Abstract
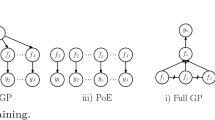
Bayesian optimization (BO) is challenging for problems with large number of observations. The main limitation of the Gaussian Process (GP) based BO is the computational cost which grows cubically with the number of sample points. To alleviate scalability issues of standard GP we propose to use the generalized product of experts (gPoE) model. This model is not only very flexible and scalable but can be efficiently computed in parallel. Moreover, we propose a new algorithm gPoETRBO for global optimization with large number of observations which combines trust region and gPoE models. In our experiments, we empirically show that our proposed algorithms are computationally more efficient and achieve similar performance to other state-of-the-art algorithms without using any specialized hardware.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mockus, J., Tiesis, V., Zilinskas, A.: The application of Bayesian methods for seeking the extremum. Towards Global Optim. 2, 117–129 (1978)
Brochu, E., Cora, V.M., De Freitas, N.: A tutorial on Bayesian optimization of expensive cost functions, with application to active user modeling and hierarchical reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1012.2599 (2010)
Frazier, P.I.: Bayesian Optimization. In: Recent Advances in Optimization and Modeling of Contemporary Problems, pp. 255–278 (2018)
Wang, Z., Hutter, F., Zoghi, M., Matheson, D., De Freitas, N.: Bayesian optimization in a billion dimensions via random embeddings. J. Artifi. Intell. Res. 55, 361–387 (2016)
Wang, Z., Gehring, C., Kohli, P., Jegelka, S.: Batched large-scale Bayesian optimization in high-dimensional spaces. In: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, AISTATS 2018, vol. 84, pp. 745–754 (2018)
Kandasamy, K., Schneider, J., Póczos, B.: High dimensional Bayesian Optimisation and bandits via additive models. In: 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 37, pp. 295–304 (2015)
Gardner, J.R., Guo, C., Weinberger, K.Q., Garnett, R., Grosse, R.: Discovering and exploiting additive structure for Bayesian optimization. Proc. Mach. Learn. Res. 54, 1311–1319 (2017)
Binois, M., Ginsbourger, D., Roustant, O.: On the choice of the low-dimensional domain for global optimization via random embeddings. J. Global Optim. 76(1), 69–90 (2020)
Munteanu, A., Nayebi, A., Poloczek, M.: A framework for Bayesian optimization in embedded subspaces. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 97, pp. 4752–4761 (2019)
Oh, C.Y., Gavves, E., Welling, M.: BOCK: Bayesian Optimization with Cylindrical Kernels. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 80, pp. 3868–3877 (2018)
Eriksson, D., Pearce, M., Gardner, J., Turner, R.D., Poloczek, M.: Scalable global optimization via local Bayesian optimization. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32, pp. 5496–5507 (2019)
Wang, L., Fonseca, R., Tian, Y.: Learning search space partition for black-box optimization using Monte Carlo Tree Search. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, pp. 19511–19522 (2020)
Jimenez, F., Katzfuss, M.: Scalable bayesian optimization using vecchia approximations of gaussian processes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.01459 (2022)
Cao, Y., Fleet, D.J.: Transductive log opinion pool of Gaussian process experts. Workshop on Nonparametric Methods for Large Scale Representation Learning at NIPS. arXiv:1511.07551 (2015)
Schilling, N., Wistuba, M., Schmidt-Thieme, L.: Scalable hyperparameter optimization with products of gaussian process experts. In: Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, pp. 33–48 (2016)
Snoek, J., Larochelle, H., Adams, R.P.: Practical Bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 25 (2012)
Shahriari, B., Swersky, K., Wang, Z., Adams, R.P., de Freitas, N.: Taking the human out of the loop: a review of Bayesian optimization. Proc. IEEE 104(1), 148–175 (2016)
Williams, C.K., Rasmussen, C.E.: Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning, vol. 2. MIT press, Cambridge (2006)
Quiñonero-Candela, J., Rasmussen, C.E.: A unifying view of sparse approximate gaussian process regression. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 6(65), 1939–1959 (2005)
