Abstract
Mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) is an important variable in anesthesia and intensive care but currently requires pulmonary artery catheterization. Recently, non-invasive determination of SvO2 (Capno-SvO2) using capnodynamics has shown good agreement against CO-oximetry in an animal model of modest hemodynamic changes. The purpose of the current study was to validate Capno-SvO2 against CO-oximetry during major alterations in oxygen delivery. Furthermore, evaluating fiberoptic SvO2 for its response to the same challenges. Eleven mechanically ventilated pigs were exposed to oxygen delivery changes: increased inhaled oxygen concentration, hemorrhage, crystalloid and blood transfusion, preload reduction and dobutamine infusion. Capno-SvO2 and fiberoptic SvO2 recordings were made in parallel with CO-oximetry. Respiratory quotient, needed for capnodynamic SvO2, was measured by analysis of mixed expired gases. Agreement of absolute values between CO-oximetry and Capno-SvO2 and fiberoptic SvO2 respectively, was assessed using Bland–Altman plots. Ability of Capno- SvO2 and fiberoptic SvO2 to detect change compared to CO-oximetry was assessed using concordance analysis. The interventions caused significant hemodynamic variations. Bias between Capno-SvO2 and CO-oximetry was + 3% points (95% limits of agreements – 7 to + 13). Bias between fiberoptic SvO2 and CO-oximetry was + 1% point, (95% limits of agreements − 7 to + 9). Concordance rate for Capno-SvO2 and fiberoptic SvO2 vs. CO-oximetry was 98% and 93%, respectively. Capno-SvO2 generates absolute values close to CO-oximetry. The performance of Capno-SvO2 vs. CO-oximetry was comparable to the performance of fiberoptic SvO2 vs. CO-oximetry. Capno-SvO2 appears to be a promising tool for non-invasive SvO2 monitoring.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) is a clinically useful monitoring parameter that provide important information regarding the whole-body oxygen delivery/consumption balance and is of particular interest in the setting of anaesthesia and intensive care [1]. The use of SvO2 as a routine monitoring parameter has so far been hampered by the fact that intermittent blood sampling from the pulmonary artery (CO-oximetry; representing “gold standard”) as well as continuous assessment by fibreoptic spectrophotometry both require invasive catherization of the pulmonary artery, which is associated with certain risks as well as increased nursing care demands and cost [2, 3].
During our development of a modern version of capnodynamic assessment of cardiac output (Effective Pulmonary Blood Flow, COEPBF), which we have found to produce similar results when compared to accepted reference methods, we have come to realize that combining COEPBF with the respiratory quotient (RQ) results in the possibility to determine SvO2 noninvasively [4,5,6,7]. In a recent proof-of-concept study we have found that this new non-invasive and continuous methodology of monitoring SvO2 (Capno-SvO2) show promising results when compared to CO-oximetry determinations of SvO2 in a porcine model, during modest hemodynamic challenges [8].
The aim of the present study was to validate Capno-SvO2 against the gold standard CO-oximetry for agreement of absolute values and ability to detect change during profound variations in oxygen delivery while measuring RQ, using our previously well-established porcine model. A comparison between CO-oximetry and another continuous SvO2 methodology, i.e., fibreoptic SvO2, was also included for comparison.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Animal preparations
The study was performed at the Hedenstierna Laboratory, Uppsala University, Uppsala Sweden. Authorization was granted from Uppsala Animal Ethics Committee (Uppsala, Sweden case number C75/16, chairperson Erik Göransson on August 26, 2016).
The animals were handled in accordance with the animal experimentation guidelines of the Uppsala Animal Ethics Committee and Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines.
Eleven domestic-breed pigs of both sexes (median weight 29.6 kg, range 27.1–31.7 kg, 6–8 weeks of age), from the same breeding colony (Mångsbo Farm, Uppsala, Sweden) were used. The animals were kept in a light- and temperature-controlled environment, with unlimited access to tap water and food on a standardized schedule. The experiments were done during daytime hours.
