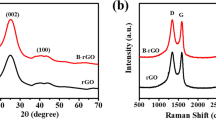
Abstract
With the rapid development of nanogenerator technology, intelligent motion sensors, wearable electronic devices, and human–computer interaction have received more and more attention. However, traditional motion sensors are limited by factors such as external power supply and their own volume and do not have the characteristics of flexibility, high intelligence, and high integration of modern sensors. This paper studied and realized a matrix motion sensor based on flexible PVDF hybrid material, which worked under piezoelectric mechanisms. The performance test of the prepared motion sensor proves that the device has good environmental adaptability. Its output performance is characterized. Under the test conditions of 3 Hz and 300 N, the output voltage of the nanogenerator is 15 mV. On this basis, the nanogenerator is used for the collection of human movement energy and the monitoring of human motion status, and through the design of electronic skin and human–computer interaction testing, it shows the huge application of flexible nanogenerator movement state monitoring and human health monitoring potential. We believe that the proposed flexible, low cost, hybrid nanogenerator will supply an effective method for energy harvesting devices.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Buongiorno, M. Corradini, J. Parsons, D. Petti, Nuclear energy in a carbon-constrained world: big challenges and big opportunities. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 17(2), 69–77 (2019)
Y. Hu, Z.L. Wang, Recent progress in piezoelectric nanogenerators as a sustainable power source in self-powered systems and active sensors. Nano Energy 14, 3–14 (2015)
Y. Manjula, R. Rakesh Kumar, P.M. Swarup Raju, G. Anil Kumar, T. Venkatappa Rao, A. Akshaykranth, P. Supraja, Piezoelectric flexible nanogenerator based on ZnO nanosheet networks for mechanical energy harvesting. Chem. Phys. 533, 110699 (2020)
S. Stassi, V. Cauda, C. Ottone, A. Chiodoni, C.F. Pirri, G. Canavese, Flexible piezoelectric energy nanogenerator based on ZnO nanotubes hosted in a polycarbonate membrane. Nano Energy 13, 474–481 (2015)
Z. Wen, M.H. Yeh, H. Guo, J. Wang, Y. Zi, W. Xu, J. Deng, L. Zhu, X. Wang, C. Hu, L. Zhu, X. Sun, Z.L. Wang, Self-powered textile for wearable electronics by hybridizing fiber-shaped nanogenerators, solar cells, and supercapacitors. Sci. Adv. 2(10), e1600097 (2016)
S. Lee, S. Bae, L. Lin, Y. Yang, C. Park, S. Kim, S.N. Cha, H. Kim, Y.J. Park, Z.L. Wang, Super-flexible nanogenerator for energy harvesting from gentle wind and as an active deformation sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23(19), 2445–2449 (2013)
J. Briscoe, S. Dunn, Piezoelectric nanogenerators - a review of nanostructured piezoelectric energy harvesters. Nano Energy 14, 15–29 (2015)
G. Xia, Y. Huang, F. Li, L. Wang, J. Pang, L. Li, K. Wang, A thermally flexible and multi-site tactile sensor for remote 3D dynamic sensing imaging. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 14(6), 1039–1051 (2020)
S. Tang, M. Zhao, D. Yuan, X. Li, Z. Wang, X. Zhang, T. Jiao, J. Ke, Fe3O4 nanoparticles three-dimensional electro-peroxydisulfate for improving tetracycline degradation. Chemosphere 268, 129315 (2021)
X. Hu, Z. Ding, L. Fei, Y. Xiang, Y. Lin, Wearable piezoelectric nanogenerators based on reduced graphene oxide and in situ polarization-enhanced PVDF-TrFE films. J. Mater. Sci. 54(8), 6401–6409 (2019)
B. Zaarour, L. Zhu, X. Jin, Controlling the surface structure, mechanical properties, crystallinity, and piezoelectric properties of electrospun PVDF nanofibers by maneuvering molecular weight. Soft Mater. 17(2), 181–189 (2019)
S. Tang, M. Zhao, D. Yuan, X. Li, X. Zhang, Z. Wang, T. Jiao, K. Wang, MnFe2O4 nanoparticles promoted electrochemical oxidation coupling with persulfate activation for tetracycline degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 255, 117690 (2021)
M. Satthiyaraju, T. Ramesh, Nanomechanical, mechanical responses and characterization of piezoelectric nanoparticle-modified electrospun PVDF nanofibrous films. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44(6), 5697–5709 (2019)
S. Wang, L. Ding, X. Fan, W. Jiang, X. Gong, A liquid metal-based triboelectric nanogenerator as stretchable electronics for safeguarding and self-powered mechanosensing. Nano Energy 53, 863–870 (2018)
W. Wang, Y. Li, L. Li, L. Wang, K. Wang, SnO2/TiO2 nanocomposite prepared by pulsed laser deposition as anode material for flexible quasi-solid-state lithium-ion batteries. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 15(12), 11709–11722 (2020)
K. Wang, W. Wang, L. Wang, L. Li, An improved SOC control strategy for electric vehicle hybrid energy storage systems. Energies 13(20), 5297 (2020)
