Abstract
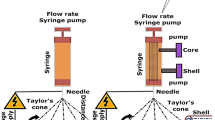
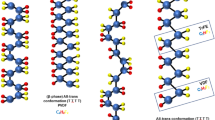
In this paper, the electrospinning of Polyvinylidene hexafluoropropylene (P(VDF-HFP)) composite nanofibers was performed by adding rare earth complexes Eu(TTA)3(TPPO)2 and FeCl3·6H2O as fillers. The effects of Eu(TTA)3(TPPO)2 and FeCl3·6H2O fillers on the morphology, crystal structure, thermal properties, and fluorescence properties of P(VDF-HFP) composite nanofibers were investigated by the scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and differential scanning calorimetry and fluorescence. The mechanical properties, sensitivity, ferroelectric properties, and piezoelectric output of monolayer and sandwich structure composite nanofiber membranes used as sensors were studied. The results show that the synergistic effect of double fillers increases the content of β-phase with piezoelectric properties by nearly 20%, reaching 96.9%. The sandwich structure of the PU/P(VDF-HFP)-Eu(TTA)3(TPPO)2-FeCl3·6H2O/PU flexible sensor has high sensitivity (~ 0.29 kPa− 1), high piezoelectric output (~ 3.7 V), high strain (~ 230%), and fluorescence characteristics. It is expected to be applied in wearable flexible sensors, photoelectric devices, and other fields.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Y. Ding, T. Xu, O. Onyilagha, H. Fong, Z. Zhu, Recent advances in flexible and wearable pressure sensors based on piezoresistive 3D monolithic conductive sponges. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 6685–6704 (2019)
Y. Badali, S. Koçyiğit, A. Aytimur, Ş Altındal, İ Uslu, Synthesis of boron and rare earth stabilized graphene doped polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanocomposite piezoelectric materials. Polym. Compos. 40(9), 3623–3633 (2019)
J. Zhao, F. Li, Z. Wang, P. Dong, G. Xia, K. Wang, Flexible PVDF nanogenerator-driven motion sensors for human body motion energy tracking and monitoring. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32(11), 14715–14727 (2021)
Y. Guo, J. Xu, W. Wu, S. Liu, J. Zhao, E. Pawlikowska, M. Szafran, F. Gao, Ultralight graphene aerogel/PVDF composites for flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators. Compos. Commun. 22, 100542 (2020)
N. Meng, X. Ren, G. Santagiuliana, L. Ventura, H. Zhang, J. Wu, H. Yan, M.J. Reece, E. Bilotti, Ultrahigh β-phase content poly(vinylidene fluoride) with relaxor-like ferroelectricity for high energy density capacitors. Nat. Commun. 10, 4535 (2019)
J.E. Trevino, S. Mohan, A.E. Salinas, E. Cueva, K. Lozano, Piezoelectric properties of PVDF-conjugated polymer nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 138(28), 50665 (2021)
Y.X. Zhao, Y.J. Chen, G.X. Pan, C. Wang, C.B. Peng, Z.X. Peng, Z.X. Sun, Y.R. Liang, Q.S. Shi, Preparation and performance of novel Tb-PEG + Eu-PEG/PANI/PAN luminescent-electrical-phase change composite fibers by electrospinning. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. Chin. 40(04), 824–831 (2019)
C.M. Azzaz, L.H. Mattoso, N.R. Demarquette, R.J. Zednik, Polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers obtained by electrospinning and blowspinning: Electrospinning enhances the piezoelectric β-phase—myth or reality? J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 138(10), 49959 (2021)
Z. He, F. Rault, M. Lewandowski, E. Mohsenzadeh, F. Salaun, Electrospun PVDF nanofibers for piezoelectric applications: a review of the influence of electrospinning parameters on the β phase and crystallinity enhancement. Polymers 13, 174 (2021)
L. Li, M. Zhang, W. Ruan, Studies on synergistic effect of CNT and CB nanoparticles on PVDF. Polym. Compos. 36(12), 2248–2254 (2015)
B. Zheng, J. Fan, B. Chen, X. Qin, J. Wang, F. Wang, X. Liu, Rare-earth doping in nanostructured inorganic materials. Chem. Rev. 122(6), 5519–5603 (2022)
V. Varkey, A.R. Chandran, E.T. Jose, I. Paul, G. Jose, Fabrication of photoluminescent electrospun poly (styrene-co-methyl methacrylate) nanofibers integrated with LaPO4: Eu3+ for optical applications. Mater. Today: Proc. 47, 921–926 (2021)
S. Bose, J.R. Summers, B.B. Srivastava, V. Padilla-Gainza, M. Peredo, C.M.T. De Leo, K. Lozano, Efficient near infrared to visible light upconversion from Er/Yb codoped PVDF fibrous mats synthesized using a direct polymer doping technique. Opt. Mater. 123, 111866 (2022)
E. Öztürk, E. Karacaoglu, The effect of Eu3+-doping on the photoluminescent properties of REInO3 (RE = Er, Sm) type phosphors. Mater. Today Commun. 25, 101556 (2020)
P. Adhikary, A. Biswas, D. Mandal, Improved sensitivity of wearable nanogenerators made of electrospun Eu3+ doped P(VDF-HFP)/graphene composite nanofibers for self-powered voice recognition. Nanotechnology 27, 495501 (2016)
