Abstract
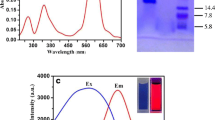
The earthworm exposed to toxics shows physiological responses as: avoidance and mucus secretion. Heavy metals are particularly toxic to earthworms and the mucus secretion has been considered as a defence mechanism against undesirable substance. The chromophores present in the mucus secretion of Eisenia foetida have been poorly studied. Mucus secretion of E. foetida was induced by PbCl2. High PbCl2 concentrations provoked abundant mucus secretion which showed fluorescence when illuminated by UV light. Dialysis membrane separation, UV Visible and Excitation-Emission Matrix Fluorescence (EEM) spectroscopy were used to characterise the fluorescent pigments. EEM spectroscopy analysis of the mucus secretion signalled three excitation-emission peaks at: 310/380 nm, 370/520 nm and 440/520 nm. Two fluorophores were separated by dialysis. One of them matched the fluorescent compound riboflavin excitation-emission profile; the other is a protein with a peak 290/350 nm. Native-PAGE electrophoresis was conducted to assess the riboflavin-biding ability of the coelomic fluid protein produced by Eisenia foetida showing a high riboflavin-biding ability.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data generated during this research work can be available upon request.
References
Jan A, Azam A, Siddiqui K, Ali A, Choi I, Hag Q (2015) Heavy metals and human health: mechanistic insight into toxicity and counter defense system of antioxidants. Int J of Mol Sci 16:29592–29630
Weiss D, Shotyk W, Appleby PG, Kramers JD, Cherburkin AK (1999) Atmospheric Pb deposition since the industrial revolution recorded by five Swiss peat profiles: enrichment factors, fluxes, isotopic composition, and sources. Environ Sci Technol 33(9):1340–1352
Abd-Elwahed MS (2018) Influence of long-term wastewater irrigation on soil quality and its spatial distribution. Ann Agrar Sci 63(2):191–199
Shamuyarira KK, Gumbo JR (2014) Assessment of heavy metals in municipal sewage sludge: a case study of Limpopo province, South Africa. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11(3):2569–2579
Neuhauser EF, Loehr RC, Milligan DL et al (1985) Toxicity of metals to the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Biol Fert of Soils 1:149–152
Chao TT, Zhou L (1983) Extraction techniques for selective dissolution of amorphous iron oxides from soils and sediments. Soil Sci Soc Am J 47:224–232
Yoncan G, Zhenzhong W, Youmei Z, Xiaoyang M (1998) Bioconcentration effects of heavy metal pollution in soil on the mucus epithelial cell ultrastructure injuring of the earthworm’s gastrointestinal tract. Bull Environ Cont Toxicol 60:280–284
Zhang X, Yang L, Li Y et al (2010) Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ Monit Assess 184:2261–2273
Verdes A, Gruber DF (2017) Glowing Worms: biological, chemical, and functional diversity of bioluminescent. Integr Comp Biol 57:18–32
Bouché ML, Habets F, Biagianti-Risbourg S, Vernet G (2000) Toxic effects and bioaccumulation of cadmium in the aquatic Oligochaete Tubifex tubifex. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:246–251
Byrne JH (2019) The Oxford handbook of invertebrate neurobiology. New York, Oxford University press pp. 451-452
Koene JM, Chase R (1998) Changes in the reproductive system of the snail Helix aspersa caused by mucus from the love dart. J Exp Biol 201(15):2313–2319
Soumya PR, Pulikeshi BM (2017) Earthworm’s coelomic fluid: extraction and importance. Inter J Adv Sci Res 2:01–04
Stephenson J (1930) The Oligochaeta. Oxford at Clarendon Press. United Kingdom pp: 9–23
