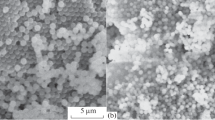
Abstract
We herein report a direct and facil sol–gel method for the preparation of porous silicon dioxide nanoparticles using dissolved silica gel and nitric acid. We prepared SiO2 nanoparticles at three different pH values: 6, 7, and 8. The washed and dried products were calcined at 800 °C for 2 h. The average crystallite size of the prepared SiO2 nanoparticles was ca. 37.7 nm. The products were characterized by using FT-IR, TEM, FE-SEM, and XRD analyses. The as-prepared SiO2 nanoparticles showed high adsorption capacities; ca. 32.2 mg g−1 and 42.2 mg g−1, for the removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions, respectively, from aqueous media. The adsorption data followed well the pseudo-second-order and Langmuir isotherm models. The determined thermodynamic parameters: ΔG° (from − 5.026 to − 5.180 kJ/mol for Cd(II) ion adsorption and from − 5.528 to − 5.732 kJ/mol for Pb(II) ion adsorption) and ΔH° (− 7.00 and − 7.607 kJ/mol, respectively), indicate the spontaneous, exothermic, and physisorption nature of the adsorption process. Besides, the excellent reusability and adsorption capacity for SiO2 nanoparticles revealed their good efficiency for the removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous media.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Rajendran, T.A.K. Priya, K.S. Khoo, T.K.A. Hoang, H.-S. Ng, H.S.H. Munawaroh, C. Karaman, Y. Orooji, P.L. Show, A critical review on various remediation approaches for heavy metal contaminants removal from contaminated soils. Chemosphere 287, 132369 (2022)
Z. Yan, Q. Zhao, M. Wen, L. Hu, X. Zhang, J. You, A novel polydentate ligand chromophore for simultaneously colorimetric detection of trace Ag+ and Fe3+. Spectrochim. Acta A 186, 17–22 (2017)
N. Zohora, D. Kumar, M. Yazdani, V.M. Rotello, R. Ramanathan, V. Bansal, Rapid colorimetric detection of mercury using biosynthesized gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A 532, 451–457 (2017)
Y. Guo, Y. Sun, Z. Li, S. Feng, R. Yang, L. Qu, Detection, detoxification, and removal of multiply heavy metal ions using a recyclable probe enabled by click and declick chemistry. J. Hazard. Mater. 423, 127242 (2022)
M. Yap, N. Mubarak, J. Sahu, E. Abdullah, Microwave induced synthesis of magnetic biochar from agricultural biomass for removal of lead and cadmium from wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 45, 287–295 (2017)
L.K. Wang, H. Yung-Tse, N.K. Shammas, Physicochemical treatment processes (2005)
M.Y. Nassar, M.F. El-Shahat, A. Osman, M.M. Sobeih, M.A. Zaid, Adsorptive removal of manganese ions from polluted aqueous media by glauconite clay-functionalized chitosan nanocomposites. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31, 4050–4064 (2021)
M.Y. Nassar, I.S. Ahmed, Template-free hydrothermal derived cobalt oxide nanopowders: synthesis, characterization, and removal of organic dyes. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 2638–2645 (2012)
M.Y. Nassar, E.I. Ali, E.S. Zakaria, Tunable auto-combustion preparation of TiO2 nanostructures as efficient adsorbents for the removal of an anionic textile dye. RSC Adv. 7, 8034–8050 (2017)
Q. Chen, Y. Yao, X. Li, J. Lu, J. Zhou, Z. Huang, Comparison of heavy metal removals from aqueous solutions by chemical precipitation and characteristics of precipitates. J. Water Process Eng. 26, 289–300 (2018)
M.M. Matlock, B.S. Howerton, D.A. Atwood, Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Water Res. 36, 4757–4764 (2002)
A. Bashir, L.A. Malik, S. Ahad, T. Manzoor, M.A. Bhat, G. Dar, A.H. Pandith, Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous system by ion-exchange and biosorption methods. Environ. Chem. Lett. 17, 729–754 (2019)
Q. Dong, X. Guo, X. Huang, L. Liu, R. Tallon, B. Taylor, J. Chen, Selective removal of lead ions through capacitive deionization: role of ion-exchange membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 361, 1535–1542 (2019)
F.S. Awad, K.M. AbouZied, W.M. Abou El-Maaty, A.M. El-Wakil, M.S. El-Shall, Effective removal of mercury(II) from aqueous solutions by chemically modified graphene oxide nanosheets. Arab. J. Chem. 13, 2659–2670 (2020)
M. Kargar, G. Zolfaghari, Hybrid nano-filtration and micro-filtration pilot processes for the removal of chromium from water. J. Water Wastewater (2018). https://doi.org/10.22093/wwj.2017.64518.2267
Z.T. Khanzada, Phosphorus removal from landfill leachate by microalgae. Biotechnol. Rep. 25, e00419 (2020)
R. Chen, Y. Cheng, P. Wang, Y. Wang, Q. Wang, Z. Yang, C. Tang, S. Xiang, S. Luo, S. Huang, C. Su, Facile synthesis of a sandwiched Ti3C2Tx MXene/nZVI/fungal hypha nanofiber hybrid membrane for enhanced removal of Be(II) from Be(NH2)2 complexing solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 421, 129682 (2021)