Y. Li, M.H. Xu, Y.S. Xia, J.M. Wu, X.K. Sun, S. Wang, G.H. Hu, C.X. Xiong, Multilayer assembly of electrospun/electrosprayed PVDF-based nanofibers and beads with enhanced piezoelectricity and high sensitivity. Chem. Eng. J. 388, 124205 (2020)
C. He, H. Wang, L.X. Huang, P. Wang, W. Gao, Study on morphology features and mechanical properties of nanofibers films prepared by different composite electrospinning methods. Key Eng. Mater. 841, 70–75 (2020)
H. Cui, Y. Li, X. Zhao, X. Yin, J. Yu, B. Ding, Multilevel porous structured polyvinylidene fluoride/polyurethane fibrous membranes for ultrahigh waterproof and breathable application. Compos. Commun. 6, 63–67 (2017)
Q. Gao, B.A.F. Kopera, J. Zhu, X. Liao, C. Gao, M. Retsch, S. Agarwal, A. Greiner, Breathable and flexible polymer membranes with mechanoresponsive electric resistance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1907555 (2020)
G. Fu, Q. Shi, Y. He, L. Xie, Y. Liang, Electroactive and photoluminescence of electrospun P(VDF-HFP) composite nanofibers with Eu3+ complex and BaTiO3 nanoparticles. Polymer 240, 124496 (2021)
F. Mokhtari, G.M. Spinks, C. Fay, Z. Cheng, R. Raad, J. Xi, J. Foroughi, Wearable electronic textiles from nanostructured piezoelectric fibers. Adv. Mater. Technol. 5, 1900900 (2020)
L. Jin, Y. Zheng, Z.K. Liu, J.S. Li, Y.P.Q. Yi, Y.Y. Fan, L.L. Xu, Y. Li, Enhancement of β-phase crystal content of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofiber web by graphene and electrospinning parameters. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 38(11), 1239–1247 (2020)
C. Merlini, G.M.O. Barra, T.M. Araujo, A. Pegoretti, Electrically pressure sensitive poly(vinylidene fluoride)/polypyrrole electrospun mats. RSC Adv. 4(30), 15749–15758 (2014)
M. Khalifa, A. Mahendran, S. Anandhan, Durable, efficient, and flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator from electrospun PANi/HNT/PVDF blend nanocomposite. Polym. Compos. 40(4), 1663–1675 (2019)
S. Zhang, W. Tong, J. Wang, W. Wang, Z. Wang, Y. Zhang, Modified sepiolite/PVDF-HFP composite film with enhanced piezoelectric and dielectric properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 137(9), 48412 (2020)
S. Mishra, R. Sahoo, L. Unnikrishnan, A. Ramadoss, S. Mohanty, S.K. Nayak, Enhanced structural and dielectric behaviour of PVDF-PLA binary polymeric blend system. Mater. Today Commun. 26, 101958 (2021)
H. Shi, M. Al-Rubaiai, C.J. Holbrook, M. Miao, T. Pinto, C. Wang, X. Tan, Screen-printed soft capacitive sensors for spatial mapping of both positive and negative pressures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(23), 1809116 (2019)
Q. Hua, J. Sun, H. Liu, R. Bao, R. Yu, J. Zhai, Z.L. Wang, Skin-inspired highly stretchable and conformable matrix networks for multifunctional sensing. Nat. Commun. 9, 244 (2018)
Z. Lei, P. Wu, Zwitterionic skins with a wide scope of customizable functionalities. ACS Nano 12(12), 12860–12868 (2018)
S. Yu, Y. Zhang, Z. Yu, J. Zheng, Y. Wang, H. Zhou, PANI/PVDF-TrFE porous aerogel bulk piezoelectric and triboelectric hybrid nanogenerator based on in-situ doping and liquid nitrogen quenching. Nano Energy 80, 105519 (2021)
A. Ahmed, Y. Jia, H. Deb, M.F. Arain, H. Memon, K. Pasha, J. Shao, Ultra-sensitive all organic PVDF-TrFE E-spun nanofibers with enhanced β-phase for piezoelectric response. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 3965 (2022)
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52073033), the fund of the Beijing Municipal Education Commission, China (No. 22019821001), and Beijing excellent talent training fund (No. Z2019-042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GF participated in the data curation, formal analysis, investigation, validation, visualization, and writing of the original draft. YH participated in the data curation and formal analysis. YL contributed to writing, reviewing, & editing of the manuscript. SH participated in the data curation and formal analysis. RX participated in the data curation and formal analysis. YW contributed to writing, reviewing, & editing of the manuscript. WY contributed to writing, reviewing, & editing of the manuscript. QS participated in the supervision, conceptualization, and writing, reviewing, & editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, G., He, Y., Liang, Y. et al. Enhanced piezoelectric performance of rare earth complex-doped sandwich-structured electrospun P(VDF-HFP) multifunctional composite nanofiber membranes. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 22183–22195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08998-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08998-w