Wielgus-Serafinska E, Kawka E (1976) Accumulation and localization of lead in Eisenia foetida (Oligochaeta) tissues. Folia Histochem Cytochem 14:315–320
Denny MW (1989) Invertebrate mucous secretions: functional alternatives to vertebrate paradigms. Symp Soc Exp Biol 43:337–366
Yang G, Chen C, Yu Y, Zhao H, Wang W, Wang Y, Wang X (2018) Combined effects of four pesticides and heavy metal chromium (VI) on the earthworm using avoidance behaviour as an endpoint. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:191–200
Ballance S, Sheehan JK, Tkachenko A, McCrohan CR, White KN (2002) Interaction of mucus with freshly neutralized alluminum in freshwater. J Inorg Biochem 92(1):11–18
Wampler JE, Jamieson GM (1980) Earthworm bioluminescence: comparative physiology and biochemistry. Comp Biochem Physiol 66B:43–50
Jiang XC, Wang D, Halpern M (1989) Isolation and characterization of alarm pheromone from electric shock-induced earthworm secretion. Pharmacol Biochem Behavior 34:213–221
Fujita K, Tsuta M, Kokawa M, Sugiyama J (2010) Detection of deoxynivalenol using fluorescence excitation-emission matrix. Food Bioprocess Tech 3(3):922–927
Kruk J, Dziurka M, Płytycz B (2019) Identification of new fluorophores in coelomic fluid of Eisenia andrei earthworms. PLoS One 14(3):e0214757
Albani JR, Demuynck S, Grumiaux F, Lepretre A (2003) Fluorescence of Eisenia foetida and Eisneia andrei. Photochem Photobiol 78(6):599–602
Wampler JE, Jamison BG (1986) Cell bound bioluminescence from Pontodrilus bermudensis, and its similarities to other earthworm bioluminescence. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 84(1):81–87
Rodionova NS, Rota E, Tsarkova AS (2017) Progress in the study of bioluminescent earthworms. Photochem Photobiol 93:416–428
Wampler JE, Jamison BG (1980) Earthworm bioluminescence: comp physiology and biochemistry. Comp Biochem Physiol 66B:43–50
Karoui R, Blecker C (2011) Fluorescence spectroscopy measurement for quality assessment of food systems. A Review. Food Bioprocess Tech 4:364–386
Sikorka E, Gorecki T, Khmelinskii I, Sikorski M, Keukeleire DD (2004) Fluorescence spectroscopy for characterization and differentiation of beers. J I Brew 100(4):267–275
Pohlker C, Huffman JA, Poschl U (2012) Autofluorescence of atmospheric bioaerosols-fluorescent biomolecules and potential interferences. Atmos Meas Tech 5:37–71
Booksh KS, Muroski AR, Myreck ML (1996) Single-measurement excitation/emission matrix spectrofluorometer for determination of hydrocarbons in ocean water. 2. Calibration and quantitation of naphthalene and estyrene. Anal Chem 68:3539–3544
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Rodríguez MG, Rivera HB, Juarez JV, Muñoz-Ortega MH (2013) Cadmium effects. Trends Comp Biochem Physiol 17:81–92
Drewes CD, Vining EP, Callahan CA (1988) Electrophysiological detection of sublethal neurotoxic effects in intact earthworms. In earthworms in waste and environmental management. Edited by CA. Edwards and EP Neuhauser. SPB academic publishing. The Hague, Netherlands pp. 355-366
Heredia RB, Dueñas S, Castillo L, Ventura JJ, Silva Briano M, Posadas del Rio F, Rodriguez MG (2008) Autofluorescence as a tool to study mucus secretion in Eiseneia foetida. Comp Biochem Physiol A 151:407–414
Kauschke E, Mohrig W, Cooper EL (2007) Coelomic fluid proteins as basic components of innate immunity in earthworms. Eur J Soil Biol 43:S110–S115
Koziol B, Markowicz M, Kruk J, Plytycz B (2006) Riboflavin as a source of autofluorescence in Eisenia foetida coelomocytes. Photochem Photobiol 82(2):570–573
Rao VV, Ningshen TJ, Chaitanya RK, Senthilkumaran B, Dutta-Gupta A (2016) Cloning and characterization of a riboflavin-binding hexamerin from the larval fat body of a lepidopteran stored grain pest, Corcyra cephalonica. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 194:58–64