The pigs were anaesthetized as previously described and mechanically ventilated in a volume-controlled mode (Servo-I; Maquet, Solna, Sweden), with tidal volume of 10 mL kg−1 and fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) 0.3 [9]. Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) was kept at 5 cm H2O after an initial 2-min period of lung expansion using PEEP 10 cm H2O as previously described [8]. After the lung expansion manoeuvre, an air test using FiO2 0.21 was performed and repeated if necessary, aiming for sustained pulse oximetry saturation > 97% as indicative of open lung conditions [10]. The animals were given a bolus of Ringers’ acetate solution 20 mL kg− 1 after induction and thereafter kept on maintenance infusion of glucose 25 mg mL −1 8 mL kg−1 h−1 and Ringer’s acetate solution 10 mL kg−1 h−1. Exhaled CO2 was measured by a mainstream infrared CO2 sensor (Capnostat-3; Respironics Inc, Wallingford, CT), and ventilation airflow was registered through the regular flow sensor of the servo-I ventilator. Volumetric capnography was utilised for calculating the CO2 elimination rate (VCO2), as described in previous studies [11].
Adequate anesthetic depth and analgesic level were tested regularly during the experiment according to standard procedures of the laboratory. The animals were fitted with monitoring devices described in detail in previous studies [9]. In addition a 7.5 F pulmonary artery catheter with fibreoptic SvO2 monitoring (Swan-Gantz pulmonary artery catheter, model 774F75; Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine CA; USA) and a 5 F femoral artery cannula for transpulmonary thermodilution cardiac output monitoring (PICCO2™, Pulsion Medical Systems, Munich, Germany), were also included as well as an additional 7.5 F pulmonary artery introducer sheath for rapid fluid administration.
A 12 F balloon tipped catheter (Mediq Sverige AB, Uppsala, Sweden) was surgically introduced through the left femoral vein, to a depth of 30 cm corresponding to the inferior vena cava (IVC). The catheter was fitted with a 10 mL balloon allowing partial IVC occlusion when inflated with NaCl 0.9%. The animals were given a bolus dose of intravenous heparin 5000 U (LEO pharma) to minimize the risk of clotting due to the extensive intravascular monitoring setup.
SvO2 through blood samples were analysed by a CO-oximeter calibrated for porcine hemoglobin (OSM3; Radiometer Medical AbS, Brønshøj, Denmark). This also provided the hemoglobin level, necessary for the calculations of COEPBF and Capno-SvO2 as well as for calibrations of fiberoptic SvO2.
2.2 Assessment of Capno-SvO2
The principle behind continuous Capno-SvO2 method has been described in detail in previous work by our research team [8]. The Capno-SvO2 method is based on the differential Fick principle and utilizes a combination of continuous estimation of COEPBF and oxygen consumption (VO2) incorporated in a rearranged Fick’s equation [12]. COEPBF is estimated by applying a special breathing pattern of variations in I:E relationships (six breaths with normal I:E relations followed by three breaths vid an approximately 2 s expiratory pause). This breathing pattern causes small fluctuations in alveolar CO2 concentration and VCO2, related to the pulmonary blood flow participating in gas exchange which allows for estimation of COEPBF [5, 7, 13]. VO2 can be estimated using continuous volumetric capnography measurement of VCO2 combined with RQ:
where VO2 is the oxygen consumption (mL min− 1), VCO2 is the CO2 production rate (mL min− 1), RQ is the respiratory quotient.
VCO2 applied in Eq. 1 is determined as a moving mean value of measured CO2 elimination made over a period of 20 min in order to produce stable VCO2 values with the intent to reflect an assumed stable metabolism.
Using Fick’s equation for oxygen, the content of oxygen in mixed venous blood (CvO2) can be derived:
where COEPBF is the effective pulmonary blood flow (L min− 1), VO2 is the oxygen consumption (mL min− 1), CcO2 is the pulmonary end capillary oxygen content (mL L− 1), CvO2 is the pulmonary mixed venous oxygen content (mL L− 1).
Equation 2 can be further rearranged to derive CvO2:
where COEPBF is the effective pulmonary blood flow (L min− 1), VO2 is the oxygen consumption (mL min− 1), CcO2 is the pulmonary end capillary oxygen content (mL L− 1), CvO2 is the pulmonary mixed venous oxygen content (mL L− 1).
CvO2 from Eq. 3 can then be used to calculated SvO2 by using the solubility constant for oxygen in blood plasma, Hüfner’s constant and the hemoglobin value as previously described thereby generating breath-by-breath estimations of SvO2 [8].
