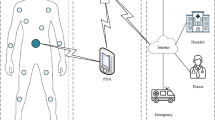
Abstract
Wireless body area sensor network is a special purpose wireless sensor network that, employing wireless sensor nodes in, on, or around the human body, makes it possible to measure biological parameters of a person for specific applications. One of the most fundamental concerns in wireless body sensor networks is accurate routing in order to send data promptly and properly, and therefore overcome some of the challenges. Routing protocols for such networks are affected by a large number of factors including energy, topology, temperature, posture, the radio range of sensors, and appropriate quality of service in sensor nodes. Since energy is highly important in wireless body area sensor networks, and increasing the network lifetime results in benefiting greatly from sensor capabilities, improving routing performance with reduced energy consumption presents a major challenge. This paper aims to study wireless body area sensor networks and the related routing methods. It also presents a thorough, comprehensive review of routing methods in wireless body area sensor networks from the perspective of energy. Furthermore, different routing methods affecting the parameter of energy will be classified and compared according to their advantages and disadvantages. In this paper, fundamental concepts of wireless body area sensor networks are provided, and then the advantages and disadvantages of these networks are investigated. Since one of the most fundamental issues in wireless body sensor networks is to perform routing so as to transmit data precisely and promptly, we discuss the same issue. As a result, we propose a classification of the available relevant literature with respect to the key challenge of energy in the routing process. With this end in view, all important papers published between 2000 and 2015 are classified under eight categories including ‘Mobility-Aware’, ‘Thermal-Aware’, ‘Restriction of Location and Number of Relays’, ‘Link-aware’, ‘Cluster- and Tree-Based’, ‘Cross-Layer’, ‘Opportunistic’, and ‘Medium Access Control’. We, then, provide a full description of the statistical analysis of each category in relation to all papers, current hybrid protocols, and the type of simulators used in each paper. Next, we analyze the distribution of papers in each category during various years. Moreover, for each category, the advantages and disadvantages as well as the number of issued papers in different years are given. We also analyze the type of layer and deployment of mathematical models or algorithmic techniques in each category. Finally, after introducing certain important protocols for each category, the goals, advantages, and disadvantages of the protocols are discussed and compared with each other.









































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta, S.K., Mukherjee, T., and Venkatasubramanian, K.K., Body area networks: Safety, security, and sustainability. Cambridge University Press, New York, United States of America, 2013.
Latré, B., Braem, B., Moerman, I., Blondia, C., and Demeester, P., A survey on wireless body area networks. Wireless Networks. 17(1):1–18, 2011. doi:10.1007/s11276-010-0252-4.
Wang, J., and Wang, Q., Body area communications: channel modeling, communication systems, and EMC. John Wiley & Sons, Singapore, 2012.
Braem, B., Reliable and Energy Efficient Protocols for Wireless Body Area Networks. University Antwepen, Doctor Thesis, 2011.
Natarajan A, De Silva B, Yap KK, Motani M. (2009) To hop or not to hop: Network architecture for body sensor networks. InSensor, Mesh and Ad Hoc Communications and Networks, 2009.SECON’09. 6th Annual IEEE Communications Society Conference on 2009 Jun 22 (pp. 1–9). IEEE.
Javaid, N., Ahmad, A., Nadeem, Q., Imran, M., and Haider, N., iM-SIMPLE: iMproved stable increased-throughput multi-hop link efficient routing protocol for Wireless Body Area Networks. Computers in Human Behavior. 51:1003–1011, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2014.10.005.
Abbasi UF, Awang A, Hamid NH. (2014) A cross-layer opportunistic MAC/routing protocol to improve reliability in WBAN. InCommunications (APCC), 2014 Asia-Pacific Conference on 2014 Oct 1 (pp. 36–41). IEEE.
Huque, U., and Ishtaique, M.T., Energy Efficient Routing for Wireless Body Area Networks. University of, Sydney, 2014.
Chebbo H, Abedi S, Lamahewa TA, Smith DB, Miniutti D, Hanlen L. (2012) reliable body area networks using relays: restricted tree topology. Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), 2012 International Conference on 2012 Jan 30 (pp. 82–88). Maui, HI, IEEE.
