Abstract
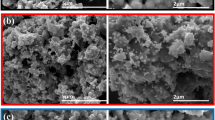
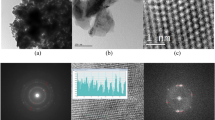
Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors are attractive because of their high sensitivity, rapid detection, low-cost and easy fabrication. Herein, a non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor based on Polyaniline/borophene nanocomposites for dopamine detection is presented. Borophene nanosheets were prepared using a clean and low-cost sonication method. The product was characterized by XRD, SEM, HRTEM and FTIR. Next, the PANI/borophene nanocomposite material was prepared and used to modify the PANI electrode for use in the detection of dopamine with cyclic voltammetry. The nanocomposite material presented the large peak currents indicating the nanocomposite reveals better electrochemical activity with the presence of borophene for dopamine detection in the concentration range of 0.15625–5 µM. At a scan rate of 50 mV/s, the PANI-based sensor exhibited a sensitivity of 153.67 μAμM−1 cm−2 with detection limit of 0.064 μM, while the PANI/borophene nanocomposite-based sensor exhibited a sensitivity of 385.05 μAμM−1 cm−2 with 0.017 μM detection limit. Due to the excellent electrochemical performance obtained in this work, PANI/borophene nanocomposites could be a promising biosensor material for dopamine electrochemical analysis for biomedical applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Mani, M. Govindasamy, S.-M. Chen, R. Karthik, S.-T. Huang, Determination of dopamine using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a graphene and carbon nanotube hybrid decorated with molybdenum disulfide flowers. Microchim. Acta 183, 2267–2275 (2016)
N. Chauhan, S. Soni, P. Agrawal, Y.P.S. Balhara, U. Jain, Recent advancement in nanosensors for neurotransmitters detection: present and future perspective. Process Biochem. 91, 241–259 (2020)
I. Anshori, L.N. Rizalputri, R.R. Althof, S.S. Surjadi, S. Harimurti, G. Gumilar, B. Yuliarto, M. Handayani, Functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube/silver nanoparticle (f-MWCNT/ AgNP) nanocomposites as non-enzymatic electrochemical biosensors for dopamine detection. Nanocomposites 7(1), 97–108 (2021)
M. Amiri, S. Dadfarnia, A.M.H. Shabani, S. Sadjadi, Non-enzymatic sensing of dopamine by localized surface plasmonresonance using carbon dots-functionalized gold nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 172, 223–229 (2019)
M. Lakshmanakumar, N. Nesakumar, A.J. Kulandaisamy, J.B.B. Rayappan, Principles and recent developments in optical and electrochemical sensing of dopamine: a comprehensive review. Measurement 183, 109873 (2021)
H. Shen, B. Jang, J. Park, H. Mun, H.-B. Cho, Y.-H. Choa, In situ synthesis of a Bi2Te3-nanosheet/reduced-graphene-oxide nanocomposite for non-enzymatic electrochemical dopamine sensing. Nanomaterials 2022, 12 (2009)
V. Carrera, E. Sabater, E. Vilanova, M.A. Sogorb, A simple and rapid HPLC–MS method for the simultaneous determination of epinephrine, norepinephrine dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine: application to the secretion of bovine chromaffin cell cultures. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 847(2), 88–94 (2007)
J. Deepika, R. Sha, S. Badhulika, A ruthenium(IV) disulfide based non-enzymatic sensor for selective and sensitive amperometric determination of dopamine. Microchim. Acta 186, 480 (2019)
M. Mamiński, M. Olejniczak, M. Chudy, A. Dybko, Z. Brzózka, Spectrophotometric determination of dopamine in microliter scale using microfluidic system based on polymeric technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 540(1), 153–157 (2005)
H. Abdolmohammad-Zadeh, M. Zamani-Kalajahi, A novel chemiluminescent-based nano-probe for ultra-trace quantification of dopamine in human plasma samples. Microchem. J. 155, 104704 (2020)