Kevin K, Leung K, Litchfiel DW, Shilton BH (2012) Flavin adenine dinucleotide content of quinine reductase 2: analysis and optimization for structure-function studies. Anal Biochem 420:84–89
Pan XW, Song W, Zhang D (2010) Earthworms (Eisenia foetida, Savigny) mucus as complexing ligand for imidacloprid. Biol Fert Soils 46:845–850
Bystra-Mieloszyk K, Balter A, Drabent R (1985) Fluorescence quenching for flavins interacting with egg white riboflavin-binding protein. Photochem Photobiol 41(2):141–147
Matthews BJH, Jones AC, Theodorou NK, Tudhope AW (1996) Excitation-emission-matrix fluorescence spectroscopy applied to humic acid bands in coral reefs. Mar Chem 55:317–332
Cygal M, Lis U, Kruk J, Plytycz B (2007) Coelomocytes and fluorophores of the earthworm Dendrobaena veneta raised at different ambient temperatures. Acta Biol Cracov Zool 49:5–11
Oster G, Bellin JS, Holmstrom B (1982) Photochemistry of riboflavin. Experientia 18:249–296
Helbling EW, Menchi CF, Villafane VE (2002) Bioaccumulation and role of Argentina. Photochem Photobiol Sci 1(10):820–825
Johnson GA, Mantha SD, Day TA (2000) A spectrofluorometric survey of UV induced blue-green fluorescence in foliage of 35 species. J Plant Physiol 156:242–252
Sinha RP, Hader DP (2002) Life under solar UV radiation in aquatic organisms. Adv Space Res 30(6):1547–1556
Rajan BM, Prasad MSK (2012) Isolation and purification of riboflavin binding protien (rfbp) from the egg white of emu (Dromaius novaehollandiae). IJPAES 2(1):5–13
Zandomeneghi G, Zandomeneghi M (2009) Determination of Holo- and Apo-riboflavin binding protein in avian egg whites through circular Dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy. J Agric Food Chem 57(15):6510–6517
Plytycz B, Klimek M, Homa J, Mazur AI, Kruk J Morgan AJ (2011) Species-specific sensitivity of earthworm coelomocytes to dermal metal (Cd,Cu,Ni,Pb,Zn) exposures: Methodological approach. Pedobiologia 54S:S203-S210
Hua Z, Wang Y, Cao H, Pu L, Cui Y (2011) Purification of a protein from coelomic fluid of the earthworm Eisenia foetida and evaluation of its hemolytic, antibacterial, and antitumor activities. Pharm Biol 49(3):269–275
Merrill AH, Froehlich JA, Mccormick DB (1979) Purification of riboflavin-binding proteins from bovine plasma and discovery of a pregnancy-specific riboflavin-binding protein. J Biol Chem 254(19):9362–9364
Du L, Wu A, Liu G, Li H, Yu B, Wang X (2020) Green autofluorescence eleocytes from earthworm as a tool for detecting environmental iron pollution. Ecol Indic 108:105695
White HB, Merrill AH (1988) Riboflavin-binding proteins. Annu Rev Nutr 8:279–299
Storey KB, Storey JM (2010) Metabolic regulation and gene expression during aestivation. Prog Mol Subcell Biol Springer, Berlin, pp 25–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure Statements
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Consent to Publication
The Author guarantees that the Contribution to the Work has not been previously published elsewhere or that if it has been published in whole or in part, any permission necessary to publish it in the Work has been obtained and provided.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heredia Rivera, B., Rodríguez, M.G., Rodríguez-Heredia, M. et al. Characterisation by Excitation-Emission Matrix Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Pigments in Mucus Secreted of Earthworm Eisenia foetida Exposed to Lead. J Fluoresc 30, 725–733 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-020-02533-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-020-02533-y