Ahmad A, Javaid N, Khan ZA, Imran M, Alnuem M. (2014) iA-MAC: Improved adaptive medium access control protocol for wireless body area networks. In Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), 2014 14th International Symposium on 2014 Sep 24 (pp. 156–160). Incheon, IEEE.
Movassaghi S, Shirvanimoghaddam M, Abolhasan M, Smith D. (2013) An energy efficient network coding approach for wireless body area networks. In Local Computer Networks (LCN), 2013 I.E. 38th Conference on 2013 Oct 21 (pp. 468–475). Sydney, IEEE.
Zhang R, Moungla H, Mehaoua A. (2014) An energy-efficient leader election mechanism for wireless body area networks. In Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), 2014 I.E. 2014 Dec 8 (pp. 2411–2416). Austin, IEEE.
Wang S, Mimis K, Bocus MZ, Watkins GT, Coon JP. (2013) Energy-efficient heterogeneous antenna selection relaying in wireless body area networks. In Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), 2013 I.E. 2013 Dec 9 (pp. 2472–2477). Atlanta, IEEE.
Deepak KS, Babu AV. (2012) Packet size optimization for energy efficient cooperative Wireless Body Area Networks. In India Conference (INDICON), 2012 Annual IEEE 2012 Dec 7 (pp. 736–741). Kochi, IEEE.
Hussein, R., Mohamed, A., and Alghoniemy, M., Scalable real-time energy-efficient EEG compression scheme for wireless body area sensor network. Biomedical Signal Processing and Contro. l19:122–129, 2015. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2015.03.005.
Kutty S, Laxminarayan JA. (2010) Towards energy efficient protocols for wireless body area networks. In Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), 2010 International Conference on 2010 Jul 29 (pp. 31–34). Mangalore, IEEE.
Piro, G., Boggia, G., and Grieco, L.A., on the design of an energy-harvesting protocol stack for Body Area Nano-NETworks. Nano Communication Networks. 6:74–84, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.nancom.2014.10.001.
Liang, T., and Smith, D.B., Energy-efficient, reliable wireless body area networks: cooperative diversity switched combining with transmit power control. Electronics Letters. 50(22):1641–1643, 2014. doi:10.1049/el.2014.2648.
Lin, C.S., and Chuang, P.J., Energy-efficient two-hop extension protocol for wireless body area networks. IET Wireless Sensor Systems. 3(1):37–56, 2013. doi:10.1049/iet-wss.2012.0070.
Sandhu MM, Javaid N, Akbar M, Najeeb F, Qasim U, Khan ZA. (2014) FEEL: Forwarding Data Energy Efficiently with Load Balancing in Wireless Body Area Networks. InAdvanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA), 2014 I.E. 28th International Conference on 2014 May 13 (pp. 783–789). IEEE.
Tauqir A, Javaid N, Akram S, Rao A, Mohammad SN. (2013) Distance aware relaying energy-efficient: DARE to monitor patients in multi-hop body area sensor networks. InBroadband and Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications (BWCCA), 2013 Eighth International Conference on 2013 Oct 28 (pp. 206–213). IEEE.
Akram S, Javaid N, Tauqir A, Rao A, Mohammad SN. (2013) The-fame: Threshold based energy-efficient fatigue measurement for wireless body area sensor networks using multiple sinks. InBroadband and Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications (BWCCA), 2013 Eighth International Conference on 2013 Oct 28 (pp. 214–220). IEEE.
Chen, C.L., Yang, T.T., Chiang, M.L., and Shih, T.F., A privacy authentication scheme based on cloud for medical environment. Journal of medical systems. 38(11):1–16, 2014. doi:10.1007/s10916-014-0143-9.
Almashaqbeh, G., Hayajneh, T., Vasilakos, A.V., and Mohd, B.J., QoS-aware health monitoring system using cloud-based WBANs. Journal of medical systems. 38(10):1–20, 2014. doi:10.1007/s10916-014-0121-2.
Ullah, S., Higgins, H., Braem, B., Latre, B., Blondia, C. ., Moerman, I., Saleem, S., Rahman, Z., Kwak, K.S., A comprehensive survey of wireless body area networks. Journal of medical systems. 36(3):1065–1094, 2012.