M.I. Khan, N. Muhammad, M. Tariq, U. Nishan, A. Razaq, T.A. Saleh, M.A. Haija, I. Ismail, A. Rahim, Non-enzymatic electrochemical dopamine sensing probe based on hexagonal shape zinc-doped cobalt oxide (Zn-Co2O4) nanostructure. Microchim. Acta 189, 37 (2022)
M. Ilgar, G. Baytemir, N. Taşaltın, S. Güllülü, I.S. Yeşilyurt, S. Karakuş, Multifunctional maca extract coated CuO nanoparticles with antimicrobial and dopamine sensing activities: A dual electrochemical – Smartphone colorimetric detection system. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 431, 114075 (2022)
M. Sabar, U. Amara, S. Riaz, A. Hayat, M. Nasir, M.H. Nawaz, Fabrication of MoS2 enwrapped carbon cloth as electrochemical probe for non-enzymatic detection of dopamine. Mater. Lett. 308, 131233 (2022)
M. Keerthi, G. Boopathy, S.-M. Chen, T.-W. Chen, B.-S. Lou, A core-shell molybdenum nanoparticles entrapped f-MWCNTs hybrid nanostructured material based non-enzymatic biosensor for electrochemical detection of dopamine neurotransmitter in biological samples. Sci. Reports 9, 13075 (2019)
M.S. Panov, A.E. Grishankina, D.D. Stupin, A.I. Lihachev, V.N. Mironov, D.M. Strashkov, E.M. Khairullina, I.I. Tumkin, M.N. Ryazantsev, In situ laser-induced fabrication of a ruthenium-based microelectrode for non-enzymatic dopamine sensing. Materials 13(23), 5385 (2020)
M. Florescu, M. David, Tyrosinase-based biosensors for selective dopamine detection. Sensors 17, 1314 (2017)
H.Y. Yue, H.J. Zhang, S. Huang, X. Gao, S.S. Song, Z. Wang, W.Q. Wang, E.H. Guan, A novel non-enzymatic dopamine sensors based on NiO-reduced graphene oxide hybrid nanosheets. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 5000–5007 (2019)
K. Amano, H. Ishikawa, A. Kobayashi, M. Satoh, E. Hasegawa, Thermal stability of chemically synthesized polyaniline. Synth. Met. 62(3), 229–232 (1994)
J. Mathiyarasu, S. Senthilkumar, K.L.N. Phani, V. Yegnaraman, Selective detection of dopamine using a functionalised polyaniline composite electrode. J. Appl. Electrochem. 35, 513–519 (2005)
F. Zuo, L. Jin, X. Fu, H. Zhang, R. Yuan, S. Chen, An electrochemiluminescent sensor for dopamine detection based on a dual-molecule recognition strategy and polyaniline quenching. Sensors Actuators B Chem 244, 282–289 (2017)
D. Li, J.X. Huang, R.B. Kaner, Polyaniline nanofibers: a unique polymer nanostructure for versatile applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 42, 135–145 (2009)
H. Zhou, Y.P. Sun, G. Li, S.J. Chen, Y. Lu, Interfacial assembly and electrochemical properties of nafion-modified-graphene/polyaniline hollow spheres. Polymer 55, 4459–4467 (2014)
Y. Hu, Z. Zhang, H. Zhang, L. Luo, S. Yao, Electrochemical determination of l-phenylalanine at polyaniline modified carbon electrode based on β-cyclodextrin incorporated carbon nanotube composite material and imprinted sol–gel film. Talanta 84(2), 305–313 (2011)
Y.G. Liu, X.M. Feng, J.M. Shen, J.J. Zhu, W.H. Hou, Fabrication of a novel glucose biosensor based on a highly electroactive polystyrene/polyaniline/Au nanocomposite. J. Phys. Chem. B 112, 9237–9242 (2008)
L. Yang, S. Liu, Q. Zhang, F. Li, Simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine and ascorbic acid using AuNPs@polyaniline core–shell nanocomposites modified electrode. Talanta 89, 136–141 (2012)
W.-F. Hsu, T.-M. Wu, Electrochemical sensor based on conductive polyaniline coated hollow tin oxide nanoparticles and nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots for sensitively detecting dopamine. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 8449–8456 (2019)
C. Ratlam, S. Phanichphant, S. Sriwichai, Development of dopamine biosensor based on polyaniline/carbon quantum dots composite. J. Polym. Res. 27, 183 (2020)
L.-Q. Xie, Y.-H. Zhang, F. Gao, Q.-A. Wu, P.-Y. Xu, S.-S. Wang, N.-N. Gao, Q.-X. Wang, A highly sensitive dopamine sensor based on a polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide/Nafion nanocomposite. Chin. Chem. Lett. 28, 41–48 (2017)
