Abstract
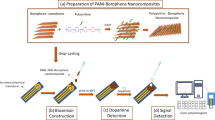
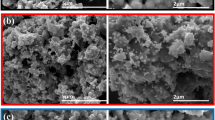
Selective and sensitive detection of dopamine (DA) is imperative for the diagnosis and management of a wide range of neurological disorders, given its vital role as a critical neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. In this study, a series of non-enzymatic electrochemical voltammetric sensors based on polyaniline (PANI), PANI:Silicene, PANI:Coronene, and PANI:Rubrene nanocomposites (NCs) were developed for the detection of dopamine. The results showed that the PANI:Silicene NCs-based sensor exhibited a highly sensitive response towards DOP, with a sensitivity of 197.84 μAμM−1 cm−2 and the lowest limit of detection (LOD) of 0.0385 μM. The incorporation of silicene significantly enhanced the sensor’s performance in terms of both sensitivity and LOD. These findings demonstrate the potential of PANI-Silicene NC-based sensors for highly sensitive and specific detection of DOP.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
A. Özcan, S. İlkbaş, A. Atılır Özcan, Development of a disposable and low-cost sensor for dopamine detection based on poly(pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid)-modified electrochemically over-oxidized pencil graphite electrode. Talanta 165, 489–495 (2017)
Y. Feng, Y. Lu, Immunomodulatory effects of dopamine in inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 12, 987 (2021)
H.S. Han, H.K. Lee, J.M. You et al., Electrochemical biosensor for simultaneous determination of dopamine and serotonin based on electrochemically reduced GO-porphyrin. Sens Actuators B Chem. 190, 886–895 (2014)
C. Cioates Negut, S.S. Gheorghe, R.I. Stefan-van Staden, J.F. van Staden, Fast screening test for molecular recognition of levodopa and dopamine in biological samples using 3D printed stochastic microsensors. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 205, 114292 (2021)
A. Martorana, F. di Lorenzo, Z. Esposito et al., Dopamine D2-agonist Rotigotine effects on cortical excitability and central cholinergic transmission in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neuropharmacology 64, 108–113 (2013)
J. Luo, J.F. Collingwood, Effective R2 relaxation rate, derived from dual-contrast fast-spin echo MRI, enables detection of hemisphere differences in iron level and dopamine function in Parkinson’s disease and healthy individuals. J. Neurosci. Methods 382, 109708 (2022)
M.M. Khalefah, A.M. Khalifah, Determining the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 infection, dopamine, and COVID-19 complications. J Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 15, 550–553 (2020)
A. Gottås, B.F. Ripel et al., Determination of dopamine concentrations in brain extracellular fluid using microdialysis with short sampling intervals, analyzed by ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 74, 75–79 (2015)
M. Bouri, M.J. Lerma-García, R. Salghi et al., Selective extraction and determination of catecholamines in urine samples by using a dopamine magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer and capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 99, 897–903 (2012)
F. Musshoff, P. Schmidt, R. Dettmeyer et al., Determination of dopamine and dopamine derived (R)-/(S)-salsolinol and norsalsolinol in various human brain areas using solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Forensic. Sci. Int. 113, 359–366 (2000)
R. Wu, S. Yu, S. Chen et al., A carbon dots-enhanced laccase-based sensor for highly sensitive detection of dopamine in human serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 1229, 340365 (2022)
A. Üğe, D. Koyuncu Zeybek, B. Zeybek, An sensor for sensitive detection of dopamine based on MWCNTs/CeO2-PEDOT composite. J. Electroanal. Chem. 813, 134–142 (2018)
G. Deffo, M. Basumatary, N. Hussain et al., Eggshell nano-CaCO3 decorated PANi/rGO composite for sensitive determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid in human blood rum and urine. Mater. Today Commun. 33, 104357 (2022)
F.S. Belaidi, A. Civélas, V. Castagnola et al., PEDOT-modified integrated microelectrodes for the detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sens Actuators B Chem. 214, 1–9 (2015)
S.E. Elugoke, O.E. Fayemi, A.S. Adekunle et al., Sensor for the detection of dopamine using carbon quantum dots/copper oxide nanocomposite modified electrode. FlatChem 33, 100372 (2022)
M. Ni, J. Chen, C. Wang et al., A high-sensitive dopamine sensor based on multilayer Ti3C2 MXene, graphitized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and ZnO nanospheres. Microchem. J. 178, 107410 (2022)
H. Yang, C. Zhou, J. An et al., Ultra-fast synthesis of iron decorated multiwalled carbon nanotube composite materials: a sensitive sensor for determining dopamine. J Alloys Compd 897, 163257 (2022)
K.P. Aryal, H.K. Jeong, Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid with polyaniline/hemin/reduced graphite oxide composite. Chem. Phys. Lett. 768, 138405 (2021)