Ahnn, J.H., Potkonjak, M., and mhealthmon, Toward energy efficient and distributed mobile health monitoring using parallel offloading. Journal of medical systems. 37(5):1–11, 2013.
Poulymenopoulou, M., Malamateniou, F., and Vassilacopoulos, G., Emergency healthcare process automation using mobile computing and cloud services. Journal of medical systems. 36(5):3233–3241, 2012.
Siddiqui Z, Abdullah AH, Khan MK, Alghamdi AS (2014) Smart Environment as a Service: Three Factor Cloud Based User Authentication for Telecare Medical Information System. Journal of Medical Systems 38(1):9997 doi:10.1007/s10916-013-9997-5
Chen, Y.-Y., Lu, J.-C., and Jan, J.-K., A secure EHR system based on hybrid clouds. Journal of Medical Systems. 36(5):3375–3384, 2012. doi:10.1007/s10916-012-9830-6.
Jiang, Q., Ma, J., Ma, Z., and Li, G., A privacy enhanced authentication scheme for telecare medical information systems. Journal of medical systems. 37:9897, 2013.
Kumari, S., Khan, M.K.,Kumar, R., Cryptanalysis and improvement of ‘a privacy enhanced scheme for telecare medical information systems’. Journal of medical systems. 37(4), Article: 9952, doi:10.1007/s10916- 013–9952–9955, 2013.
Elias J (2014) Optimal design of energy-efficient and cost-effective wireless body area networks. Ad Hoc Networks13: 560–574. doi:10.1016/j.adhoc.2013.10.010
Ortiz AM, Ababneh N, Timmons N, Morrison J. (2012) Adaptive routing for multihop IEEE 802.15. 6 wireless body area networks. InSoftware, Telecommunications and Computer Networks (SoftCOM), 2012 20th International Conference on 2012 Sep 11 (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Fang G, Dutkiewicz E. (2009) BodyMAC: Energy efficient TDMA-based MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. InCommunications and Information Technology, 2009.ISCIT 2009. 9th International Symposium on 2009 Sep 28 (pp. 1455–1459). IEEE.
Timmons NF, Scanlon WG. (2009) An adaptive energy efficient MAC protocol for the medical body area network.InWireless Communication, Vehicular Technology, Information Theory and Aerospace & Electronic Systems Technology, 2009.Wireless VITAE 2009. 1st International Conference on 2009 May 17 (pp. 587–593). IEEE.
Ren H, Meng MQ. (2006) Understanding the mobility model of wireless body sensor networks. InInformation Acquisition, 2006 I.E. International Conference on 2006 Aug 20 (pp. 306–310). IEEE.
Braem B, Blondia C. (2011) Supporting mobility in wireless body area networks: an analysis. InCommunications and Vehicular Technology in the Benelux (SCVT), 2011 18th IEEE Symposium on 2011 Nov 22 (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Braem B, De Cleyn P, Blondia C. (2010) Supporting mobility in body sensor networks. InBody Sensor Networks (BSN), 2010 International Conference on 2010 Jun 7 (pp. 52–55). IEEE.
Braem B, Blondia C. (2012) An analysis of requirements to supporting mobility in body area networks. InComputing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), 2012 International Conference on 2012 Jan 30 (pp. 89–93). IEEE.
Chen, C.L., Yang, T.T., and Shih, T.F., A secure medical data exchange protocol based on cloud environment. Journal of medical systems. 38(9):1–12, 2014. doi:10.1007/s10916-014-0112-3.
Mihai G, Alina DA, (2010) Ion B. Performance analysis on T-MAC protocol over a body area network. InElectrical and Electronics Engineering (ISEEE), 2010 3rd International Symposium on 2010 Sep 16 (pp. 224–227). IEEE.
Liu J, Li M, Yuan B, Liu W (2015) A novel energy efficient MAC protocol for Wireless Body Area Network. Communications, China, 12(2): 11–20. doi:10.1109/CC.2015.7084398
Hossain MU, Kalyan M, Rana MR, Rahman MO. (2014) Multi-dimensional traffic adaptive energy-efficient MAC protocol for Wireless Body Area Networks. InStrategic Technology (IFOST), 2014 9th International Forum on 2014 Oct 21 (pp. 161–165). IEEE.