X. Zhang, X. Sun, T. Lv, L. Weng, M. Chi, J. Shi, S. Zhang, Preparation of PI porous fiber membrane for recovering oil-paper insulation structure. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 13344–13351 (2020)
N.C.L. de Beluci, G.A.P. Mateus, C.S. Miyashiro, N.C. Homem, R.G. Gomes, M.R. Fagundes-Klen, R. Bergamasco, A.M.S. Vieira, Hybrid treatment of coagulation/flocculation process followed by ultrafiltration in TiO2-modified membranes to improve the removal of reactive black 5 dye. Sci. Total Environ. 664, 222–229 (2019)
P. Jia, Y. Zhou, X. Zhang, Y. Zhang, R. Dai, Cyanobacterium removal and control of algal organic matter (AOM) release by UV/H2O2 pre-oxidation enhanced Fe(II) coagulation. Water Res. 131, 122–130 (2018)
S. Zhang, S. Zhao, S. Huang, B. Hu, M. Wang, Z. Zhang, L. He, M. Du, Photocatalytic degradation of oxytetracycline under visible light by nanohybrids of CoFe alloy nanoparticles and nitrogen-/sulfur-codoped mesoporous carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 420, 130516 (2021)
H. Liu, X.-X. Li, X.-Y. Liu, Z.-H. Ma, Z.-Y. Yin, W.-W. Yang, Y.-S. Yu, Schiff-base-rich g-CxN4 supported PdAg nanowires as an efficient Mott–Schottky catalyst boosting photocatalytic dehydrogenation of formic acid. Rare Met. 40, 808–816 (2021)
L. Bulgariu, D. Bulgariu, Functionalized soy waste biomass—a novel environmental-friendly biosorbent for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 197, 875–885 (2018)
X. Liang, X. Fan, R. Li, S. Li, S. Shen, D. Hu, Efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water by quaternized chitin/branched polyethylenimine biosorbent with hierarchical pore structure. Bioresour. Technol. 250, 178–184 (2018)
D. Pradhan, L.B. Sukla, B.B. Mishra, N. Devi, Biosorption for removal of hexavalent chromium using microalgae Scenedesmus sp. J. Clean. Prod. 209, 617–629 (2019)
G. Wang, S. Zhang, P. Yao, Y. Chen, X. Xu, T. Li, G. Gong, Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions by Phytolacca americana L. biomass as a low cost biosorbent. Arab. J. Chem. 11, 99–110 (2018)
M.M. Sobeih, M.F. El-Shahat, A. Osman, M.A. Zaid, M.Y. Nassar, Glauconite clay-functionalized chitosan nanocomposites for efficient adsorptive removal of fluoride ions from polluted aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 10, 25567–25585 (2020)
M.Y. Nassar, I.S. Ahmed, H.S. Hendy, A facile one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanostructures and cephalexin antibiotic sorptive removal from polluted aqueous media. J. Mol. Liq. 271, 844–856 (2018)
M.Y. Nassar, M. Khatab, Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles via a template-free hydrothermal route as an efficient nano-adsorbent for potential textile dye removal. RSC Adv. 6, 79688–79705 (2016)
M.Y. Nassar, I.S. Ahmed, M.A. Raya, A facile and tunable approach for synthesis of pure silica nanostructures from rice husk for the removal of ciprofloxacin drug from polluted aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 282, 251–263 (2019)
H. Liu, W. Sha, A.T. Cooper, M. Fan, Preparation and characterization of a novel silica aerogel as adsorbent for toxic organic compounds. Colloids Surf. A 347, 38–44 (2009)
S. Wan, H. Bi, L. Sun, Graphene and carbon-based nanomaterials as highly efficient adsorbents for oils and organic solvents. J. Nanotechnol. Rev. 5, 3–22 (2016)
R.N. Amador, M. Carboni, D. Meyer, Sorption and photodegradation under visible light irradiation of an organic pollutant by a heterogeneous UiO-67–Ru–Ti MOF obtained by post-synthetic exchange. J. RSC Adv. 7, 195–200 (2017)
G.-S. Kim, S.-H. Hyun, Synthesis of window glazing coated with silica aerogel films via ambient drying. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 320, 125–132 (2003)
W. Ackerman, M. Vlachos, S. Rouanet, J. Fruendt, Use of surface treated aerogels derived from various silica precursors in translucent insulation panels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 285, 264–271 (2001)
T. Asefa, Z. Tao, Biocompatibility of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 25, 2265–2284 (2012)
A.S. Abdel-Bary, D.A. Tolan, M.Y. Nassar, T. Taketsugu, A.M. El-Nahas, Chitosan, magnetite, silicon dioxide, and graphene oxide nanocomposites: synthesis, characterization, efficiency as cisplatin drug delivery, and DFT calculations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 154, 621–633 (2020)
S. Bettini, R. Pagano, G. Bosco, S. Pal, C. Ingrosso, L. Valli, G. Giancane, SiO2 based nanocomposite for simultaneous magnetic removal and discrimination of small pollutants in water. Colloids Surf. A 633, 127905 (2022)