Snelson, E., Ghahramani, Z.: Sparse gaussian processes using pseudo-inputs. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 18 (2006)
Titsias, M.: Variational learning of inducing variables in sparse gaussian processes. In: Proceedings of the Twelth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 5, pp. 567–574. PMLR, USA (2009)
Hinton, G.E.: Products of experts. In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, vol. 1, pp. 1–6 (1999)
Tresp, V.: A Bayesian committee machine. Neural Comput. 12(11), 2719–2741 (2000)
Cao, Y., Fleet, D.J.: Generalized product of experts for automatic and principled fusion of Gaussian process predictions. Modern Nonparametrics 3: Automating the Learning Pipeline workshop at NIPS. arXiv:1410.7827 (2014)
Deisenroth, M.P., Ng, J.W.: Distributed Gaussian processes. In: 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2015, vol. 2 (2015)
Liu, H., Cai, J., Wang, Y., Ong, Y.S.: Generalized robust Bayesian committee machine for large-scale Gaussian process regression. In: 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2018, vol. 80, pp. 3131–3140 (2018)
Trapp, M., Peharz, R., Pernkopf, F., Rasmussen, C.E.: Deep structured mixtures of gaussian processes. In: Proceedings of the Twenty Third International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 108, pp. 2251–2261 (2020)
Wang, K., Pleiss, G., Gardner, J., Tyree, S., Weinberger, K.Q., Wilson, A.G.: Exact gaussian processes on a million data points. In: Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., d’ Alché-Buc, F., Fox, E., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Cohen, S., Mbuvha, R., Marwala, T., Deisenroth, M.P.: Healing Products of Gaussian Process Experts. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning (2020)
Hinton, G.E.: Training products of experts by minimizing contrastive divergence. Neural Comput. 14(8), 5550 (2002)
Cao, Y.: Scaling gaussian processes. Ph.D. thesis, University of Toronto (Canada) (2018)
Heskes, T.: Selecting weighting factors in logarithmic opinion pools. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 10, pp. 266–272 (1998)
Bailey, T., Julier, S., Agamennoni, G.: On conservative fusion of information with unknown non-Gaussian dependence. In: 15th International Conference on Information Fusion, FUSION 2012, pp. 1876–1883 (2012)
Bauer, M., van der Wilk, M., Rasmussen, C.E.: Understanding probabilistic sparse gaussian process approximations. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 29 (2016)
Liu, H., Cai, J., Ong, Y.-S., Wang, Y.: Understanding and comparing scalable gaussian process regression for big data. Knowl.-Based Syst. 164, 324–335 (2019)
Sobol, I.M.: On the distribution of points in a cube and the approximate evaluation of integrals. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 7(4), 86–112 (1967)
Srinivas, N., Krause, A., Kakade, S., Seeger, M.: Gaussian process optimization in the bandit setting: No regret and experimental design. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1015–1022 (2010)
Regis, R.G.: Trust regions in kriging-based optimization with expected improvement. Eng. Optim. 48(6), 1037–1059 (2016)
Yuan, Y.-x.: A review of trust region algorithms for optimization. In: Iciam, vol. 99, pp. 271–282 (2000)
Conn, A.R., Scheinberg, K., Vicente, L.N.: Introduction to Derivative-free Optimization. SIAM, New York (2009)
Wan, X., Nguyen, V., Ha, H., Ru, B., Lu, C., Osborne, M.A.: Think global and act local: Bayesian optimisation over high-dimensional categorical and mixed search spaces. In: 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2021), pp. 10663–10674 (2021)
Regis, R.G., Shoemaker, C.A.: Improved strategies for radial basis function methods for global optimization. J. Global Optim. 37(1), 113–135 (2007)
Shylo, O.V., Middelkoop, T., Pardalos, P.M.: Restart strategies in optimization: parallel and serial cases. Parallel Comput. 37(1), 60–68 (2011)
Bibby, J.: Axiomatisations of the average and a further generalisation of monotonic sequences. Glasg. Math. J. 15(1), 63–65 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tautvaišas, S., Žilinskas, J. Scalable Bayesian optimization with generalized product of experts. J Glob Optim 88, 777–802 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-022-01236-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-022-01236-x