Ullah S, Higgins H, Braem B, Latre B, Blondia C, Moerman I, Saleem SH, Rahman Z, Kwak K S (2012) a comprehensive survey of wireless body area networks. Journal of medical systems, 36(3): 1065–1094. doi:10.1007/s10916-010-9571-3
Javaid N, Abbas Z, Fareed M S, Khan Z A, Alrajeh N (2013) M-ATTEMPT: A new energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless body area sensor networks. Procedia Computer Science19: 224–231, doi:10.1016/j.procs.2013.06.033
Movassaghi S, Abolhasan M, Lipman J. (2012) Energy efficient thermal and power aware (ETPA) routing in body area networks. InPersonal Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), 2012 I.E. 23rd International Symposium on 2012 Sep 9 (pp. 1108–1113). IEEE.
Ge Y, Liang L, Ni W, Wai AA, Feng G. (2012) A measurement study and implication for architecture design in wireless body area networks. InPervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PERCOM Workshops), 2012 I.E. International Conference on 2012 Mar 19 (pp. 799–804). IEEE.
Seo SH, Gopalan SA, Chun SM, Seok KJ, Nah JW, Park JT. (2010) An energy-efficient configuration management for multi-hop wireless body area networks. InBroadband Network and Multimedia Technology (IC-BNMT), 2010 3rd IEEE International Conference on 2010 Oct 26 (pp. 1235–1239). IEEE.
Maskooki A, Soh CB, Gunawan E, Low KS. (2011) Opportunistic routing for body area network. InConsumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC), 2011 I.E. 2011 Jan 9 (pp. 237–241). IEEE.
Liang, L., Ge, Y., Feng, G., Ni, W., and Wai, A.A.P., A low overhead tree-based energy-efficient routing scheme for multi-hop wireless body area networks. Computer Networks. 70:45–58, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2014.05.004.
Khan, Z.A., Sivakumar, S., Phillips, W., and Aslam, N., A new patient monitoring framework and Energy-aware Peering Routing Protocol (EPR) for Body Area Network communication. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. 5(3):409–423, 2014. doi:10.1007/s12652-013-0195-6.
Khan, Z.A., Sivakumar, S., Phillips, W., and Robertson, B., A QoS-aware routing protocol for reliability sensitive data in hospital body area networks. Procedia Computer Science. 19:171–179, 2013. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2013.06.027.
Kamal R, Hong CS, (2012). Fault Tolerant Virtual Backbone for Minimum Temperature in Vivo Sensor Networks. 2012 I.E. international conference on Ad-hoc and sensor networking symposium, 3394–3398.
Liang X, Balasingham I. (2007) A QoS-aware routing service framework for biomedical sensor networks.InWireless Communication Systems, 2007.ISWCS 2007. 4th International Symposium on 2007 Oct 17 (pp. 342–345). IEEE.
Takahashi D, Xiao Y, Hu F. (2007) LTRT: Least total-route temperature routing for embedded biomedical sensor networks. InGlobal Telecommunications Conference, 2007.GLOBECOM’07. IEEE 2007 Nov 26 (pp. 641–645). IEEE.
Ahourai F, Tabandeh M, Jahed M, Moradi S. (2009) A thermal-aware shortest hop routing algorithm for in vivo biomedical sensor networks. In2009 Sixth International Conference on Information Technology: New Generations 2009 Apr 27 (pp. 1612–1613). IEEE.
Mao, X., Tang, S., Xu, X., Li, X.Y., and Ma, H., Energy-efficient opportunistic routing in wireless sensor networks. Parallel and Distributed Systems, IEEE Transactions on. 22(11):1934–1942, 2011. doi:10.1109/TPDS.2011.70.
Braem B, Latre B, Moerman I, Blondia C, Reusens E, Joseph W, Martens L, Demeester P. (2007) The need for cooperation and relaying in short-range high path loss sensor networks.InSensor Technologies and Applications, 2007.SensorComm 2007. International Conference on 2007 Oct 14 (pp. 566–571). IEEE.
Sandhu MM, Akbar M, Behzad M, Javaid N, Khan ZA, Qasim U. (2014) REEC: Reliable Energy Efficient Critical Data Routing in Wireless Body Area Networks. InBroadband and Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications (BWCCA), 2014 Ninth International Conference on 2014 Nov 8 (pp. 446–451). IEEE.