K. Wang, X. Feng, J. Pang, J. Ren, C. Duan, L. Li, State of charge (SOC) estimation of lithium-ion battery based on adaptive square root unscented Kalman filter. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 15(9), 9499–9516 (2020)
P. Cheng, H. Guo, Z. Wen, C. Zhang, X. Yin, X. Li, D. Liu, W. Song, X. Sun, J. Wang, Z.L. Wang, Largely enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator for efficient harvesting of water wave energy by soft contacted structure. Nano Energy 57, 432–439 (2019)
C. Zhao, Q. Zhang, W. Zhang, X. Du, Y. Zhang, S. Gong, K. Ren, Q. Sun, Z.L. Wang, Hybrid piezo/triboelectric nanogenerator for highly efficient and stable rotation energy harvesting. Nano Energy 57, 440–449 (2019)
C. Jeong, C. Joung, S. Lee, M.Q. Feng, Y. Park, Carbon nanocomposite based mechanical sensing and energy harvesting. Int. J. Precis Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 7(1), 247–267 (2020)
Y. Zhou, Y. Wang, K. Wang, L. Kang, F. Peng, L. Wang, J. Pang, Hybrid genetic algorithm method for efficient and robust evaluation of remaining useful life of supercapacitors. Appl. Energy 260, 114169 (2020)
Y. Zhou, Y. Huang, J. Pang, K. Wang, Remaining useful life prediction for supercapacitor based on long short-term memory neural network. J. Power Sources. 440, 227149 (2019)
G. Xia, C. Li, K. Wang, L. Li, Structural design and electrochemical performance of PANI/CNTs and MnO2/CNTs supercapacitor. Sci. Adv. Mater. 11(8), 1079–1086 (2019)
K. Wang, L. Li, T. Zhang, Z. Liu, Nitrogen-doped graphene for supercapacitor with long-term electrochemical stability. Energy 70, 612–617 (2014)
X. Luo, F. Zhang, Q. Li, Q. Xia, Z. Li, X. Li, W. Ye, S. Li, C. Ge, Reversible control of magnetization in Fe3O4 nanoparticles by a supercapacitor. J. Phys.-Condes. Matter. 32(33), 334001 (2020)
F. Wang, J. Jiang, Q. Liu, Y. Zhang, J. Wang, S. Wang, L. Han, H. Liu, Y. Sang, Piezopotential gated two-dimensional InSe field-effect transistor for designing a pressure sensor based on piezotronic effect. Nano Energy 70, 104457 (2020)
Y. Yang, K. Kim, Size dependency of a ZnO nanorod-based piezoelectric nanogenerator evaluated by conductive atomic force microscopy. J. Korean Inst. Met. Mater. 58(1), 67–75 (2020)
L. Yang, S. Chi, S. Dong, F. Yuan, Z. Wang, J. Lei, L. Bao, J. Xiang, J. Wang, Preparation and characterization of a novel piezoelectric nanogenerator based on soluble and meltable copolyimide for harvesting mechanical energy. Nano Energy 67, 104220 (2020)
X. Feng, Q. Li, K. Wang, Waste plastic triboelectric nanogenerators using recycled plastic bags for power generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(1), 400–410 (2021)
C. Bu, F. Li, K. Yin, J. Pang, L. Wang, K. Wang, Research progress and prospect of triboelectric nanogenerators as self-powered human body sensors. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2(4), 863–878 (2020)
Z. Yuan, T. Zhou, Y. Yin, R. Cao, C. Li, Z.L. Wang, Transparent and flexible triboelectric sensing array for touch security applications. ACS Nano 11(8), 8364–8369 (2017)
Q. Jing, Y. Xie, G. Zhu, R.P.S. Han, Z.L. Wang, Self-powered thin-film motion vector sensor. Nat. Commun. 6(1), 8031 (2015)
L. Cheng, Y. Zheng, Q. Xu, Y. Qin, A light sensitive nanogenerator for self-powered UV detection with two measuring ranges. Adv. Opt. Mater. 5(1), 1600623 (2017)
K. Wang, L. Li, W. Xue, S. Zhou, Y. Lan, H. Zhang, Z. Sui, Electrodeposition synthesis of PANI/MnO2/graphene composite materials and its electrochemical performance. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 12(9), 8306–8314 (2017)
S. Siddiqui, D. Kim, L.T. Duy, M.T. Nguyen, S. Muhammad, W. Yoon, N. Lee, High-performance flexible lead-free nanocomposite piezoelectric nanogenerator for biomechanical energy harvesting and storage. Nano Energy 15, 177–185 (2015)
Y. Yang, H. Zhang, Z. Lin, Y.S. Zhou, Q. Jing, Y. Su, J. Yang, J. Chen, C. Hu, Z.L. Wang, Human skin based triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting biomechanical energy and as self-powered active tactile sensor system. ACS Nano 7(10), 9213–9222 (2013)
X. Yin, D. Liu, L. Zhou, X. Li, G. Xu, L. Liu, S. Li, C. Zhang, J. Wang, Z.L. Wang, A motion vector sensor via direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(34), 2002547 (2020)
H. He, C. Dong, Y. Fu, W. Han, T. Zhao, L. Xing, X. Xue, Self-powered smelling electronic-skin based on the piezo-gas-sensor matrix for real-time monitoring the mining environment. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 267, 392–402 (2018)
X. Feng, Y. Zhang, L. Kang, L. Wang, C. Duan, K. Yin, J. Pang, K. Wang, Integrated energy storage system based on triboelectric nanogenerator in electronic devices. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 15(2), 238–250 (2021)
