Abstract
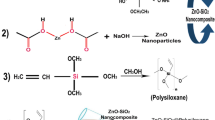
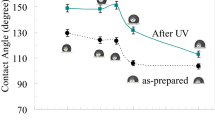
The polysiloxane–TiO2 nanocomposites were prepared by a solvent casting method in triethanolamine and tetrahydrofuran solvents. The prepared nanocomposites were characterized by X-ray diffraction technique, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscopy for structural analysis and surface morphology. The amorphous nature of polysiloxane observed in XRD spectra and FTIR spectra shows the characteristic peaks of Si–CH2, Si–CH3, and Ti–O–Ti, confirming the formation of nanocomposites. The surface morphology shows the nanoparticles are completely embedded in the polysiloxane. Furthermore, the DC conductivity shows the increase in conductivity with the increase in temperature due to tunneling phenomena. The wet contact angle of pure polysiloxane was 78.3° before being exposed to UV light and upon the addition of TiO2 in PS the WAC increased to 88.2° which clearly indicates that the nanocomposites are superhydrophobic in nature. Among all the nanocomposites of different weight percentages, 0.3 wt% shows the highest DC conductivity of 6 × 10−5 S/cm. The dielectric spectroscopy study reveals low dielectric constant and tangent loss for 0.3 wt% nanocomposite; as a result it shows the highest conductivity of 1.35 × 10−4 S/cm. The quality factor confirms that there is a small damping loss for 0.3 wt% of nanocomposites which is favourable for high conductivity.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Tabakci, M. Ersoz, M. Yilmaz, A calix[4]arene-containing polysiloxane resin for removal of heavy metals and dichromate anion. J. Macromol. Sci. A 43, 57 (2006)
P. Hammer, M.G. Schiavetto, F.C. Dos Santos, A.V. Benedetti, S.H. Pulcinelli, C.V. Santilli, Improvement of the corrosion resistance of polysiloxane hybrid coatings by cerium doping. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 356, 2606 (2010)
M. Barletta, S.V.G. Rubino, M. Puopolo, S. Venettacci, Functionalized polysiloxane coatings on hot-rolled and high‐strength Fe 430 B steel: analysis of mechanical response and resistance to chemicals. Appl. Polym. Sci. 131, 40624 (2014)
S. Dewasthale, C. Andrews, D. Graiver, R. Narayan, Water soluble polysiloxanes. Silicon 9, 619 (2017)
S. Jodeh, B. Khalaf, S. Radi, S. Tighadouini, R. Salghi, S. Samhan, I. Warad, D. Jodeh, New polysiloxane surfaces modified with ortho-, meta-, or para-nitrophenyl moieties for cadmium removal from water. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 6, 18 (2016)
S.J. Dünki, E.C. Reyes, D.M. Opris, A facile synthetic strategy to polysiloxanes containing sulfonyl side groups with high dielectric permittivity. Polym. Chem. 8, 715 (2017)
C. Racles, V. Cozan, A. Bele, M. Dascalu, Polar silicones: structure-dielectric properties relationship. Des. Monomers Polym. 19, 496 (2016)
S. Giaveri, P. Gronchi, A. Barzoni, Polysiloxane-epoxy resin for high-temperature coatings: structure effects on layer performance after 450 °C treatment. Coatings. 7, 213 (2017)
N. Riehle, S. Thude, T. Götz, A. Kandelbauer, S. Thanos, G.E.M. Tovar, G. Lorenz, Influence of PDMS molecular weight on transparency and mechanical properties of soft polysiloxane-urea-elastomers for intraocular lens application. Eur. Polym. J. 101, 190 (2018)
K. Lu, D. Erb, M. Liu, Phase transformation, oxidation stability, and electrical conductivity of TiO2-polysiloxane derived ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 10166 (2016)
M.A. Basit, M.M. Butt, M. Nazir, Muhammad Naeem Ashiq, Conjunction of macroporosity and NH4F treatment for improved performance of TiO2 photoanode in quantum-dot sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Sci. 30, 1861 (2019)
M.A. Basit, M.A. Abbas, E.S. Jung, J.H. Bang, T.J. Park, Improved light absorbance and quantum-dot loading by macroporous TiO2 photoanode for PbS quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Chem. Phys. 196, 170 (2017)
