Abstract
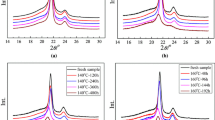
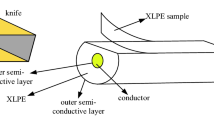
As a typical semi-crystalline polymer, the macroscopic properties of crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) are closely related to the crystal structure. During service, thermal aging caused by overheating of the cable will cause the deterioration of the crystal structure, which in turn will cause the deterioration of macroscopic properties of XLPE. In this paper, 110 kV XLPE cable insulation was thermally aged at 160 °C. The melting characteristics of crystals in different aged samples and the influence of cooling rate after aging were investigated by Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) Technology. The results show that the melting temperature (Tm) and the crystallinity of XLPE samples aged at 160 °C are basically unchanged and then decrease rapidly with the further increase of aging time. A new melting peak can be observed around 50 °C after 96 h. This peak moves toward lower temperature and the area gradually increases with the aging time. The appearance of this peak is mainly due to the destruction of the crystal structure by the oxidation reaction not the cooling process of the sample after aging, which can be confirmed by results of Oxidative Induction Time measurement and DSC curves of aged samples with different cooling methods. It is deduced that the oxidation reaction at elevated temperature can lead to drastic chains scission after antioxidants in XLPE are totally consumed. When the aged samples were taken out of the oven and then recrystallized, the number of molecular chains which can be folded to form lamellas decreases and the regularity of the crystals formed again becomes worse, resulting in the decrease in Tm and the crystallinity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Englund, R. Huuva, S.M. Gubanski, T. Hjertberg, Synthesis and efficiency of voltage stabilizers for XLPE cable insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 16(5), 1455–1461 (2009)
J.Y. Li, H. Li, F.S. Zhou, S.H. Wang, J.K. Zhao, B.H. Ouyang, Copper-catalyzed oxidation caused by copper-rich impurities in cross-linked polyethylene cable insulation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(1), 806–810 (2016)
H. Li, J.Y. Li, W.W. Li, X.T. Zhao, G.L. Wang, M.A. Alim, Fractal analysis of side channels for breakdown structures in XLPE cable insulation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24(5), 1640–1643 (2013)
J. Muccigrosso, P.J. Phillips, The morphology of crosslinked polyethylene insulation. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. EI-13, 172–178 (1978)
J.P. Jones, J.P. Llewellyn, T.J. Lewis, The contribution of field-induced morphological change to the electrical aging and breakdown of polyethylene. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 12(5), 951–966 (2005)
P.S. He, Structure and Properties of Polymers (Alpha Science International Ltd, Britain, 2014).
J.Y. Li, F.S. Zhou, M.D. Min, S.T. Li, R. Xia, The energy distribution of trapped charges in polymers based on isothermal surface potential decay model. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 22(3), 1723–1732 (2015)
J.Y. Li, H. Li, Q.M. Wang, X. Zhang, B.H. Ouyang, J.K. Zhao, Accelerated inhomogeneous degradation of XLPE insulation caused by copper-rich impurities at elevated temperature. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23(3), 1789–1797 (2016)
M. Nedjar, Effect of thermal ageing on the electrical properties of crosslinked polyethylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 111(4), 1985–1990 (2009)
A.S. Xie, S.T. Li, X.Q. Zheng, Investigations of electrical trees in the inner layer of XLPE cable insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 17(3), 685–693 (2008)
B. Larbi, B. Ahmed, L. Chirstian, L. Mouhamed, Observations on structural changes under thermal ageing of cross-linked polyethylene used as power cables insulation. Iran. Polym. J. 17(8), 611–624 (2008)
A. Tzimas, S.M. Rowland, L.A. Dissado, Effect of electrical and thermal stressing on charge traps in XLPE cable insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 19(6), 2145–2154 (2012)
J.P. Flory, The configuration of real polymer chains. J. Chem. Phys. 17(17), 303–310 (1951)
H. Li, J.Y. Li, Y.X. Ma, Q.M. Wang, B.H. Ouyang, The role of thermo-oxidative aging at different temperatures on the crystal structure of crosslinked polyethylene. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29(5), 3696–3703 (2018)
Y. Xu, P. Luo, M. Xu, T.X. Sun, Investigation on insulation material morphological structure of 110 and 220 kV XLPE retired cables for reusing. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21(4), 1687–1696 (2014)
R.L. Morgan, M.J. Hill, P.J. Barham, Morphology, melting behaviour and co-crystallization in polyethylene blends: the effect of cooling rate on two homogeneously mixed blends. Polymer 40(2), 337–348 (1999)
Funding
This project is supported by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (18JK0152).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Li, H., Duan, Y. et al. Study on melting characteristics of crystals in thermal aged XLPE cable insulation at elevated temperature. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 16194–16202 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06166-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06166-0