2.3 RQ-measurements
The RQ was determined immediately before the start of the first challenge (morning) and immediately before the start of the last challenge (afternoon), approximately 4 h apart (shown in Fig. 1). Measurements were performed in all animals, by analysis of mixed expired gas collected in a Douglas bag. Each RQ measurement was conducted in the following way:
-
Ventilator bias flow during expiration phase ((normally 2 L min−1 in Servo-I ventilator (Maquet, Solna, Sweden)) was turned off to avoid diluting the gas in the bag with inspiration gas.
-
FiO2 was changed from 0.30 to 0.21 (i.e., room air), which was done for two reasons; it gives the best conditions for the RQ calculation (as shown in Eq. 1 below) and the inspired gas concentration is well-defined without relying on accurate gas mixing by the ventilator.
-
To reach a stable state of nitrogen (N2), 20 min wash-in of N2 was allowed after the change of FiO2 and before the bag was connected to the ventilator exhaust port.
-
Gas was collected for about 10 min; roughly 70 L of expiratory gas was collected.
-
The content of the bag was analyzed using the side-stream gas analyzer of a Flow-i anesthesia system (Maquet, Solna, Sweden). Gas was alternatingly sampled from the bag or from the room air.
Gas concentrations of FiO2 (room air), FemixO2 (bag) and FemixCO2 (bag) were measured at ATPD state (Ambient temperature and pressure, dry). RQ was calculated using the following formula, which is based on the Haldane transformation to account for the imbalance between inspiration and expiration volumes:
RQ is the respiratory quotient, FiO2 is the fraction of inspired oxygen, FemixCO2 is the carbon dioxide concentration in the Douglas bag, FemixO2 is the oxygen concentration in the Douglas bag.
A detailed derivation of the RQ-equation can be found in Supplemental Description Content 1.
2.4 Study protocol
After preparation, the animals were allowed a 20-minute stabilizing period. Following this, an arterial blood sample was taken for calibration of the fiberoptic (Hb and CO-oximetry SvO2 as per the manufacturers recommendation) and the capnodynamic monitoring system (Hb). Subsequently, five paired baseline measurement of all three methods were performed, 1 min apart, for calculation of inherent precisions. After this, the animals were subjected to six different hemodynamic challenges anticipated to affect SvO2 (Fig. 1):
-
1.
Stepwise increase in FiO2: (0.21–0.4–0.75–1.0). Each FiO2 level was applied for 3 min and simultaneous SvO2 recordings were made at the end of each FiO2 level. After this, FiO2 was returned to baseline 0.3 and an air test was performed to ensure open lung conditions after FiO2 1.0 and lungs expanded as described if needed as described above.
-
2.
Hemorrhage: 15 mL kg−1 of blood were drawn under 5–10 min and kept in a plastic bag intended for donor blood, containing 5000 U of Heparin (LEO pharma). SvO2 values were recorded just before and 5 min after the hemorrhage.
-
3.
Crystalloid bolus: 15 mL kg−1 of Ringer’s acetate solution was given centrally in the 7.5 F PA introducer sheath to simulate crystalloid resuscitation of acute hypovolemia, over 5 min, 6 simultaneous SvO2 measurements were obtained: before crystalloid infusion and 0, 5, 10, 15 and 20 min after completions of infusion where 0 is just after completed infusion.
-
4.
Blood transfusion: blood drawn under step 2 was transfused back over 5–10 min and SvO2 data were recorded before transfusion and 0, 5, 10, 15 and 20 min after completion of the transfusion where 0 is just after completed infusion.
-
5.
Cava balloon: the cava balloon was inflated (reducing cardiac output by 30–50%). SvO2 data was collected prior to inflating the balloon, 2 min after inflation, and 3 min after deflation.
-
6.
Dobutamine: a central infusion of dobutamine (Hameln pharma gmbh, Hameln, Germany) 10 mcg kg−1 min−1 was started immediately after the 3-min recording after cava balloon deflation. SvO2 was then recorded 5, 10 and 15 min after starting the dobutamine infusion.
