Abstract
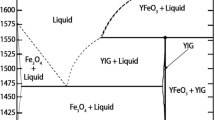
Micro-size and nano-size samples of (GdxY3−xFe5O12; x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1) garnet ferrites were prepared by the standard ceramic method (CER) and the coprecipitation (COP) method. The influences of Gd3+ doping and preparation methods on the optical and dielectric properties were compared for these micro-size and nano-size compositions for the first time. X-ray diffraction data confirmed the formation of a single phase of the garnet cubic structure for all samples. It was found that there is a good agreement between the theoretical and experimental lattice parameter estimated values. The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was used to study the cation distributions among the different crystallographic sites. Moreover, values of energy gap (Eg) for the investigated samples were determined from the diffused reflectance spectroscopy measurements. These values were found to be higher for (COP) samples than for (CER) ones and slightly increased by increasing Gd3+ content in both series prepared via the two techniques. Furthermore, resistivity (ρac), dielectric constant (ε′), and dielectric loss (ε″) showed a decrease with increasing frequency (f) for all samples. For the samples prepared by (CER) method, ρac increases with increasing Gd3+ content while for the samples prepared by (COP) method, ρac increases for 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 except for the sample x = 0.5. Values of ρac for samples prepared by (COP) method are higher than those prepared by (CER) method. Both ε′ and ε″ had the reverse behavior of ρac. Obtained results were explained according to different models.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Jin, S.R. Boona, Z. Yang, R.C. Myers, J.P. Heremans, Phys. Rev. B 92, 1 (2015)
S. Tao, H. Chao, D. Hailong, Y. Wenlong, L. Hongchen, W. Xinlao, Mater. Sci. Poland 33, 169 (2018)
B. Raneesh, I. Rejeena, P.U. Rehana, P. Radhakrishnan, Ceram. Int. 38, 1823 (2012)
H.K. Jung, C.H. Kim, A.R. Hong, S.H. Lee, T.C. Kim, H.S. Jang, D.H. Kim, Ceram. Int. 45, 9846 (2019)
A. Goldman, Modern Ferrite Technology, 2nd edn. (Springer, Pittsburg, 2006)
S. Aakansha, S. Ravi, Solid State Commun. 300, 113690 (2019)
S. Aakansha, S. Ravi, Appl. Phys. Mater. Sci. Process. 125, 1 (2019)
Y.S. Cho, V.L. Burdick, V.R.W. Amarakoon, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 1605 (2005)
P. Grosseau, A. Bachiorrini, B. Guilhot, Powder Technol. 93, 247 (1997)
L. Sirdeshmukh, K. Krishna Kumar, S. Bal Laxman, A. Rama Krishna, G. Sathaiah, Bull. Mater. Sci. 21, 219 (1998)
T. Ramesh, R.S. Shinde, S.R. Murthy, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 3668 (2012)
R.A. Serra, T. Ogasawara, A.S. Ogasawara, Quím. Nova 30, 1545 (2007)
F. Nanni, F.R. Lamastra, A. Bianco, F. Leonardi, G. Gusmano, Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 5, 624 (2008)
H.M. El-Sayed, W.R. Agami, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 4866 (2016)
W.R. Agami, M.A. Ashmawy, A.A. Sattar, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23, 604 (2014)
A.A. Sattar, H.M. El-Sayed, W.R. Agami, Phys. Status Solidi (A) 205, 2716 (2008)
B. Strocka, P. Holst, W. Tolksdorf, Philips J. Res. 33, 186 (1978)
B.D. Cullity, C.D. Graham, Introduction to Magnetic Materials (Wiley, Hoboken, 2009)
H. Xu, H. Yang, Phys. Status Solidi (A) 204, 1203 (2007)
R.D. Shannon, Acta Crystallogr. A 32, 751 (1976)
J. Su, X. Lu, C. Zhang, J. Zhang, S. Peng, X. Wu, K. Min, F. Huang, J. Zhu, J. Mater. Sci. 46, 3488 (2011)
M. Rajendran, S. Deka, P.A. Joy, A.K. Bhattacharya, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 301, 212 (2006)
P. Ayyub, V.R. Palkar, S. Chattopadhyay, M. Multani, Phys. Rev. B 51, 6135 (1995)
A.A. Sattar, H.M. El-Sayed, M.M. El-Tabey, J. Mater. Sci. 40, 4873 (2005)
Z. Cheng, H. Yang, L. Yu, Y. Cui, S. Feng, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302, 259 (2006)
B.J. Evans, S.S. Hafner, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 29, 1573 (1968)
L. Yu, J. Wang, S. Cao, S. Yuan, J. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. 42, 5335 (2007)
S.R. Naik, A.V. Salker, J. Alloys Compd. 600, 137 (2014)
E. Hild, E. Beregi, Period. Polytechn. Chem. Eng. 30, 235 (1986)
M. Niyaifar, H. Mohammadpour, A. Behmanesh, J. Alloys Compd. 683, 495 (2016)
D.M. Hemeda, A. Tawfik, O.M. Hemeda, S.M. Dewidar, Solid State Sci. 11, 1350 (2009)
R.D. Waldron, Phys. Rev. 99, 1727 (1955)
Y. Kim, S.J. Atherton, E.S. Brigham, T.E. Mallouk, J. Phys. Chem. 97, 11802 (1993)
A.B. Murphy, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 91, 1326 (2007)
K. Nama Manjunatha, S. Paul, Appl. Surf. Sci. 352, 10 (2015)
G.B. Scott, J.L. Page, Phys. Status Solidi (B) 79, 203 (1977)
P. Hansen, J.-P. Krumme, Thin Solid Films 114, 69 (1984)
R. López, R. Gómez, J. Sol Gel. Sci. Technol. 61, 1 (2012)
R. Banerjee, R. Jayakrishnan, P. Ayyub, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 12, 10647 (2000)
K. Sadhana, S.R. Murthy, K. Praveena, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 5130 (2014)
S. Geller, H.J. Williams, R.C. Sherwood, G.P. Espinosa, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 23, 1525 (1962)
K.B. Modi, R.P. Vara, H.G. Vora, M.C. Chhantbar, H.H. Joshi, J. Mater. Sci. 39, 2187 (2004)
C.G. Koops, Phys. Rev. 83, 121 (1951)
J.B. Goodenough, P.E. Tannenwald, Solid State Electron. 7, 556 (1964)
H. Zhao, J. Zhou, Y. Bai, Z. Gui, L. Li, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 280, 208 (2004)
G. Ranga Mohan, D. Ravinder, A.V. Ramana, Reddy, B.S. Boyanov, Mater. Lett. 40, 39 (1999)
Ü Özgür, Y. Alivov, H. Morkoç, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 20, 789 (2009)
T.M. Meaz, S.M. Attia, A. El Ata, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 257, 296 (2003)
A. Lipare, P. Vasambekar, A. Vaingankar, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 279, 160 (2004)
D. Bahadur, O. Parkash, D. Kumar, Bull. Mater. Sci. 3, 325 (1981)
M.A. Ahmed, S.T. Bishay, S.I. El-Dek, Mater. Chem. Phys. 126, 780 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors express their deep thanks to Prof. Dr. A.A. Sattar and Prof. Dr. H.M. El-Sayed (Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University) for facilitating the preparation of samples and measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agami, W.R., Faramawy, A.M. Influence of Gd3+ substitution and preparation technique on the optical and dielectric properties of Y3Fe5O12 garnet synthesized by standard ceramic and coprecipitation methods. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 11654–11664 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03717-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03717-9