Abstract
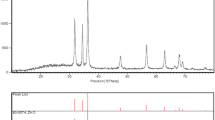
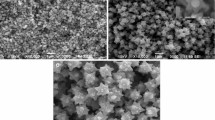
The purpose of this paper is to describe a novel method for producing zinc oxide (ZnO). Within only 10 min of the synthesis procedure, ZnO nanoparticles were precipitated directly from a sodium zincate after partial neutralization with sulfuric acid. The entire synthesis process was carried out at room temperature. There were no additives or additional operations, such as calcination, required in the proposed method. XRD, FESEM, and BET techniques were used to characterize the product, and XRD confirmed the formation of crystalline ZnO devoid of other phases. Consideration of the height of XRD peaks revealed that ZnO crystallites grow preferentially along the c-axis. FESEM revealed particles with a diameter of 30–50 nm which was also confirmed by analysis of the broadening of XRD peaks. Nearly spherical particles were observed by the FESEM. These nanospheres were primarily adhered together to form platelets. Finally, the BET analysis revealed a substantial specific surface area of 20 m2 g− 1.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data that support the study’s findings are included in the article. Additional information is available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Code availability
Visual MINTEQ is free software and is available at https://vminteq.lwr.kth.se/.
References
A.S. Lanje, S.J. Sharma, R.S. Ningthoujam, J.-S. Ahn, R.B. Pode, Adv. Powder Technol. 24, 331 (2013)
D. Piva, R. Piva, M. Rocha, J. Dias, O. Montedo, I. Malavazi, M. Morelli, Adv. Powder Technol. 28, 463 (2017)
A.K. Babaheydari, M. Salavati-Niasari, A. Khansari, Particuology 10, 759 (2012)
M. Goudarzi, M. Mousavi-Kamazani, M. Salavati-Niasari, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 8423 (2017)
S. Mukhopadhyay, P.P. Das, S. Maity, P. Ghosh, P.S. Devi, Appl. Catal. B 165, 128 (2015)
S. Swathi, E.S. Babu, R. Yuvakkumar, G. Ravi, A. Chinnathambi, S.A. Alharbi, D. Velauthapillai, Ceram. Int. 47, 9785 (2021)
A. Mohammadzadeh, M. Azadbeh, B. Shokriyan, S.N.K. Abad, Ceram. Int. 46, 2552 (2020)
S. Agarwal, P. Rai, E.N. Gatell, E. Llobet, F. Güell, M. Kumar, K. Awasthi, Sens. Actuators B 292, 24 (2019)
S. Arya, P. Mahajan, S. Mahajan, A. Khosla, R. Datt, V. Gupta, S.-J. Young, S.K. Oruganti, ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 10, 023002 (2021)
Y. Bao, L. Gao, C. Feng, J. Ma, S. Lyu, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 263, 114887 (2021)
M. Yousefi, E. Noori, D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, T. Gholami, J. Clust. Sci. 25, 397 (2014)
S. Moshtaghi, S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M. Salavati-Niasari, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 834 (2016)
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, S. Mortazavi-Derazkola, M. Salavati-Niasari, J. Mol. Liq. 231, 306 (2017)
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M.S. Morassaei, O. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, L.K. Foong, Ceram. Int. 46, 17186 (2020)
A. Moezzi, M.B. Cortie, A.M. McDonagh, Dalton Trans. 42, 14432 (2013)
A. Moezzi, M. Cortie, A. Dowd, A. McDonagh, J. Nanopart. Res. 16, 1 (2014)
C.K. Srikanth, P. Jeevanandam, J. Alloy. Compd. 486, 677 (2009)
M. Wang, Y. Zhou, Y. Zhang, S.H. Hahn, E.J. Kim, CrystEngComm 13, 6024 (2011)
J. Xie, P. Li, Y. Wang, Y. Wei, Phys. Status Solidi A 205, 1560 (2008)
J. Xie, P. Li, Y. Li, Y. Wang, Y. Wei, Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 943 (2009)
J. Wang, L. Xiang, J. Cryst. Growth 401, 279 (2014)
P. Li, H. Liu, F. Xu, Y. Wei, Mater. Chem. Phys. 112, 393 (2008)
M.-H. Wang, F. Zhou, B. Zhang, C. Yao, J. Alloys Compd. 581, 308 (2013)
A.M. Pourrahimi, D. Liu, L.K. Pallon, R.L. Andersson, A.M. Abad, J.-M. Lagarón, M.S. Hedenqvist, V. Ström, U.W. Gedde, R.T. Olsson, RSC Adv. 4, 35568 (2014)
S. Sepulveda-Guzman, B. Reeja-Jayan, E. de La Rosa, A. Torres-Castro, V. Gonzalez-Gonzalez, M. Jose-Yacaman, Mater. Chem. Phys. 115, 172 (2009)
M. Aghazadeh Ghomi, J. Moghaddam, N. Parvini, Ahmadi, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 70, 1697 (2017)
M.A. Ghomi, J. Moghaddam, N.P. Ahmadi, Rare Met. 39, 1341 (2020)
P. Perillo, M. Atia, D. Rodríguez, Physica E 85, 185 (2017)
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M. Salavati-Niasari, J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 3313 (2014)
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M. Salavati-Niasari, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 5812 (2015)
J. Wang, P. Ma, L. Xiang, Mater. Lett. 141, 118 (2015)
Funding
This research received no specific funding from public, commercial, or not-for-profit funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA-G was responsible for conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, resource provision, data curation, writing—original draft, and project administration. ZP: performing the experiments. Each author has contributed significantly to the paper's development and will accept public responsibility for its content.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Consent to participate
This research is not related to human subjects.
Consent for publication
The author assigns non-exclusive publication rights to Springer and warrants that his contribution is unique and that he possesses all necessary authority to make this grant. The author assumes responsibility for the material’s release on behalf of all co-authors. This assignment of publication rights includes the non-exclusive right to reproduce and distribute the article in any format, including reprints, translations, photographic reproductions, microform, electronic form (offline, online), or other reproductions of a similar nature.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aghazadeh-Ghomi, M., Pourabbas, Z. Rapid synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from an alkaline zinc solution via direct precipitation. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 24363–24368 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06907-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06907-1