The fiberoptic SvO2 measurement was calibrated with Hb-level and CO-oximetry SvO2 values as per manufacturer’s instructions. This was performed totally 4 times during the experiment as marked in Fig. 1 to ensure continuous optimal performance during the experiment. At the same time points, the capnodynamic method was calibrated with the corresponding Hb-level. Throughout the study protocol, Capno-SvO2 and fiberoptic SvO2, were recorded just before the blood samples for CO-oximetry were drawn. Due to previous experiences from caval occlusion causing extensive hemodynamic strain on the animals, no baseline recordings were made before the dobutamine step. Instead, dobutamine was started immediately after the last recording of step 5 as described above. The 3-minute recordings after cava balloon deflation, i.e., just before start of the dobutamine infusion, was used as comparison point for concordance analysis for the dobutamine step.
The animals were euthanized at the end of the experiment, according to the laboratory’s routines.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Raw data for absolute values of all three SvO2 methods (CO-oximetry, Capno-SvO2 and fibreoptic SvO2), as well as paired differences between Capno-SvO2 and CO-oximetry and between fibreoptic SvO2 and CO-oximetry, were controlled for normal distribution by D’Agostino and Pearson test and visual inspection of the corresponding histograms. Values are presented as mean and 95% confidence interval (CI).
The first five measurements, during hemodynamically stable baseline conditions, were used for calculation of inherent precision for each SvO2 method respectively. Inherent precision was defined as 2 times the coefficient of variation (CV = SD/mean) and was in turn used to quantify the least significant change (LSC) for the reference method CO-oximetry [14]. The LSC reflects the minimum change measured and recognized as a true change [14]. LSC was then used to determine the exclusion zone in the concordance analysis as previously described [8].
Bland–Altman analysis corrected for repeated measurements was used to assess agreement of absolute values between paired recording of CO-oximetry and Capno-SvO2 as well as between CO-oximetry and fibreoptic SvO2. Bias was defined as the mean difference between the tested methods and the reference method [15, 16]. Limits of agreement (bias ± [1.96 × SD]) were used when presenting the spread of included data points and are shown with the corresponding 95% CI. Mean percentage error (PE) was calculated as 1.96 × SD of the differences, divided by the mean of the reference method [17]. A predefined PE of < 30% was defined a priori to indicate a clinically useful agreement. The predefined maximum allowed difference for agreement between the tested methods and the reference method was set to 15% points (based on previous published performance of fibreoptic SvO2 devices and Capno-SvO2) [8, 18,19,20]. Based on our previous study, given the maximally allowed difference between the tested method and the reference method, a minimum of approximately 250 paired data points (corresponding to 10 animals with 25 paired recording per animal) was required to show that the 95% confidence interval of the limits of agreement would fall within the pre-defined maximal allowed difference thus showing that the methods are in agreement (80% power, 0.05 significance level) [8, 15, 21]. The ability of Capno-SvO2 and fibreoptic SvO2 to track changes in SvO2 compared to the refence method, was assessed by calculating the concordance rate, i.e., the percentage of data points moving in the same direction when comparing two different techniques [22]. Recorded changes between baseline measurements before each hemodynamic intervention, and the value corresponding to the highest change from baseline within that intervention, were used for calculation of the concordance rate. The LSC for CO-oximetry was found to be 9.5%. Based on this, changes in SVO2 of less than 9.5% (rounded up to 10%) of the mean of all SvO2 CO-oximetry recordings (corresponding to a minimal change in CO-oximetry SvO2 of 5% points) were not regarded as true changes and excluded from the concordance analysis [14].
Due to the increasingly unreliable performance of CO-oximetry method for low SvO2 levels, i.e., for values under 30%, CO-oximetry SvO2 values under 30% and its associated Capno-SvO2 and fibreoptic SvO2 values were excluded in the analysis [23, 24].
GraphPad Prism (version 9.0.0 for Windows, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) and Medcalc Statistical Software version 16.8.4 (MedCalc Software, Ostend, Belgium) was used for statistical calculations and Microsoft Excel for Mac 2020 version 16.41 for data handling.
3 Results
All animals survived the experiment. SvO2 data for step 1–3 in the protocol was excluded from one animal due malposition of the PA-catheter which was then repositioned correctly for step 4–6. The dobutamine step was introduced after the first animal and thus includes only 10 animals.
3.1 Calculated inherent precision
The inherent precision was found to be ± 7% for CO-oximetry SvO2 and ± 8% and ± 6% for Capno-SvO2 and fiberoptic SvO2, respectively which is in line with previous publications [8, 19].
3.2 RQ
The mean RQ for morning and afternoon recordings for all eleven animals, i.e., in total 22 RQ values, was found to be 0.97 (range 0.88–1.06) and RQ 0.97 was then used for all SvO2-capno calculations.