A. Ali, R. Jamal, T. Abdiryim, X. Huang, Synthesis of monodispersed PEDOT/Au hollow nanospheres and its application for electrochemical determination of dopamine and uric acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 787, 110–117 (2017)
T. Cao, Y. Zhou, H. Wang et al., Preparation of polyfluorinated azobenzene/niobate composite as sensor for detection of ascorbic acid and dopamine. Microchem. J. 179, 107422 (2022)
T.C. Girija, M.V. Sangaranarayanan, Analysis of polyaniline-based nickel electrodes for electrochemical supercapacitors. J Power Sources 156, 705–711 (2006)
K. Ghanbari, M. Moloudi, Flower-like ZnO decorated polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide NCs for simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid. Anal. Biochem. 512, 91–102 (2016)
K. Ghanbari, Z. Babaei, Fabrication and characterization of non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on ternary NiO/CuO/polyaniline nanocomposite. Anal Biochem 498, 37–46 (2016)
A. Krishnan, S. Beena, S.M.A. Shibli, A novel high performance Ti/Ti–W- reinforced polyaniline functionalized Ni–P electrode for high sensitive detection of dopamine from urine sample. Mater. Chem. Phys. 244, 122680 (2020)
M. Afzali, A. Mostafavi, T. Shamspur, Square wave voltammetric determination of anticancer drug flutamide using carbon paste electrode modified by CuO/GO/PANI nanocomposite. Arab. J. Chem. 13, 3255–3265 (2020)
P. Paulraj, A. Umar, K. Rajendran et al., Solid-state synthesis of Ag-doped PANI NCs for their end-use as an sensor for hydrogen peroxide and dopamine. Electrochim. Acta 363, 137158 (2020)
Y. You, C. Yang, X. Zhang et al., Emerging two-dimensional silicene nanosheets for biomedical applications. Mater. Today Nano. 16, 100132 (2021)
Fumagalli, E.M., Growth and physical properties of crystalline rubrene. 2012, Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca.
Özdemir, H.G., Spin Kaplama Yontemiyle Rubrene ince filmlerinin hazırlanması ve optik özelliklerinin incelenmesi, in Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü. 2013, Giresun University.
J.-S. Kim, H. Kajii, Y. Ohmori, Characteristics of optical response in red organic light emitting diodes using two dopant system for application to the optical link devices. Thin Solid Films 499(1), 343–348 (2006)
K.Y. Lin, Y.J. Wang, K.L. Chen, C.Y. Ho, C.C. Yang, J.L. Shen, K.C. Chiu, Role of molecular conformations in rubrene polycrystalline films growth from vacuum deposition at various substrate temperatures. Sci. Rep. 7, 40824 (2017)
Du. Chuan, W. Wang, L. Li, H. Fuchs, L. Chi, Growth of rubrene crystalline thin films using thermal annealing on DPPC LB monolayer. Org. Electron. 14, 2534–2539 (2013)
J. Xiao, Huiying Yang, Zongyou Yin, Jun Guo, Freddy Boey, Hua Zhang, Qichun Zhang, Preparation, characterization, and photoswitching/light-emitting behaviors of coronene nanowires. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 1423–1427 (2011)
T.M. Krygowski, M. Cyranski, A. Ciesielski, B. Swirska, P. Leszczynski, J. Chem. Inform. Comput. Sci. 36, 1135 (1996)
M. Shabani-Nooshabadi, F. Karimian-Taheri, Electrosynthesis of a polyaniline/zeolite nanocomposite coating on copper in a three-step process and the effect of current density on its corrosion protection performance. RSC Adv. 5(117), 96601–96610 (2015)
Y. Zhang, J. Liu, Y. Zhang, J. Liu, Y. Duan, Facile synthesis of hierarchical NCs of aligned polyaniline nanorods on reduced graphene oxide nanosheets for microwave absorbing materials. RSC Adv. 7, 54031–54038 (2017)
P. Paulraj, A. Umar, K. Rajendrane, A. Manikandana, R. Kumar, E. Manikandang, K. Pandianb, M.H. Mahnashi, M.A. Alsaiari, A.A. Ibrahimc, N. Bouropoulos, S. Baskoutas, Solid-state synthesis of Ag-doped PANI nanocomposites for their end-use as an electrochemical sensor for hydrogen peroxide and dopamine. Electrochim. Acta 363, 137158 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) due to the financial support for the Project 122N962.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GB: Investigation, Methodology, Writing-original draf. NT: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft, Writing—review & editing, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision. BK: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft. SK: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft, Writing—review & editing, GG: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft, Writing—review & editing. BB: Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft. DEY: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft, Writing—review & editing, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Baytemir, G., Taşaltın, N., Karaca, B. et al. PANI: silicene nanocomposites based non-enzymatic electrochemical voltammetric sensor for dopamine detection. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1374 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10809-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10809-9