Abstract
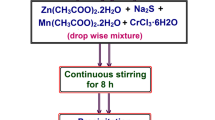
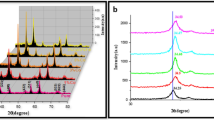
Single-phase pure, Fe-doped and glucose-capped CdO nanoparticles (NPs) were prepared by a chemical precipitation method. The structure, morphology, composition, optical and luminescence properties of all samples were investigated using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, photoluminescence (PL), and ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis) spectroscopy. XRD study revealed the single-phase hexagonal crystal structure of all samples with P63/mmc space group. SEM detected the microstructural behaviour of all samples. The functional groups of the synthesized samples were also identified by FTIR spectroscopy. The calculated direct band energy values were estimated as 3.78 eV for pure, 3.65 eV for Fe-doped, and 3.63 eV for glucose-capped CdO NPs. From PL study, it was identified that glucose-capped CdO NPs showed the strongest photoluminescence signal (543 nm) comparing to the Fe-doped (436 nm) and pure (308 nm) CdO NPs. As compared to all samples, glucose-capped CdO NPs exhibited significant antibacterial activity against E. coli bacteria.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.K. Gupta, K. Ghosh, R. Patel, S.R. Mishra, P.K. Kahol, Highly conducting and transparent tin-doped CdO thin films for optoelectronic applications. Mater. Lett. 62(25), 4103–4108 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2008.06.008
M. Norouzi, M. Kolahdouz, P. Ebrahimi, M. Ganjian, R. Soleimanzadeh, K. Narimani, H. Radamson, Thermoelectric energy harvesting using array of vertically aligned Al-doped ZnO nanorods. Thin Solid Films 619, 41–47 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2016.10.041
A.T. Ravichandran, A. Robert Xavier, K. Pushpanathan, B.M. Nagabhushana, R. Chandramohan, Structural and optical properties of Zn doped CdO nanoparticles synthesized by chemical precipitation method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 2693–2700 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-4079-8
R. Kondo, H. Okimura, Y. Sakai, Electrical properties of semiconductor photodiodes with semitransparent films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 10(11), 1547–1554 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.10.1547
F.A. Benko, F.P. Koffyberg, Quantum efficiency and optical transitions of CdO photoanodes. Solid State Commun. 57(12), 901–903 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-1098(86)90920-8
A. Ratkovich, R.L. Penn, Zinc oxide nanoparticle growth from homogenous solution: influence of Zn:OH, water concentration, and surfactant additives. Mater. Res. Bull. 44(5), 993–998 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2008.11.012
Y.L. Wu, A.I.Y. Tok, X.T. Zeng, C.S. Lim, L.C. Kwek, F.C.Y. Boey, A dual-colored bio-marker made of doped ZnO nanocrystals. Nanotechnology 19(34), 345605 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/34/345605
P. Raveendran, J. Fu, S.L. Wallen, Completely “green” synthesis and stabilization of metal nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(46), 13940–13941 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja029267j
K.M. Reddy, K. Feris, J. Bell, D.G. Wingett, C. Hanley, A. Punnoose, Selective toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(213902), 2139021–2139023 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2742324
Y. Xie, Y. He, P.L. Irwin, T. Jin, X. Shi, Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Campylobacter jejuni. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77(7), 2325–2331 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02149-10
A. Lipovsky, Y. Nitzan, A. Gedanken, R. Lubart, Antifungal activity of ZnO nanoparticles—the role of ROS mediated cell injury. Nanotechnology 22(10), 105101 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/22/10/105101
X.R. Ye, C. Daraio, C. Wang, J.B. Talbot, Room temperature solvent-free synthesis of monodisperse magnetite nanocrystals. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 6(3), 852–856 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2006.135
Z. Guo-hua, L. Ming-fang, L. Ming-Li, Differential pulse voltammetric determination of dopamine with the coexistence of ascorbic acid on boron-doped diamond surface. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 5(4), 1114–1123 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11532-007-0049-1
K.M. Abd El-Salaam, E.A. Hassan, Active surface centres in a heterogeneous CdO catalyst for ethanol decomposition. Surf. Technol. 16(2), 121–128 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0376-4583(82)90031-0
S. Sivakumar, A. Venkatesan, P. Soundhirarajan, C.P. Khatiwada, Thermal, structural, functional, optical and magnetic studies of pure and Ba doped CdO nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 151, 760–772 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.06.105
C.J. Johnson, Q.H. Yan, D.P. Yang, J.R. Saykally, Optical cavity effects in ZnO nanowire lasers and waveguides. J Phys. Chem. B 107(34), 8816–8828 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp034482n
A. Moorthy, A.R. Subramaniam, T.G. Manivasagam, D. Kumaresan, Surfactant-assisted synthesis of metallic cadmium, cadmium hydroxide nanostructures and their electrochemical charge storage properties. Dalton Trans. 47(26), 8683–8689 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8DT00638E
W.S. Khan, C. Cao, I. Aslam, Z. Ali, F.K. Butt, T. Mahmood, G. Nabi, A. Ihsan, Z. Usman, A. Rehman, Single crystalline multi-petal Cd nanoleaves prepared by thermal reduction of CdO. Mater. Res. Bull. 48(2), 819–822 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.11.068
W.Z. Tawfik, M. Esmat, S.I. El-Dek, Drastic improvement in magnetization of CdO nanoparticles by Fe doping. Appl. Nanosci. 7, 863–870 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-017-0623-6
S. Balamurugan, A.R. Balu, K. Usharani, M. Suganya, S. Anitha, D. Prabha, S. langovan, Synthesis of CdO nanopowders by a simple soft chemical method and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. Pac. Sci. Rev. A Nat. Sci. Eng. 18(3), 228–232 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psra.2016.10.003
