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9913-8
Fan, Z., & Zhou, W. (2006). Dithizone–chloroform single drop microextraction system combined with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry using Ir as permanent modifier for the determination of Cd in water and biological samples. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 61, 870874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2006.05.011
Fu, F. L., & Wang, Q. (2011). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 92, 407–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011
Ghazanfar, S., Komal, A., Waseem, A., Hassan, W., Iqbal, I. J., Toor, S., Asif, M., Saleem, I. A., Khan, S. U., Tarar, Z. H., Nazar, S., Rehman, H. U., Ahmed, M. I., & Rebi, A. (2021). Physiological effects of nickel contamination on plant growth. Natural Volatiles & Essential Oils, 8, 13457–13469.
Gomes-Gomes, M. M., Hidalgo Garcia, M. M., & Palacio Corvillo, M. A. (1995). On-line preconcentration of silver on a sulfhydryl cotton microcolumn and determination by flow injection atomic absorption spectrometry. Analyst, 120, 1911–2915. https://doi.org/10.1039/AN9952001911
Izatt, R. M., Bradshaw, J. S., Nielsen, S. A., Lamb, J. D., Christensen, J. J., & Sen, D. (1985). Thermodynamic and kinetic data for cation-macrocycle interaction. Chemical Reviews, 85, 271–399. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00068a003
Jiang, T., Liu, W., Mao, Y., Zhang, L., Cheng, J., Gong, M., Zhao, H., Dai L., Zhang S., Zhao Q. (2015). Adsorption behavior of copper ions from aqueous solution onto graphene oxide–CdS composite. Chemical Engineering Journal, 259, 603-610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.08.022
Joshi, S., & Srivastava, R. K. (2019). Adsorptive removal of lead (Pb), copper (Cu), nickel (Ni) and mercury (Hg) ions from water using chitosan silica gel composite. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7777-5
Kanmaz, N., Acar, M., Yılmazoğlu, M., & Hızal, J. (2020). Rhodamine B and murexide retention onto sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) (sPEEK). Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 605, 125341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125341
Khan, A., Badshah, S., & Airoldi, C. C. (2011). Biosorption of some toxic metal ions by chitosan modified with glycidylmethacrylate and diethylenetriamine. Chemical Engineering Journal, 171, 159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.03.081
Kouotou, D., Ghalit, M., Ndi, J. N., Martinez, L. M. P., Ouahabi, M. E., Ketcha, J. M., & Gharibi, E. K. (2021). Removal of metallic trace elements (Pb2+, Cd2+, Cu2+, and Ni2+) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto cerium oxide modified activated carbon. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193, 467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09267-9
Kvitek, R. J., Evans, J. F., & Carr, P. W. (1982). Diamine/silane-modified controlled pore glass: The covalent attachment reaction from aqueous solution and the mechanism of reaction of bound diamine with copper(II). Analytica Chimica Acta, 144, 93–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(01)95522-9
Liu, X., Ma, R., Zhuang, L., Hu, B., Chen, J., Liu, X., Wang,X. (2021). Recent developments of doped g-C3N4 photocatalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 51, 751-790. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1734433
Miretzky, P., Cirelli, A.F. (2009). Hg (II) removal from water by chitosan and chitosan derivatives. A review, Journal of Hazardous Materials 167, 10–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.060
Moghimi, A. (2013). Detection of trace amounts of Pb (II) by schiff base-chitosan-grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 87, 1203–1209. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0036024413070388
Mourya, V. K., & Inamdar, N. N. (2008). Chitosan-modifications and applications : Opportunities galore. Reactive and Functional polymers, 68, 1013–1051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2008.03.002
Navarro, R., Guzmán, J., Saucedo, I., Revilla, J., & Guibal, E. (2003). Recovery of metal ions by chitosan: Sorption mechanisms and influence of metal speciation. Macromolecular Bioscience, 3, 552–561. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.200300013
Peer, F. E., Bahramifar, N., & Younesi, H. (2018). Removal of Cd (II), Pb (II) and Cu (II) ions from aqueous solution by polyamidoamine dendrimer grafted magnetic graphene oxide nanosheets. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 87, 225–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.03.039
Rahangdale, D., & Kumar, A. (2018). Acrylamide grafted chitosan based ion imprinted polymer for the recovery of cadmium from Nickel -Cadmium battery waste. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6, 1828–1839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.02.027
Rasoulzadeh, H., Sheikhmohammadi, A., Abtahi, M., Roshan, B., & Jokar, R. (2021). Eco-friendly rapid removal of palladium from aqueous solutions using alginate-diatomite magnano composite. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9, 105954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105954
Sadeghi-Kiakhani, M., Safapour, S., & Ghanbari-Adivi, F. (2019). Grafting of chitosan-acrylamide hybrid on the wool: Characterization, reactive dyeing, antioxidant and antibacterial studies. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 134, 1170–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.144
Salehi, N., Moghimi, A., & Shahbazi, H. (2020). Preparation of cross-linked magnetic chitosan with methionine-glutaraldehyde for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 102, 2305–2321. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1753718
Salehi, N., Moghimi, A., & Shahbazi, H. (2022). Magnetic nanobiosorbent (MG-Chi/Fe3O4) for dispersive solid-phase extraction of Cu(II), Pb(II), and Cd(II) followed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry determination, IET . Nanobiotechnology, 15, 575–584. https://doi.org/10.1049/nbt2.12025
Varma, A. J., Deshpande, S. V., & Kennedy, J. F. (2004). Metal complexation by chitosan and its derivatives : a review. Carbohydrate Polymers, 55, 77–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2003.08.005
Wang, J., & Hansen, E. H. (2002). Sequential injection on-line matrix removal and trace metal preconcentration using a PTFE beads packed column as demonstrated for the determination of cadmium by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 17, 248–252. https://doi.org/10.1039/b111089f
Wierucka, M., & Biziuk, M. (2014). Application of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic solid-phase extraction in preparing biological, environmental and food samples. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 59, 50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2014.04.007
Xiang, B., Ling, D., Lou, H., & Gu, H. (2017). 3D hierarchical flower-like nickel ferrite/manganese dioxide toward lead (II) removal from aqueous water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 325, 178–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.11.011
Yuan, S., Guو, J., Zheng, Y., Jiang, W., Liang, B., & Pehkonen, S. O. (2015). Purification of phenol-contaminated water by adsorption with quaternized poly (dimethylaminopropyl methacrylamide)-grafted PVBC microspheres. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 3, 4620–4636. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta06363e
Zhu, X., Zhu, X., & Wang, B. (2006). Determination of trace cadmium in water samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction. Microchimica Acta, 154, 95–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-005-0476-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Morteza Parsayi Arvand performed the analysis. Ali Moghimi supervised the analyses and he is the corresponding author. Narges Salehi Performed the analysis and wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare they have no financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arvand, M.P., Moghimi, A. & Salehi, N. A novel removal of Ni2+ ions from water solutions using dispersive solid-phase extraction method with nano Fe3O4/chitosan-acrylamide hydrogel. Environ Monit Assess 196, 136 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12149-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12149-x