3.3 Response to hemodynamic interventions
All animals displayed SvO2 reactions in an anticipated manner when exposed to the various hemodynamic interventions. Both Capno-SvO2 and fiberoptic SvO2 showed parallel changes when compared to the reference method CO-oximetry with increase in SvO2 in response to increased FiO2, crystalloid infusion, blood transfusion and dobutamine administration. Correspondingly, hemorrhage and partial cava occlusion led to decreases in SvO2 for all methods. The changes in SvO2 for each hemodynamic intervention for all three SvO2 methods are shown in the event plot in Fig. 2.
Event plot showing SvO2 responses to the various hemodynamic challenges for all three SvO2 monitoring methods. Values are mean (95% CI). N = 11. Arrows indicate recalibration points for SvO2-capno and fiberoptic SvO2. BL Baseline, BLmean mean of precision recordings, FiO2 fraction inspired oxygen; BLcava Baseline cava occlusion step, Cavaoccl.2 min 2 min after cava occlusion, Cava defl. 3 min 3 min after cava balloon deflation
3.4 Agreement of absolute values
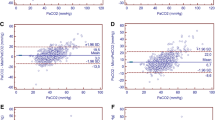
Bland–Altman analysis for all paired data showed a bias between Capno-SvO2 and CO-oximetry of + 3% points with 95% limits agreement of – 7 (CI − 10 to -4) to + 13 (CI 11 to 17) percentage points and a mean percentage error of 18%. Correspondingly, the bias between fiberoptic SvO2 and CO-oximetry was found to be + 1% point with 95% limits of agreement of − 7 (CI − 8 to − 6) to + 9 (CI 8 to 11) percentage points and PE 16%. Bland Altman plots for Capno-SvO2 vs. CO-oximetry and fiberoptic SvO2 vs. CO-oximetry are shown in Fig. 3. Table 1 shows the agreement of absolute values between the reference method and the tested methods for each hemodynamic intervention.
Bland–Altman plots for pooled recordings for Capno-SvO2 vs. CO-oximetry (A) and fiberoptic SvO2 vs. CO-oximetry (B). Dotted line represents bias, blue dotted lines represent upper and lower limits of agreement and black broken lines represents the corresponding CI for the limits of agreements. N = 11. A 271 paired data points, B 272 paired data points
3.5 Trending ability
The trending ability for Capno-SvO2 and fiberoptic SvO2, compared to CO-oximetry, are presented as four-quadrant plot illustrations in Fig. 4.
For Capno-SvO2, a total of 45 data points were found to lie outside the predefined 10% exclusion zone. 44 out of 45 values changed in the same direction as the reference method CO-oximetry which generates a concordance rate of 98%. The corresponding data for fiberoptic SvO2 was 46 data points outside the exclusion zone with 43 data points moving in the same direction as the reference method i.e., a concordance rate of 93%.
4 Discussion
The main finding of the current study was that Capno-SvO2 generates absolute values close to the gold standard CO-oximetry during major hemodynamic provocations. The agreement between Capno-SvO2 and CO-oximetry was comparable to that found for fiberoptic SvO2 vs. CO-oximetry. Furthermore, Capno-SvO2 demonstrated a slightly more accurate ability to detect change in SvO2 than fiberoptic SvO2.
4.1 Agreement of absolute values between CO-oximetry and the tested methods
Reliability in consistency during repeated measures and the ability to generate absolute values that corresponds acceptably with the gold standard can be considered absolute prerequisites for any new monitoring technique. During stable baseline conditions, Capno-SvO2 displayed an inherent precision matching those of both CO-oximetry and fiberoptic SvO2, thus, indicating a reliable monitoring system. During the following hemodynamic interventions Capno-SvO2 generated values close to the gold standard method and the overall agreement between Capno-SvO2 and CO-oximetry was within the predefined 95% limits of agreement of 15% points and well below the a priori determined limit for a PE of < 30%. There was an overall tendency for Capno-SvO2 to display slightly higher SvO2 values compared to CO-oximetry even if this difference was relatively small and within clinically acceptable limits. Fiberoptic SvO2 showed a smaller bias and narrower limits of agreement against CO-oximetry than that recorded for Capno-SvO2. Even if the difference in agreement against gold standard was relatively similar for both methods, the fact that fiberoptic SvO2 showed slightly better agreement is not entirely surprising since this value is generated from direct estimation of SvO2 in the actual pulmonary artery whereas the Capno-SvO2 is a figure derived from mathematical analysis of an induced variability exhaled CO2.