I.G. Morozov, O.V. Belousova, M.V. Kuznetcov, Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nanostructured submicron Cd/CdO particles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 6664–6670 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03222-z
P.S. Kumar, M. Selvakumar, P. Bhagabati, B. Bharathi, S. Karuthapandian, S. Balakumar, CdO/ZnO nanohybrids: facile synthesis and morphologically enhanced photocatalytic performance. RSC Adv. 4(62), 32977–32986 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA02502D
C.P. Khatiwada, Synthesis, characterizations and anti-bacterial activities of pure and Ag doped CdO nanoparticles by chemical precipitation method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 136, 1751–1759 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.10.078
K. Karthik, S. Dhanuskodi, C. Gobinath, S. Prabukumar, S. Sivaramakrishnan, Photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of hydrothermally prepared CdO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 11420–11429 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6937-z
S. Gandhi, R.H.H. Subramani, T. Ramankrishnan, A. Sivabalan, V. Dhanalakshmi, M.R.G. Gopinath Nair, R. Anbarasan, Ultrasound assisted one pot synthesis of nano-sized CuO and its nanocomposite with poly(vinyl alcohol). J. Mater. Sci. 45, 1688–1694 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-4158-4
Z. Guo, M. Li, J. Liu, Highly porous CdO nanowires: preparation based on hydroxy-and carbonate-containing cadmium compound precursor nanowires, gas sensing and optical properties. Nanotechnology 19(24), 245611 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/24/245611
R. Ranjithkumar, A.A. Irudayaraj, G. Jayakumar, A.D. Raj, S. Karthick, R. Vinayagamoorthy, Synthesis and properties of CdO and Fe doped CdO nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 3(6), 1378–1382 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2016.04.018
N.M. Al-Hada, H. Mohamed Kamari, C.A.C. Abdullah, E. Saion, A.H. Shaari, Z.A. Talib, K.A. Matori, Down-top nanofabrication of binary (CdO)x (ZnO)1-x nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 12, 8309–8323 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S150405
R. Saravanan, H. Shankar, T. Prakash, V. Narayanan, A. Stephen, ZnO/CdO composite nanorods for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under visible light. Mater. Chem. Phys. 125(1–2), 277–280 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.09.030
R. Kumari, P. Singh, V. Kumar, Study on structural, optical and electrical properties of CdO and Cd0.98Al0.02O films prepared by innovative sol–gel screen-printing method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 8989–8994 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8923-5
P. Velusamy, R.R. Babu, K. Ramamurthi, M.S. Dahlem, E. Elangovan, Highly transparent conducting cerium incorporated CdO thin films deposited by a spray pyrolytic technique. RSC Adv. 5(124), 102741–102749 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA15262C
N. Bel Haj Mohamed, M. Haouari, Z. Zaaboub, M. Nafoutti, F. Hassen, H. Maaref, H. Ben Ouada, Time resolved and temperature dependence of the radiative properties of thiol-capped CdS nanoparticles films. J. Nanopart. Res. 16, 2242 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2242-9
R. Tripathi, A. Dutta, S. Das, A. Kumar, T.P. Sinha, Dielectric relaxation of CdO nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 6, 175–181 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0427-5
K. Kaviyarasu, E. Manikandan, J. Kennedy, M. Jayachandran, Quantum confinement and photoluminescence of well-aligned CdO nanofibers by a solvothermal route. Mater. Lett. 120, 243–245 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.01.048
R. Wahab, Y.S. Kim, A. Mishra, S.-I.I. Yun, H.S. Shin, Formation of ZnO micro-flowers prepared via solution process and their antibacterial activity. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5(10), 1675 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11671-010-9694-y
R.B. Zhao, D.L. Hou, J.M. Guo, C.M. Zhen, G.D. Tang, Room temperature ferromagnetism in Ni doped ZnO powders. J. Superconduct. Nov. Magn. 23(7), 1261–2165 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-010-1043-y
P.J. Rivero, A. Urrutia, J. Goicoechea, C.R. Zamarreno, F.J. Arregui, I.R. Matias, An antibacterial coating based on a polymer/sol–gel hybrid matrix loaded with silver nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 305 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-6-305
C. Dong, D. Song, J. Cairney, O.L. Maddan, G. He, Y. Deng, Antibacterial study of Mg(OH)2 nanoplatelets. Materials Research Bulletin. 46(4), 576–582 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2010.12.023
B.K. Holt, J.A. Bard, Interaction of silver (I) ions with the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli: an electrochemical and scanning electrochemical microscopy study of the antimicrobial mechanism of micromolar Ag+. Biochemistry 44(39), 13214–13223 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0508542
M.A. Fayaz, K. Balaji, M. Girilal, R. Yadav, T.P. Kalaichelvan, R. Venketesan, Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their synergistic effect with antibiotics: a study against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 6(1), 103–109 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2009.04.006
M. Nasrullah, F.Z. Gul, S. Hanif, A. Mannan, S. Naz, J.S. Ali, M. Zia, Green and chemical syntheses of CdO NPs: a comparative study for yield attributes, biological characteristics, and toxicity concerns. ACS Omega 5(11), 5739–5747 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03769
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gudla, U.R., Suryanarayana, B., Raghavendra, V. et al. Structural, optical and luminescence properties of pure, Fe-doped and glucose-capped CdO Semiconductor nanoparticles for their Antibacterial activity. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 3920–3928 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05135-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05135-3