Abstract
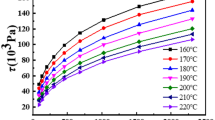
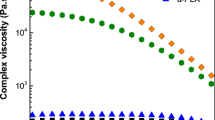
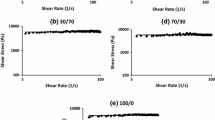
The present investigation dealt with the flow behavior and processability of polylactic acid/polystyrene (PLA/PS) polymer blends using a capillary rheometer. For this purpose, PLA/PS blends with different ratios of the concentrations were prepared using a single screw extruder. The shear viscosity, shear stress, shear rate, power-law index, viscous activation energy at a constant shear stress, and elongational stress were determined. PLA/PS blends exhibited a typical shear-thinning behavior over the entire range of shear rates tested, and the viscosity values of the blends would tend to decrease with increasing amount of PLA. In addition, the polymer blend of 70 % PLA and 30 % PS was found to be relatively less sensitive to the processing temperature, implying that the extrusion process was more desirable for fabrication of PLA/PS polymer blend than the injection process.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamad K, Kaseem M, Yang HW, Ko YG (2015) Express Polym Lett 9:435
Lim LT, Auras R, Rubino M (2008) Prog Polym Sci 33:820
Avella M, Bogoeva-Gaceva G, Buzˇarovska A, Errico ME, Gentile G, Grozdanov A (2008) J Appl Polym Sci 108:3542
Dimzoski B, Bogoeva-Gaceva G, Avella M, Errico ME, Srebrenkoska V (2008) J Polym Eng 28:369
Roberto A, Rachele C, Gennaro G, Veronica A, Stefano F, Avella M, Mariacristina C, Errico ME (2015) Eur Polym J 66:533
Ishida S, Nagasaki R, Chino K, Dong T, Inoue Y (2009) J Appl Polym Sci 113:558
Wang N, Yu J, Ma X (2007) Polym Int 56:1440
Hamad K, Kaseem M, Deri F (2011) J Polym Res 18:1799
Hamad K, Kaseem M, Deri F (2012) Asia Pac J Chem Eng 7:S310
Mihai M, Huneault M, Favias B (2007) J Cell Plast 43:215
Schlemmer D, Sales M, Resck IS (2009) Carbohydr Polym 75:58
Hamad K, Kaseem M, Deri F, Ko YG (2016) Mater Lett 164:409
Biresaw G, Carriere CJ (2002) J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 40:2248
Sarazin P, Favis BD (2003) Biomacromolecules 4:1669
Vital A, Vayer M, Tillocher T, Dussart R, Boufnichel M, Sinturel C (2017) Appl Surf Sci 393:133
Tadmor Z, Gogos CG (2006) Principles of polymer processing. Wiley, New Jersey
Bagley EB (1957) J Appl Phys 28:624
Han CD (2007) Rheology and processing of polymeric materials (polymer rheology). Oxford University Press, New York
Kaseem M, Hamad K, Yang HW, Lee YH, Deri F, Ko YG (2015) Polym Sci Ser A 57:233
Hamad K, Kaseem M, Deri F (2012) J Biomater Nanobiotechnol 3:405
Wang N, Yu J, Chang P, Ma X (2008) Carbohydr Polym 71:109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaseem, M., Ko, Y.G. Melt Flow Behavior and Processability of Polylactic Acid/Polystyrene (PLA/PS) Polymer Blends. J Polym Environ 25, 994–998 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0873-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0873-5