J. Zhu, J. Qian, X. Hou, J. He, X. Niu, W. Geng, J. Mu, W. Zhang, X. Chou, High-performance stretchable PZT particles/Cu@Ag branch nanofibers composite piezoelectric nanogenerator for self-powered body motion monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 28(9), 95014 (2019)
Y. Chen, C. Cheng, S. Shen, Design and fabrication of a displacement sensor using screen printing technology and piezoelectric nanofibers in d33 mode. Sensor. Mater. 31(2), 233–244 (2019)
Y. Hua, N. Wang, K. Zhao, Simultaneous unknown input and state estimation for the linear system with a rank-deficient distribution matrix. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 6693690 (2021)
M. Koç, L. Paralı, O. Şan, Fabrication and vibrational energy harvesting characterization of flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator (PEN) based on PVDF/PZT. Polym. Test. 90, 106695 (2020)
L. Lu, W. Ding, J. Liu, B. Yang, Flexible PVDF based piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 78, 105251 (2020)
C. Duan, Y. Yu, P. Yang, X. Zhang, F. Li, L. Li, H. Xi, Engineering new defects in MIL-100(Fe) via a mixed-ligand approach to effect enhanced volatile organic compound adsorption capacity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 59(2), 774–782 (2019)
X. Wang, W. Song, M. You, J. Zhang, M. Yu, Z. Fan, S. Ramakrishna, Y. Long, Bionic single-electrode electronic skin unit based on piezoelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 12(8), 8588–8596 (2018)
X. Pu, H. Guo, Q. Tang, J. Chen, L. Feng, G. Liu, X. Wang, Y. Xi, C. Hu, Z.L. Wang, Rotation sensing and gesture control of a robot joint via triboelectric quantization sensor. Nano Energy 54, 453–460 (2018)
X. Wang, G. Yu, J. Zhang, M. Yu, S. Ramakrishna, Y. Long, Conductive polymer ultrafine fibers via electrospinning: preparation, physical properties and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 115, 100704 (2021)
H. Qiu, W. Song, X. Wang, J. Zhang, Z. Fan, M. Yu, S. Ramakrishna, Y. Long, A calibration-free self-powered sensor for vital sign monitoring and finger tap communication based on wearable triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 58, 536–542 (2019)
J. Zhou, X. Chen, U. Chang, J. Lu, C.C.Y. Leung, Y. Chen, Y. Hu, Z. Wang, A soft-robotic approach to anthropomorphic robotic hand dexterity. IEEE Access. 7, 101483–101495 (2019)
T. Li, J. Zou, F. Xing, M. Zhang, X. Cao, N. Wang, Z.L. Wang, From dual-mode triboelectric nanogenerator to smart tactile sensor: a multiplexing design. ACS Nano 11(4), 3950–3956 (2017)
J. Wu, K. Yin, S. Xiao, Z. Wu, Z. Zhu, J.A. Duan, J. He, Laser fabrication of bioinspired gradient surfaces for wettability applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 8(5), 2001610 (2021)
K. Wang, C. Liu, J. Sun, K. Zhao, L. Wang, J. Song, C. Duan, L. Li, State of charge estimation of composite energy storage systems with supercapacitors and lithium batteries. Complexity 2021, 8816250 (2021)
T. Chen, Q. Shi, M. Zhu, T. He, L. Sun, L. Yang, C. Lee, Triboelectric self-powered wearable flexible patch as 3D motion control interface for robotic manipulator. ACS Nano 12(11), 11561–11571 (2018)
W. Deng, T. Yang, L. Jin, C. Yan, H. Huang, X. Chu, Z. Wang, D. Xiong, G. Tian, Y. Gao, H. Zhang, W. Yang, Cowpea-structured PVDF/ZnO nanofibers based flexible self-powered piezoelectric bending motion sensor towards remote control of gestures. Nano Energy 55, 516–525 (2019)
Z. Wu, K. Yin, J. Wu, Z. Zhu, J. Duan, J. He, Recent advances in femtosecond laser-structured Janus membranes with asymmetric surface wettability. Nanoscale 13(4), 2209–2226 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Youth Fund of Shandong Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. ZR2020QE212), Key Projects of Shandong Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. ZR2020KF020), the Development Plan of Shandong Province (Grant No. 2019GGX104019), and Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 2019A1515110706).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ, FL, and ZW explored the whole research ideas and wrote the paper. PD and GX carried out the synthesis and experiments. KW provided the guidance for the research process. KW proposed the idea, supervised the entire project, and revised the manuscript. All the authors participated in this research project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Li, F., Wang, Z. et al. Flexible PVDF nanogenerator-driven motion sensors for human body motion energy tracking and monitoring. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 14715–14727 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06027-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06027-w