Both Capno-SvO2 and fiberoptic SvO2 showed variable levels of agreement against CO-oximetry depending on the type of hemodynamic intervention. During stable baseline conditions, both Capno-SvO2 and fiberoptic SvO2 showed near enough equal agreement against gold standard. This pattern was repeated for the FiO2 step which is reassuring since increased FiO2 is a common method of augmenting oxygen delivery in the clinical setting.
Differences between Capno-SvO2 and CO-oximetry can be attributed to mainly two factors. Firstly, issues related to COEPBF calculations i.e., disturbances in the prerequisites for the capnodynamic method, mainly the assumption of stable or slowly varying mixed venous CO2 content and the use of updated Hb levels. Secondly the incorporated RQ value will affect the Capno-SvO2 and thus its level of agreement against CO-oximetry.
The relatively high bias and limits of agreements seen during the fluid resuscitation (especially data points 0 and 5 min) and cava occlusion step is most likely due to initial disturbances in the mixed venous CO2 content and Hb level.
4.2 Ability to track changes in SvO2 for Capno-SvO2 and fiberoptic SvO2
Agreement of absolute values is central, but in the clinical context trending ability may be even more important [25]. In this study, Capno-SvO2 showed a very good concordance rate when compared to the gold standard, detecting 98% of the changes, which is well in line with the established fiberoptic method. In addition, the agreement between CO-oximetry and Capno-SvO2 during stable baseline conditions was very good. Appropriate agreement during stable conditions in combination with a high concordance rate against CO-oximetry, makes Capno-SvO2 potentially interesting as an early warning sign of not only more major hemodynamic deteriorations but also minor hemodynamic changes (as shown in our previous publication) [8].
4.3 Limitations
Even if the Capno-SvO2 technique showed potentially promising performance in the current study, like most monitoring methods it has inherent limitations that needs to be considered and further investigated, particularly if applied in a clinical setting.
4.3.1 Issues related to calibration of the fiberoptic method
The fiberoptic SvO2 method was recalibrated against CO-oximetry four times during the protocol to optimize its performance as shown in Fig. 1. Normally, the fiberoptic system is intended to be calibrated once daily and not frequently recalibrated [26]. As a consequence of these frequent recalibrations, not corresponding to normal clinical routine, the subsequent fiberoptic SvO2 values will have affected the performance of the fiberoptic catheter in a positive way. The Capno-SvO2 was recalibrated at the same time points as the fiberoptic system but only against the current Hb level since the Capno-SvO2 method is independent from repeated alignment against gold standard CO-oximetry obtained mixed venous saturations (as is the case for fiberoptic SvO2).
4.3.2 Influence of respiratory quotient
The RQ value is an important determinant in estimating Capno-SvO2 and will affect the agreement between Capno-SvO2 and CO-oximetry. Mathematically, choosing a higher RQ will elevate the Capno-SvO2 and vice versa. Statistically this affects accuracy, but not precision – i.e., bias will shift and will subsequently move upper and lower limit of agreements equally in parallel [14]. It will, however, not have an impact on the trending ability, maybe the most important feature of a monitoring method, as discussed above.
In this study the RQ was directly measured, and the mean value of all measurements was used for calculations of Capno-SvO2. In the clinical setting it is more likely that RQ will be taken from tabulated values since a direct measurement is impractical with currently available methods. Furthermore, RQ depends on fasting time and the nutritional substrate given and this needs to be taken into consideration when evaluating the recorded RQ [27, 28]. In the current study, the animals were fasted and kept on a low-level glucose maintenance infusion, a common practice during anaesthesia. The scenario may have been different if nutritional status and/or infusions had been altered regarding glucose concentration or type of substrate, something that can be of importance in the intensive care setting [27]. Despite this, using the mean RQ for the whole group still resulted in acceptable agreement and trending ability.
4.4 Clinical applicability
In its current form, the Capno-SvO2 method requires controlled mechanical ventilation [7, 29]. However, most of the patients that would benefit from continuous non-invasive assessment of SvO2 will already be subjected to controlled mechanical ventilation both in the operating room and in the intensive care unit. Still, the fact that the method requires controlled ventilation will exclude patients that are spontaneously breathing or are treated with various modes of patient triggered ventilation.