B. Sun, W. Zhao, Y. Liu, P. Chen, White-light-controlled resistive switching and photovoltaic effects in TiO2/ZnO composite nanorods array at room temperature. J. Mater. Sci. 25, 4306 (2014)
P. Huang, H.Q. Shi, H.M. Xiao, Y.Q. Li, N. Hu, S.Y. Fu, High performance surface-modified TiO2/silicone nanocomposite. Sci. Rep. 7, 5951 (2017)
A.S. Roy, S. Gupta, S. Seethamraju, G. Madras, P.C. Ramamurthy, Impedance spectroscopy of novel hybrid composite films of polyvinylbutyral (PVB)/ functionalized mesoporous silica. Composites B 58, 134 (2014)
A.S. Roy, S. Gupta, S. Sindhu, A. Parveen, P.C. Ramamurthy, Dielectric properties of novel PVA/ZnO hybrid nanocomposite films. Composites B 47, 314 (2013)
W. Li, R. Liang, A. Hu, Z. Huang, Y.N. Zhou, Generation of oxygen vacancies in visible light-activated one-dimensional iodine TiO2 photocatalysts. RSC Adv. 4, 36959 (2014)
I. Ahmad, C.W. Kan, A review on development and applications of bio-inspired superhydrophobic textiles. Materials 9, 892 (2016)
C.-H. Xue, W. Yin, P. Zhang, J. Zhang, P.-T. Ji, S.-T. Jia, UV-durable superhydrophobic textiles with UV-shielding properties by introduction of ZnO/SiO2 core/shell nanorods on PET fibers and hydrophobization. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 427, 7 (2013)
J. Wu, J. Xia, W. Lei, B.-P. Wang, Fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces with double-scale roughness. Mater. Lett. 64, 1251 (2010)
X. X.Zhou, W.Y. GuoDing, Chen, Superhydrophobic or superhydrophilic surfaces regulated by micro-nano structured ZnO powders. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 3371 (2008)
D. C.Guo, Y.M.Y. ZhaoSunWang, Liu, Droplet impact on anisotropic superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 34, 3533 (2018)
D.J. Lin, L. Wang, X.D. Wang, W.M. Yan, Reduction in the contact time of impacting droplets by decorating a rectangular ridge on superhydrophobic surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 132, 1105 (2019)
Y. Shen, L. Wang, H. Zhang, T. Wu, H.Y. Pan, Preparation and characterization of titania/silicone nanocomposite material. Mat. Sci. Eng. 87, 012021 (2015)
A.S. Roy, Antistatic and dielectric properties of one-dimensional Al2+:Nd2O3 nanowire doped polyaniline nanocomposites for electronic application. Sens. Actuators A 280, 1 (2018)
J.W. Lee, H.B. Cho, T. Nakayama, T. Suzuki, H. Suematsu, K. Niihara, Internal structure control of the TiO2 nanotubes and polysiloxane nanocomposites by nanosecond pulsed electric field. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2, 97 (2014)
Y.C. Chiu, C.C. Huang, H.C. Tsai, Synthesis, characterization, and thermomechanical properties of siloxane-modified epoxy‐based nanocomposite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 131, 40984 (2014)
T. Ma, R. Yang, Z. Zheng, Y. Song, Rheology of fumed silica/polydimethylsiloxane suspensions. J. Rheol. 61, 205 (2017)
P. Cassagnau, Melt rheology of organoclay and fumed silica nanocomposites. Polymer 49, 2183 (2008)
K.U. Kirst, F. Kremer, V.M. Litvinov, Broad-band dielectric spectroscopy on the molecular dynamics of bulk and adsorbed poly(dimethylsiloxane). Macromolecules 26, 975 (1993)
A.S. Roy, S. Gupta, S. Seethamraju, P.C. Ramamurthy, G. Madras, Fabrication of poly(vinylidene chloride-co-vinyl chloride)/TiO2 nanocomposite films and their dielectric properties. Sci. Adv. Mater. 6, 946 (2014)
J.N. Ansari, S. Khasim, A. Parveen, O.A.A. Hartomy, Z. Khattari, N. Badi, A.S. Roy, Synthesis, characterization, dielectric and rectification properties of PANI/Nd2O3:Al2O3 nanocomposites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 27, 1064 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, M.N., Goud, S.C. & Roy, A.S. A facile and large-area fabrication method of superhydrophobic self-cleaning polysiloxane/TiO2 nanocomposite films and its dielectric properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 12570–12578 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03807-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03807-8