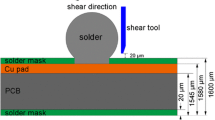
Abstract
In this work, the effects of adding 0.5 wt% Ni or 1.0 wt% In on the microstructure, interfacial growth behavior, and mechanical properties of Sn–35Bi–1Ag solder joints during reflowing and isothermal aging at 120 °C were investigated by scanning electron microscopy and ball shear test. During soldering, In addition did not enroll in the reaction between solder and Cu and increased the shear force of as-soldered joints. The interfacial intermetallic compound (IMC) grew with a rod shape. However, Ni atoms would enter into the IMC to produce (Cu, Ni)6Sn5 at the interface, changed the IMC shape, and decreased the shear force of solder joints. During isothermal aging at 120 °C, the addition of 0.5 wt% Ni or 1 wt% In had an acceleration on the growth of interfacial IMC, but the growth rate with the addition of Ni was nearly twice faster than that with In addition. Meanwhile, In addition enhanced the ductility of solder joints with the fracture mode changing to ductile modes, while Ni addition led to the loss of ductility of solder joints with the fracture mode changing to brittle modes.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and materials that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
O. Mokhtari, H. Nishikawa, Effects of In and Ni addition on microstructure of Sn–58Bi solder joint. J. Electron. Mater. 43(11), 4158–4170 (2014)
D.A. Shnawah, M.F.M. Sabri, I.A. Badruddin, A review on thermal cycling and drop impact reliability of SAC solder joint in portable electronic products. Microelectron. Reliab. 52(1), 90–99 (2012)
H. Ma, J.C. Suhling, A review of mechanical properties of lead-free solders for electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. 44(5), 1141–1158 (2009)
S.R. Sidhu, R. Aspandiar, S. Vandervoort, D. Amir, G. Murtagian, Impact of processing conditions and solder materials on surface mount assembly defects. JOM: Electron. Mater. Solidif. 63, 10 (2011)
H.R. Kotadia, P.D. Howes, S.H. Mannan, A review: on the development of low melting temperature Pb-free solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 54(6–7), 1253–1273 (2014)
F. Wang, H. Chen, Y. Huang, L. Liu, Z. Zhang, Recent progress on the development of Sn–Bi based low-temperature Pb-free solders. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(4), 3222–3243 (2019)
P.L. Liu, J.K. Shang, Interfacial embrittlement by bismuth segregation in copper/tin-bismuth Pb-free solder interconnect. J. Mater. Res. 16, 1 (2001)
Q. Wang, H. Chen, F. Wang, Effect of trace Zn addition on interfacial evolution in Sn-10Bi/Cu solder joints during aging condition. Mater. (Basel) 12(24), 4240 (2019)
W.-R. Myung, M.-K. Ko, Y. Kim, S.-B. Jung, Effects of Ag content on the reliability of LED package component with Sn–Bi–Ag solder. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26(11), 8707–8713 (2015)
S. Sakuyama, T. Akamatsu, K. Uenishi, T. Sato, Effects of a third element on microstructure and mechanical properties of eutectic Sn–Bi solder. Trans. Jpn. Inst. Electron. Packag. 2, 1 (2009)
H. Sun, Q. Li, Y.C. Chan, A study of Ag additive methods by comparing mechanical properties between Sn57.6Bi0.4Ag and 0.4 wt% nano-Ag-doped Sn58Bi BGA solder joints. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25(10), 4380–4390 (2014)
Z. Lai, D. Ye, Microstructure and fracture behavior of non eutectic Sn–Bi solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27(4), 3182–3192 (2015)
F. Wang, Y. Huang, Z. Zhang, C. Yan, Interfacial reaction and mechanical properties of Sn–Bi solder joints. Mater. (Basel) 10(8), 920 (2017)
L. Shen, P. Septiwerdani, Z. Chen, Elastic modulus, hardness and creep performance of SnBi alloys using nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Engineering: A 558, 253–258 (2012)
L. Zhang, L. Sun, Y. Guo, Microstructures and properties of Sn58Bi, Sn35Bi0.3Ag, Sn35Bi1.0Ag solder and solder joints. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26(10), 7629–7634 (2015)
C. Peng, J. Shen, W. Xie, J. Chen, C. Wu, X. Wang, Influence of minor Ag nano-particles additions on the microstructure of Sn30Bi0.5Cu solder reacted with a Cu substrate. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 22(7), 797–806 (2010)
J. Shen, C. Wu, S. Li, Effects of rare earth additions on the microstructural evolution and microhardness of Sn30Bi0.5Cu and Sn35Bi1Ag solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 23(1), 156–163 (2011)
Y. Li, Z. Wang, X. Li, X. Hu, M. Lei, Growth behavior of IMCs layer of the Sn–35Bi–1Ag on Cu, Ni–P/Cu and Ni–Co–P/Cu substrates during aging. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(2), 1519–1530 (2018)
Z. Wang, Q.K. Zhang, Y.X. Chen, Z.L. Song, Influences of Ag and in alloying on Sn-Bi eutectic solder and SnBi/Cu solder joints. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(20), 18524–18538 (2019)
M. Omid, N. Hirdshi, Effect of Indium content on the tensile properties of Sn–Bi–In solder. Trans. JWRI 44, 2 (2015)
O. Mokhtari, H. Nishikawa, Correlation between microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn–Bi–X solders. Mater. Sci. Engineering: A 651, 831–839 (2016)
Y. Li, Z. Wang, W. Long, M. Lei, X. Hu, Wetting kinetics and spreading phenomena of Sn-35Bi-1Ag solder on different substrates. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29(16), 13914–13924 (2018)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, Effect of thin gold/nickel coating on the microstructure, wettability and hardness of lead-free tin–bismuth–silver solder. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28(6), 4885–4896 (2016)
T. Fouzder, A.K. Gain, D.K. Chan, Microstructure, wetting characteristics and hardness of tin-bismuth-silver (Sn–Bi–Ag) solders on silver (Ag)-surface finished copper (Cu) substrates. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28(22), 16921–16931 (2017)
K.N. Tu, R.D. Thompson, Acta Metall. 30, 947 (1982)
P.T. vianco, K.L. Erickson, P.L. Hopkins, J. Electron. Mater. 23, 721 (1994)
C.Z. Liu, W. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. 44, 149 (2009)
T.Y. Kang, Effect of Ni addition on the formation and growth of intermetallic compound at eutectic SnBi/Cu interface. Adv. Mater. Res. 160, 709 (2011)
G.D. Waduge, G. Baty, Y. Lee, T.K. Lee, Isothermal aging effect on Sn-58Bi interconnect mechanical shear stability. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 1169–1179 (2022)
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant No. 51875269, and by Qing Lan Project from Jiangsu Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JC methodology, formal analysis, data curation, and writing. ML methodology, formal analysis, and data curation. FW conceptualization, methodology, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human tissues or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
This research is not related to human subjects.
Consent for publication
The author assigns non-exclusive publication rights to Springer and warrants that his contribution is unique and that he possesses all necessary authority to make this grant. The author assumes responsibility for the material’s release on behalf of all co-authors. This assignment of publication rights includes the non-exclusive right to reproduce and distribute the article in any format, including reprints, translations, photographic reproductions, microform, electronic form (offline, online), or other reproductions of a similar nature.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Liao, M. & Wang, F. In or Ni addition on mechanical properties and interfacial growth in Sn–35Bi–1Ag solder joint during isothermal aging. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1558 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10971-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10971-0