Abstract
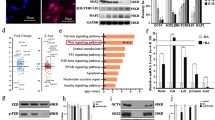
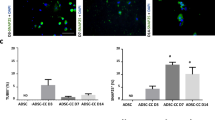
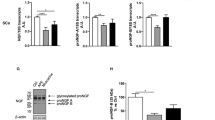
Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) have promising effects on nerve repair due to the differentiation ability to neural cells. Ghrelin has been shown to promote the neural differentiation of ADSCs. This work was designed to explore its underlying mechanism. Herein, we found high expression of LNX2 in ADSCs after neuronal differentiation. Knockdown of LNX2 might block neuronal differentiation of ADSCs, as evidenced by the decreased number of neural-like cells and dendrites per cell, and the reduced expressions of neural markers (including β-Tubulin III, Nestin, and MAP2). We also demonstrated that LNX2 silencing suppressed the nuclear translocation of β-catenin in differentiated ADSCs. Luciferase reporter assay indicated that LNX2 inhibited wnt/β-catenin pathway by reducing its transcriptional activity. In addition, results showed that LNX2 expression was increased by ghrelin, and its inhibition diminished the effects of ghrelin on neuronal differentiation. Altogether, the results suggest that LNX2 is involved in the role of ghrelin to facilitate neuronal differentiation of ADSCs.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the authors on reasonable request.
References
Andrews ZB (2011) The extra-hypothalamic actions of ghrelin on neuronal function. Trends Neurosci 34(1):31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2010.10.001
Camps J, Pitt JJ, Emons G, Hummon AB, Case CM, Grade M et al (2013) Genetic amplification of the NOTCH modulator LNX2 upregulates the WNT/β-catenin pathway in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 73(6):2003–2013. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-12-3159
Date Y, Kojima M, Hosoda H, Sawaguchi A, Mondal MS, Suganuma T et al (2000) Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology 141(11):4255–4261. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.141.11.7757
de la Rocha-Muñoz A, Núñez E, Arribas-González E, López-Corcuera B, Aragón C, de Juan-Sanz J (2019) E3 ubiquitin ligases LNX1 and LNX2 are major regulators of the presynaptic glycine transporter GlyT2. Sci Rep 9(1):14944. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51301-x
Flynn M, Saha O, Young P (2011) Molecular evolution of the LNX gene family. BMC Evol Biol 11:235. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-11-235
Galipeau J, Sensébé L (2018) Mesenchymal stromal cells: clinical challenges and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Stem Cell 22(6):824–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2018.05.004
Gong B, Jiao L, Du X, Li Y, Bi M, Jiao Q et al (2020) Ghrelin promotes midbrain neural stem cells differentiation to dopaminergic neurons through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Cell Physiol 235(11):8558–8570. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29699
Joo HJ, Kim JH, Hong SJ (2017) Adipose tissue-derived stem cells for myocardial regeneration. Korean Circ J 47(2):151–159. https://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2016.0207
Kondo T, Matsuoka AJ, Shimomura A, Koehler KR, Chan RJ, Miller JM et al (2011) Wnt signaling promotes neuronal differentiation from mesenchymal stem cells through activation of Tlx3. Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 29(5):836–846. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.624
Kunze KN, Burnett RA, Wright-Chisem J, Frank RM, Chahla J (2020) Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatments and available formulations. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 13(3):264–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-020-09624-0
Lam MT, Longaker MT (2012) Comparison of several attachment methods for human iPS, embryonic and adipose-derived stem cells for tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 6 Suppl 3(0 3):s80-86. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.1499
Lee S, Chae DS, Song BW, Lim S, Kim SW, Kim IK et al (2021) ADSC-Based cell therapies for Musculoskeletal Disorders: a review of recent clinical trials. Int J Mol Sci 22(19). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910586
Lian X, Hsiao C, Wilson G, Zhu K, Hazeltine LB, Azarin SM, Lian Xiaojun, Hsiao Cheston, Wilson Gisela, Zhu Kexian, Hazeltine Laurie B., Azarin Samira M., Raval Kunil K., Zhang Jianhua, Kamp Timothy J., Palecek Sean P. (2012) Robust cardiomyocyte differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells via temporal modulation of canonical wnt signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(27):E1848-1857. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200250109
Liu GB, Pan YM, Liu YS, Hu JH, Zhang XD, Zhang DW et al (2020) Ghrelin promotes neural differentiation of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell via AKT/mTOR and β-catenin signaling pathways. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 36(6):405–416. https://doi.org/10.1002/kjm2.12188
Lynn BD, Li X, Hormuzdi SG, Griffiths EK, McGlade CJ, Nagy JI (2018) E3 ubiquitin ligases LNX1 and LNX2 localize at neuronal gap junctions formed by connexin36 in rodent brain and molecularly interact with connexin36. Eur J Neurosci 48(9):3062–3081. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.14198