Although Capno-SvO2 has the potential to considerably expand the ability to continuously monitor SvO2 compared to today, it is important to emphasize that Capno-SvO2 is not a substitute for the proper use of a pulmonary artery catheter since it does not provide information regarding relevant pressure and resistance parameters. However, it could potentially provide real time SvO2 monitoring in situations where a pulmonary artery catheter is neither practical or justifiable due to its invasive nature, associated risks, and cost. Thus, the potential role of Capno-SvO2 deserves further translational studies to define its place in monitoring of patients that are cared for in the operating room or in intensive care.
In conclusion, the current study shows that the Capno-SvO2 method is in close agreement with the gold standard CO-oximetry and displays good trending ability even during major changes in oxygen delivery. These features of the Capno-SvO2 method, in combination with its non-invasive nature, may offer a novel real time option for SvO2-monitoring. Even if a pulmonary artery catheter is of seminal importance for complete hemodynamic assessment, the Capno-SvO2 method could facilitate more advanced hemodynamic surveillance when a pulmonary artery catheter is not warranted, technically possible (such as in pediatric practice) or even contraindicated, thereby acting as a useful adjunct to more traditional hemodynamic monitoring.
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Holm J, Håkanson E, Vánky F, Svedjeholm R. Mixed venous oxygen saturation predicts short- and long-term outcome after coronary artery bypass grafting surgery: a retrospective cohort analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2011;107:344–50.
Kalra A, Heitner S, Topalian S. Iatrogenic pulmonary artery rupture during Swan-Ganz catheter placement: a novel therapeutic approach. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;81:57–9.
Hadian M, Pinsky MR. Evidence-based review of the use of the pulmonary artery catheter: impact data and complications. Crit Care. 2006;10(Suppl 3):8.
Karlsson J, Wallin M, Hallbäck M, Lönnqvist PA. Capnodynamic determination of cardiac output in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in pigs. Br J Anaesth. 2019;122:335–41.
Hällsjö Sander C, Hallbäck M, Wallin M, Emtell P, Oldner A, Björne H. Novel continuous capnodynamic method for cardiac output assessment during mechanical ventilation. Br J Anaesth. 2014;112:824–31.
Sigmundsson TS, Öhman T, Hallbäck M, Redondo E, Sipmann FS, Wallin M, Oldner A, Hällsjö Sander C, Björne H. Performance of a capnodynamic method estimating effective pulmonary blood flow during transient and sustained hypercapnia. J Clin Monit Comput. 2018;32:311–9.
Peyton PJ, Wallin M, Hallbäck M. New generation continuous cardiac output monitoring from carbon dioxide elimination. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019;19:28.
Karlsson J, Lönnqvist PA, Wallin M, Hallbäck M. A continuous noninvasive method to assess mixed venous oxygen saturation: a proof-of-concept study in pigs. Anesth Analg. 2021;132(6):1768–76. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000005188.
Karlsson J, Winberg P, Scarr B, Lönnqvist PA, Neovius E, Wallin M, Hallbäck M. Validation of capnodynamic determination of cardiac output by measuring effective pulmonary blood flow: a study in anaesthetised children and piglets. Br J Anaesth. 2018;121:550–8.
Ferrando C, Romero C, Tusman G, Suarez-Sipmann F, Canet J, Dosdá R, Valls P, Villena A, Serralta F, Jurado A, Carrizo J, Navarro J, Parrilla C, Romero JE, Pozo N, Soro M, Villar J, Belda FJ. The accuracy of postoperative, non-invasive Air-Test to diagnose atelectasis in healthy patients after surgery: a prospective, diagnostic pilot study. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e015560.
Suarez-Sipmann F, Bohm SH, Tusman G. Volumetric capnography: the time has come. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2014;20:333–9.
Fick A. Uber die messung des Blutquantums in den Hertzvent rikeln. Sitzber Physik Med Ges Wurzburg, 1870, pp 290–91.
Gedeon A, Krill P, Osterlund B. Pulmonary blood flow (cardiac output) and the effective lung volume determined from a short breath hold using the differential Fick method. J Clin Monit Comput. 2002;17:313–21.