Braem B, Latré B, Blondia C, Moerman I, Demeester P. (2008) Improving reliability in multi-hop body sensor networks. InSensor Technologies and Applications, 2008.SENSORCOMM’08. Second International Conference on 2008 Aug 25 (pp. 342–347). IEEE.
Chang, J.Y., and Ju, P.H., an energy-saving routing architecture with a uniform clustering algorithm for wireless body sensor networks. Future Generation Computer Systems. 35:128–140, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.future.2013.09.012.
Hu H, Yang Z. (2007) Cooperative opportunistic routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. InWireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, 2007.WiCom 2007. International Conference on 2007 Sep 21 (pp. 2551–2554). IEEE.
Abbasi UF, Awang A, Hamid NH. (2013) Performance investigation of using direct transmission and opportunistic routing in wireless body area networks. InComputers & Informatics (ISCI), 2013 I.E. Symposium on 2013 Apr 7 (pp. 60–65). IEEE.
Nadeem Q, Javaid N, Mohammad SN, Khan MY, Sarfraz S, Gull M. (2013) Simple: Stable increased-throughput multi-hop protocol for link efficiency in wireless body area networks. InBroadband and Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications (BWCCA), 2013 Eighth International Conference on 2013 Oct 28 (pp. 221–226). IEEE.
Omeni, O., Wong, A., Burdett, A.J., and Toumazou, C., Energy efficient medium access protocol for wireless medical body area sensor networks. Biomedical Circuits and Systems, IEEE Transactions on. 2(4):251–259, 2008. doi:10.1109/TBCAS.2008.2003431.
Cai, X., Li, J., Yuan, J., Zhu, W., and Wu, Q., Energy-aware adaptive topology adjustment in wireless body area networks. Telecommunication Systems. 58(2):139–152, 2015. doi:10.1007/s11235-014-9899-y.
Lu, X., Chen, X., Li, Y., Jin, D., Zeng, L., and Rashvand, H.F., ZebraBAN: a heterogeneous high-performance energy efficient wireless body sensor network. IET Wireless Sensor Systems. 3(4):247–254, 2013. doi:10.1049/iet-wss.2012.0164.
Latre B, Braem B, Moerman I, Blondia C, Reusens E, Joseph W, Demeester P. (2007) A low-delay protocol for multihop wireless body area networks. InMobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Networking & Services, 2007. MobiQuitous 2007. Fourth Annual International Conference on 2007 Aug 6 (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Braem B, Latre B, Moerman I, Blondia C, Demeester P. (2006) The wireless autonomous spanning tree protocol for multihop wireless body area networks. InMobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Networking & Services, 2006 Third Annual International Conference on 2006 Jul (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Tang Q, Tummala N, Gupta S K, Schwiebert L (2005) TARA: thermal-aware routing algorithm for implanted sensor networks. In Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems 3560:pp. 206–217 doi:10.1007/11502593_17
Oey, C.H.W., and Moh, S., a survey on temperature-aware routing protocols in wireless body sensor networks. Sensors. 13(8):9860–9877, 2013. doi:10.3390/s130809860.
Ahmed, S., Javaid, N., Yousaf, S., Ahmad, A., Sandhu, M.M., Imran, M., Khan, Z.A., and Alrajeh, N., Co-LAEEBA: Cooperative link aware and energy efficient protocol for wireless body area networks. Computers in Human Behavior. 51:1205–1215, 2015. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2014.12.051.
Marinkovi S J, Popovici E M, Spagnol C, Faul S, and Marnane W P, “Energy-efficient low duty cycle MAC protocol for wireless body area networks,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 13(6): 915–925, 2009.
Gopalan SA, Park JT. (2010) Energy-efficient MAC protocols for wireless body area networks: survey. InUltra Modern Telecommunications and Control Systems and Workshops (ICUMT), 2010 International Congress on 2010 Oct 18 (pp. 739–744). IEEE.
Bag A, Bassiouni MA. (2006) Energy efficient thermal aware routing algorithms for embedded biomedical sensor networks. InMobile Adhoc and Sensor Systems (MASS), 2006 I.E. International Conference on 2006 Oct (pp. 604–609). IEEE.