Omar AM, Meleis AE, Arfa SA, Zahran NM, Mehanna RA (2019) Comparative study of the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue and bone marrow on Acute Myocardial Infarction Model. Oman Med J 34(6):534–543. https://doi.org/10.5001/omj.2019.97
Pradhan G, Samson SL, Sun Y (2013) Ghrelin: much more than a hunger hormone. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 16(6):619–624. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0b013e328365b9be
Rice DS, Northcutt GM, Kurschner C (2001) The lnx family proteins function as molecular scaffolds for numb family proteins. Mol Cell Neurosci 18(5):525–540. https://doi.org/10.1006/mcne.2001.1024
Russo C, Mannino G, Patanè M, Parrinello NL, Pellitteri R, Stanzani S et al (2021) Ghrelin peptide improves glial conditioned medium effects on neuronal differentiation of human adipose mesenchymal stem cells. Histochem Cell Biol 156(1):35–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-021-01980-3
Sapir T, Levy T, Kozer N, Shin I, Zamor V, Haffner-Krausz R, Sapir Tamar, Levy Talia, Kozer Noga, Shin Irina, Zamor Vanessa, Haffner-Krausz Rebecca, McGlade Jane C, Reiner Orly (2018) Notch activation by Shootin1 opposing activities on 2 Ubiquitin Ligases. Cereb Cortex 28(9):3115–3128. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhx180
Wang Y, Cheng L, Zhao H, Li Z, Chen J, Cen Y et al (2022) The therapeutic role of ADSC-EVs in skin regeneration. Front Med (Lausanne) 9:858824. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.858824
Ye N, Wang L, Dou Z, Huang J (2018) Ghrelin accelerates the cartilagic differentiation of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells through the ERK1/2 pathway. Cytotechnology 70(1):415–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-017-0156-6
Ye N, Yang Y, Ma Z, Huang J (2020) Ghrelin promotes the osteogenic differentiation of rMSCs via miR-206 and the ERK1/2 pathway. Cytotechnology 72(5):707–713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-020-00413-8
Yin FT, Futagawa T, Li D, Ma YX, Lu MH, Lu L et al (2015) Caspr4 interaction with LNX2 modulates the proliferation and neuronal differentiation of mouse neural progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev 24(5):640–652. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2014.0261
Young PW (2018) LNX1/LNX2 proteins: functions in neuronal signalling and beyond. Neuronal Signal 2(2):Ns20170191. https://doi.org/10.1042/ns20170191
Yu Q, Liu L, Duan Y, Wang Y, Xuan X, Zhou L, Yu Qin, Liu Lizhen, Duan Yanping, Wang Yan, Xuan Xiaobo, Zhou Liping, Liu Wei (2013) Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 439(2):297–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.08.030
Yu YL, Chou RH, Chen LT, Shyu WC, Hsieh SC, Wu CS, Yu Yung-Luen, Chou Ruey-Hwang, Chen Ling-Tzu, Shyu Woei-Cherng, Hsieh Su-Ching, Wu Chen-Shiou, Zeng Hong-Jie, Yeh Su-Peng, Yang De-Ming, Hung Shih-Chieh, Hung Mien-Chie (2011) EZH2 regulates neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through PIP5K1C-dependent calcium signaling. J Biol Chem 286(11):9657–9667. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.185124
Zhou Z, Chen Y, Zhang H, Min S, Yu B, He B, Zhou Zhilai, Chen Yinhai, Zhang Hui, Min Shaoxiong, Yu Bo, He Bing, Jin Anmin (2013) Comparison of mesenchymal stromal cells from human bone marrow and adipose tissue for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Cytotherapy 15(4):434–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2012.11.015
Zhou Z, Tian X, Mo B, Xu H, Zhang L, Huang L, Zhou Zhilai, Tian Xiaobo, Mo Biling, Xu Huali, Zhang Li, Huang Lishan, Yao Shun, Huang Zixiang, Wang Yeyang, Xie Huan, Xu Liwei, Zhang Hui (2020) Adipose mesenchymal stem cell transplantation alleviates spinal cord injury-induced neuroinflammation partly by suppressing the Jagged1/Notch pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther 11(1):212. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01724-5
Funding
This research was supported by the Joint Guidance Project of Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (grant number LH2020H074).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gui-Bo Liu: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft, Funding acquisition.Tao Zhan: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft.Yan-Ming Pan: Investigation, Formal analysis, Methodology.Da-Wei Zhang: Investigation, Formal analysis, Methodology.Hui-Zhe Zheng: Formal analysis, Methodology, Data curation.Biao Xu: Formal analysis, Methodology, Data curation.Ting-Ting Li: Software, Validation, Visualization.Chuan-Ling Dong: Software, Validation, Visualization.Yong-Xia Cheng (ORCID: 0000-0003-2652-2061): Supervision, Writing-review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Disclosure of interest
No competing financial interests exist.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.22 MB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, GB., Zhan, T., Pan, YM. et al. LNX2 involves in the role of ghrelin to promote the neuronal differentiation of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Bioenerg Biomembr 55, 195–205 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-023-09967-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-023-09967-6