Cecconi M, Rhodes A, Poloniecki J, Della Rocca G, Grounds RM. Bench-to-bedside review: the importance of the precision of the reference technique in method comparison studies–with specific reference to the measurement of cardiac output. Crit Care. 2009;13:201.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;1:307–10.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Agreement between methods of measurement with multiple observations per individual. J Biopharm Stat. 2007;17:571–82.
Critchley LA, Critchley JA. A meta-analysis of studies using bias and precision statistics to compare cardiac output measurement techniques. J Clin Monit Comput. 1999;15:85–91.
Herner A, Haller B, Mayr U, Rasch S, Offman L, Schmid R, Huber W. Accuracy and precision of ScvO2 measured with the CeVOX-device: A prospective study in patients with a wide variation of ScvO2-values. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0192073.
Kissoon N, Spenceley N, Krahn G, Milner R. Continuous central venous oxygen saturation monitoring under varying physiological conditions in an animal model. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2010;38:883–9.
Iodice FG, Ricci Z, Haiberger R, Favia I, Cogo P. Fiberoptic monitoring of central venous oxygen saturation (PediaSat) in small children undergoing cardiac surgery: continuous is not continuous. F1000Res. 2014;3:23.
Lu MJ, Zhong WH, Liu YX, Miao HZ, Li YC, Ji MH. Sample size for assessing agreement between two methods of measurement by Bland–Altman method. Int J Biostat. 2016;10:20. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijb-2015-0039.
Critchley LA, Lee A, Ho AM. A critical review of the ability of continuous cardiac output monitors to measure trends in cardiac output. Anesth Analg. 2010;111:1180–92.
Porath M, Sinha P, Dudenhausen JW, Luttkus AK. Systematic instrumental errors between oxygen saturation analysers in fetal blood during deep hypoxemia. Clin Chim Acta. 2001;307:151–7.
Beards SC, Edwards JD, Nightingale P. The need for quality control in measurement of mixed venous oxygen saturation. Anaesthesia. 1994;49:886–8.
Shepherd SJ, Pearse RM. Role of central and mixed venous oxygen saturation measurement in perioperative care. Anesthesiology. 2009;111:649–56.
LLC EL. Edwards hemosphere advanced monitor operator’s manual 2017. https://www.iccueducation.org.uk/uploads/2/3/1/0/23109338/hemosphere_cardiac_output_monitor.pdf. Accessed 25 Mar 2021
Frankenfield DC. Impact of feeding on resting metabolic rate and gas exchange in critically ill patients. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2019;43:226–33.
Liu H, Chen Y, Ming D, Wang J, Li Z, Ma X, van Milgen J, Wang F. Integrative analysis of indirect calorimetry and metabolomics profiling reveals alterations in energy metabolism between fed and fasted pigs. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2018;9:41.
Sander CH, Sigmundsson T, Hallbäck M, Sipmann FS, Wallin M, Oldner A, Björne H. A modified breathing pattern improves the performance of a continuous capnodynamic method for estimation of effective pulmonary blood flow. J Clin Monit Comput. 2017;31:717–25.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Karolinska Institute. This work was supported by the Karolinska Institute and partially by unrestricted grants from Maquet Critical Care AB and the regional agreement on medical training and research (ALF) between Stockholm County Council and the Karolinska Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS, JK, MK and P-AL: Study design, data collection, analysis and manuscript writing. MH and MW: study design, data collection and analysis and critical manuscript review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Per-Arne Lönnqvist received an unrestricted research grant from Maquet Critical Care AB. Mats Wallin and Mark Konrad was employed by Maquet Critical Care AB at the time of the study. Magnus Hallbäck is employed at Maquet Critical Care AB. Anders Svedmyr and Jacob Karlsson report no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Authorization was granted from Uppsala Animal Ethics Committee (Uppsala, Sweden case number C75/16, chairperson Erik Göransson on August 26, 2016). The animals were handled in accordance with the animal experimentation guidelines of the Uppsala Animal Ethics Committee and Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines.
Consent to participate:
Not applicable.
Consent for publication:
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Svedmyr, A., Konrad, M., Wallin, M. et al. Non-invasive capnodynamic mixed venous oxygen saturation during major changes in oxygen delivery. J Clin Monit Comput 36, 1315–1324 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-021-00762-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-021-00762-5