Bag A, Bassio MA. (2008) Routing algorithm for network of homogeneous and id-less biomedical sensor nodes (RAIN). InSensors Applications Symposium, 2008. SAS 2008. IEEE 2008 Feb 12 (pp. 68–73). IET.
Elias J, Mehaoua A. (2012) Energy-aware topology design for wireless body area networks. In Communications (ICC), 2012 I.E. International Conference on 2012 Jun 10 (pp. 3409–3410). IEEE.
Guo C, Prasad RV, Jacobsson M. (2010) Packet forwarding with minimum energy consumption in body area sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE the 7th International Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC) 2010 Jan 9 (pp. 1–6).
Huang X, Shan H, Shen X. (2011) On energy efficiency of cooperative communications in wireless body area network. InWireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), 2011 I.E. 2011 Mar 28 (pp. 1097–1101). IEEE.
Xiao, S., Dhamdhere, A., Sivaraman, V., and Burdett, A., Transmission power control in body area sensor networks for healthcare monitoring. Selected Areas in Communications, IEEE Journal on. 27(1):37–48, 2009. doi:10.1109/JSAC.2009.090105.
Zhang Q, Kortermand K, Jacobsen RH, Toftegaard TS. (2012) Reactive virtual coordinate routing protocol for body sensor networks. InCommunications (ICC), 2012 I.E. International Conference on 2012 Jun 10 (pp. 3388–3393). IEEE.
Abreu, C., Ricardo, M., and Mendes, P.M., Energy-aware routing for biomedical wireless sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications. 40:270–278, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2013.09.015.
Liang X, Balasingham I, Byun SS. (2008) A reinforcement learning based routing protocol with QoS support for biomedical sensor networks. InApplied Sciences on Biomedical and Communication Technologies, 2008. ISABEL’08. First International Symposium on 2008 Oct 25 (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Djenouri D, Balasingham I. (2009) New QoS and geographical routing in wireless biomedical sensor networks.InBroadband Communications, Networks, and Systems, 2009.BROADNETS 2009. Sixth International Conference on 2009 Sep 14 (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Razzaque M A, Hong C S, Lee, S (2011) Data-centric multiobjective QoS-aware routing protocol for body sensor networks. Sensors11(1): 917–937. doi:10.3390/s110100917
Culpepper, B.J., Dung, L., and Moh, M., Design and analysis of Hybrid Indirect Transmissions (HIT) for data gathering in wireless micro sensor networks. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review. 8(1):61–83, 2004. doi:10.1145/980159.980169.
Lindsey S, Raghavendra CS. (2002) PEGASIS: Power-efficient gathering in sensor information systems. InAerospace conference proceedings, 2002. IEEE 2002 (Vol. 3, pp. 3–1125). IEEE.
Ruzzelli A G, Jurdak R, O’Hare G M, Van Der Stok P (2007, June) Energy-efficient multi-hop medical sensor networking. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM SIGMOBILE international workshop on Systems and networking support for healthcare and assisted living environments pp. 37–42. ACM, doi:10.1145/1248054.1248064
Joseph W, Braem B, Reusens E, Latré B, Martens L, Moerman I, Blondia C. (2011) Design of energy efficient topologies for wireless on-body channel. InWireless Conference 2011-Sustainable Wireless Technologies (European Wireless), 11th European 2011 Apr 27 (pp. 1–7). VDE.
Marinkovic S, Spagnol C, Popovici E. (2009) Energy-efficient TDMA-based MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. In Sensor Technologies and Applications, 2009.SENSORCOMM’09. Third International Conference on 2009 Jun 18 (pp. 604–609). IEEE.
Marinković S J, Popovici E M, Spagnol C, Faul S, Marnane W P (2009) Energy-efficient low duty cycle MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. Information Technology in Biomedicine, IEEE Transactions on, 13(6): 915–925. doi:10.1109/TITB.2009.2033591
Javaid N, Ahmad A, Rahim A, Khan Z A, Ishfaq M, Qasim U (2014) Adaptive medium access control protocol for wireless body area networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2014:10 PAGES, doi:10.1155/2014/254397
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Mobile Systems
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Effatparvar, M., Dehghan, M. & Rahmani, A.M. A comprehensive survey of energy-aware routing protocols in wireless body area sensor networks. J Med Syst 40, 201 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0556-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0556-8