S. Goktuna, N. Tasaltin, Preparation and characterization of PANI: α borophene electrode for supercapacitors. Physica E: 134, 114833 (2021)
T.A. Türkmen, N. Taşaltın, C. Taşaltın, G. Baytemir, S. Karakuş, PEDOT: PSS/β12 borophene nanocomposites as an inorganic-organic hybrid electrode for high performance supercapacitors. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 139, 109329 (2022)
C. Taşaltın, T.A. Türkmen, N. Taşaltın, S. Karakus, Highly sensitive non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose biosensor based on PANI: b12 Borophene. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 10750–10760 (2021)
N. Taşaltın, C. Taşaltın, S. Güngör, S. Karakuş, İ Gürol, M. Teker, Volatile organic compound detection performance of Borophene and PANI: β Borophene nanocomposite-based sensors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 24173–24181 (2022)
S. Gungor, C. Tasaltin, I. Gurol, G. Baytemir, S. Karakus, T. Nevin, Copper phthalocyanine-borophene nanocomposite-based non-enzymatic electrochemical urea biosensor. Appl. Phys. A 128, 89 (2022)
G. Baytemir, İ Gürol, S. Karakuş, C. Taşaltın, N. Taşaltın, Nickel phthalocyanine-borophene nanocomposite-based electrodes for non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of glucose. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 33(20), 16586–16596 (2022)
M. Ou, X. Wang, L. Yu, C. Liu, W. Tao, X. Ji, L. Mei, The emergence and evolution of borophene. Adv. Sci. 8, 1–29 (2021)
V. Nagarajan, R. Chandiramouli, Borophene nanosheet molecular device for detection of ethanol – A first-principles study. Comput. Theor. Chem. 1105, 52–60 (2017)
B. Callmer, An accurate refinement of the [beta]-rhombohedral boron structure. Acta Crystallogr. 33, 1951–1954 (1977)
D. Ma, J. Zhao, J. Xie, F. Zhang, R. Wang, L. Wu, W. Liang, D. Li, Y. Ge, J. Li, Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, Ultrathin boron nanosheets as an emerging two-dimensional photoluminescence material for bioimaging. Nanoscale Horizons 5(4), 705–713 (2020)
H. Li, L. Jing, W. Liu, J. Lin, R.Y. Tay, S.H. Tsang, E.H.T. Teo, Scalable production of few-layer boron sheets by liquid-phase exfoliation and their superior supercapacitive performance. ACS Nano 12, 1262–1272 (2018)
M. Ni, Y. Xu, C. Wang, P. Zhao, P. Yang, C. Chen, K. Zheng, H. Wang, X. Sun, C. Li, Y. Xie, J. Fei, A novel thermo-controlled acetaminophen electrochemical sensor based on carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes and thermosensitive polymer. Diam. Relat. Mater. 107, 107877 (2020)
S.J. Konopka, B. McDuffie, Diffusion coefficients of ferri- and ferrocyanide ions in aqueous media, using twin-electrode thin-layer electrochemistry. Anal. Chem. 42(14), 1741–1746 (1970)
X. Liu, J. Liu, Biosensors and sensors for dopamine detection. View 2, 1 (2021)
J. Ahmed, M. Faisal, S.S. Alsareii, M. Jalalah, F.A. Harraz, A novel gold-decorated porous silicon-poly (3-hexylthiophene) ternary nanocomposite as a highly sensitive and selective non-enzymatic dopamine electrochemical sensor. J. Alloy. Compd. 931, 167403 (2023)
S. Karakus, G. Baytemir, N. Tasaltin, Digital colorimetric and non-enzymatic biosensor with nanoarchitectonics of Lepidium meyenii-silver nanoparticles and cotton fabric: real-time monitoring of milk freshness. Appl. Phys. A 128, 390 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there are no competing financial and non-financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Baytemir, G. A non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor based on polyaniline/borophene nanocomposites for dopamine detection. Appl. Phys. A 129, 85 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06364-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06364-5