Abstract
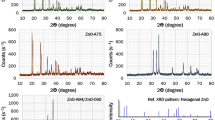
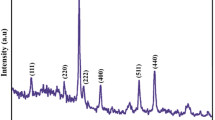
This paper reports on a novel processing route for producing ZnO nanoparticles by solid-state thermal decomposition of zinc(II) acetate nanostructures obtained by the sublimation of zinc(II) acetate powder. The sublimation process of the Zn(OAc)2 powder was carried out in the temperature 150 °C for 2 h. In addition, nanoparticles of ZnO were obtained by solid-state thermal decomposition of the synthesized Zn(OAc)2 nanostructures. The synthesized products were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, photoluminescence spectroscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The sublimation process of the Zn(OAc)2 powder was carried out within the range of 150–180 °C. The XRD studies indicated the production of pure hexagonal ZnO nanoparticles after thermal decomposition.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani and M. Ramezani (2014). Mater. Lett. 130, 259–262.
S. M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani, M. Ramezani, and M. Vatanparast (2014). Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 26, 112–118.
S. M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani, K. Venkateswara Rao, Z Chamanzadeh, International Conference on Nanoscience Engineering and Technology ICONSET (IEEE¸ 2011), pp. 653–655.
K. Westermark, H. Rensmo, T. A. C. Lees, J. G. Vos, and H. T. Siegbahn (2002). J. Phys. Chem. B. 10, 10108–10113.
H. M. Lin, S. J. Tzeng, P. J. Hsiau, and W. L. Tsai (1998). Nanostruct. Mater. 10, 465–477.
M. Nanu, J. Schoonman, and A. Goossens (2012). Nano Lett. 5, 1716–1720.
I. Tsuji, H. Kato, and A. Kudo (2011). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44, 356–361.
S. M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani, F. Mohandes, M. Salavati-Niasari, and K. Venkateswara-Rao (2012). Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 314–319.
S. M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani, K. Venkateswara-Rao, and Z. Chamanzadeh (2011). IEEE ICONSET 47, 653–659.
W. Zhou, Z. Yin, D. H. Sim, H. Zhang, J. Ma, H. H. Hng, and Q. Yan (2011). Nanotechnology 22, 195–199.
M. L. A. Aguilera, M. Ortega-Lopez, V. M. S. Resendiz, J. A. Hernandez, and M. A. G. Trujillo (2003). Mater. Sci. Eng. B 102, 380–385.
K. Yoshino, H. Komaki, T. Kakeno, Y. Akaki, and T. Ikari (2003). J. Phys. Chem. Solids 64, 183–189.
S. Shen, L. Zhao, and L. Guo (2011). Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 100–105.
F. Soofivand, M. Salavati-Niasari, and F. Mohandes (2012). Micro. Nano. Lett. 7, 283–289.
L. Andronic, L. Isac, A. Duta, and J. Photoch (2011). Photobiology A 221, 30–36.
M. Mousavi-Kamazani, M. Salavati-Niasari, and H. Emadi (2012). Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 398–401.
M. Mousavi-Kamazani, M. Salavati-Niasari, and H. Emadi (2012). Micro. Nano. Lett. 7, 896–901.
H. Kim, M. Suh, B. H. Kwon, D. S. Jang, S. W. Kim, and D. Y. Jeon (2011). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 363, 703–708.
D. C. Pan, L. J. An, Z. M. Sun, W. Hou, Y. Yang, Z. Z. Yang, and Y. F. Lu (2008). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 562–569.
M. Salavati-Niasari, J. Javidi, and F. Davar (2010). Ultrason. Sonochem. 17, 870–877.
Y. Akaki, S. Kurihara, M. Shirahama, K. Tsurugida, S. Seto, T. Kakeno, and K. Yoshino (2005). J. Phys. Chem. Solids 66, 185–189.
I. Tsuji, H. Kato, and A. Kudo (2011). Chem. Mater. 18, 196–200.
M. Ortega-Lopez, O. Vigil-Galan, F. C. Gandarilla, and O. Solorza-Feria (2003). Mater. Res. Bull. 38, 55–61.
Z. Aissa, A. Bouzidi, and M. Amlouk (2010). J. Alloys Compd. 506, 492–496.
M. Salavati-Niasari, N. Mir, and F. Davar (2009). J. Alloys Compd. 476, 908–912.
L. Tian and J. J. Vittal (2007). New J. Chem. 31, 208–211.
M. L. A. Aguilera, J. R. A. Hernandez, M. A. G. Trujillo, M. O. Lopez, and G. C. Puente (2007). Thin Solid Films 515, 627–630.
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to council of University of Shahid Bahonar Kerman and Gol-E-Gohar Iron Mine for supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjbar, M., Taher, M.A. & Sam, A. Solvent-Free Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles by a Simple Thermal Decomposition Method. J Clust Sci 25, 1657–1664 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-014-0764-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-014-0764-7