P. Feng, H. Chang, X. Liu, S. Ye, X. Shu, Q. Ran, The significance of dispersion of nano-SiO2 on early age hydration of cement pastes. Mater. Des. 186, 108320 (2020)
L. Giraldo, B. López, L. Pérez, S. Urrego, L. Sierra, M. Mesa, Mesoporous silica applications. Macromol. Symp. 258, 129–141 (2007)
M.M. Sobeih, M. El-Shahat, A. Osman, M. Zaid, M.Y. Nassar, Glauconite clay-functionalized chitosan nanocomposites for efficient adsorptive removal of fluoride ions from polluted aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 10, 25567–25585 (2020)
J. Aguado, J.M. Arsuaga, A. Arencibia, Adsorption of aqueous mercury(II) on propylthiol-functionalized mesoporous silica obtained by cocondensation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 44, 3665–3671 (2005)
J. Gallo, H. Pastore, U. Schuchardt, Silylation of [Nb]-MCM-41 as an efficient tool to improve epoxidation activity and selectivity. J. Catal. 243, 57–63 (2006)
R. Jenkins, R.L. Snyder, Introduction to X-Ray Powder Diffractometry (Wiley, New York, 1996)
M.Y. Nassar, M.M. Moustafa, M.M. Taha, Hydrothermal tuning of the morphology and particle size of hydrozincite nanoparticles using different counterions to produce nanosized ZnO as an efficient adsorbent for textile dye removal. RSC Adv. 6, 42180–42195 (2016)
M.Y. Nassar, T.Y. Mohamed, I.S. Ahmed, I. Samir, MgO nanostructure via a sol-gel combustion synthesis method using different fuels: an efficient nano-adsorbent for the removal of some anionic textile dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 225, 730–740 (2017)
M.P. Gatabi, H.M. Moghaddam, M. Ghorbani, Point of zero charge of maghemite decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes fabricated by chemical precipitation method. J. Mol. Liq. 216, 117–125 (2016)
M.P. Gatabi, H.M. Moghaddam, M. Ghorbani, Efficient removal of cadmium using magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotube nanoadsorbents: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic study. J. Nanopart. Res. 18, 1–17 (2016)
Q. Wang, W. Gao, Y. Liu, J. Yuan, Z. Xu, Q. Zeng, Y. Li, M. Schröder, Simultaneous adsorption of Cu(II) and SO42− ions by a novel silica gel functionalized with a ditopic zwitterionic Schiff base ligand. Chem. Eng. J. 250, 55–65 (2014)
M. Ghaedi, H. Mazaheri, S. Khodadoust, S. Hajati, M. Purkait, Application of central composite design for simultaneous removal of methylene blue and Pb2+ ions by walnut wood activated carbon. Spectrochim. Acta A 135, 479–490 (2015)
Y.-S. Ho, G. McKay, Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 34, 451–465 (1999)
Y.-Y. Wang, Y.-X. Liu, H.-H. Lu, R.-Q. Yang, S.-M. Yang, Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) ions onto hydroxyapatite-biochar nanocomposite in aqueous solutions. J. Solid State Chem. 261, 53–61 (2018)
G.D. Halsey, The role of surface heterogeneity in adsorption, in Advances in Catalysis. ed. by V.I.K.W.G. Frankenburg, E.K. Rideal (Academic Press, Cambridge, 1952), pp. 259–269
S. Liu, Y. Ding, P. Li, K. Diao, X. Tan, F. Lei, Y. Zhan, Q. Li, B. Huang, Z. Huang, Adsorption of the anionic dye Congo red from aqueous solution onto natural zeolites modified with N,N-dimethyl dehydroabietylamine oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 248, 135–144 (2014)
X. Zhang, S. Lin, X.-Q. Lu, Z.-L. Chen, Removal of Pb(II) from water using synthesized kaolin supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 163, 243–248 (2010)
H. Ravishankar, J. Wang, L. Shu, V. Jegatheesan, Removal of Pb(II) ions using polymer based graphene oxide magnetic nano-sorbent. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 104, 472–480 (2016)
N.K. Koju, X. Song, Q. Wang, Z. Hu, C. Colombo, Cadmium removal from simulated groundwater using alumina nanoparticles: behaviors and mechanisms. J. Enivron. Pollut. 240, 255–266 (2018)
G. Bhanjana, N. Dilbaghi, K.-H. Kim, S. Kumar, Carbon nanotubes as sorbent material for removal of cadmium. J. Mol. Liq. 242, 966–970 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The second author (Mohamed S. Behiry) thanks A.A. Ali, Benha University, Egypt, for providing him some commercial chemicals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is not applicable to this study.
Research Involving Human and/or Animal Participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Feky, H.H., Behiry, M.S., Amin, A.S. et al. Facile Fabrication of Nano-sized SiO2 by an Improved Sol–Gel Route: As an Adsorbent for Enhanced Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) Ions. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 1129–1141 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02214-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02214-8