Abstract
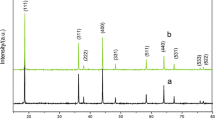
Li1.05Cu0.05Mn1.90O4 cathode materials were synthesized by liquid phase combustion method at different temperatures from 400 to 700 °C. All samples show good crystallinity and conform to the Fd3m space group of spinel LiMn2O4. The Li1.05Cu0.05Mn1.90O4 sample prepared at 600 °C has a sharp diffraction peak compared to the pristine LiMn2O4, while no impurities are detected. Both the Li–Cu co-doping and calcination temperature have effects on the morphology and particle size distribution. The electrochemical properties reveal that initial discharge capacity of the Li1.05Cu0.05Mn1.90O4 is 102.4 mAh g−1 and pristine LiMn2O4 electrode is 105.3 mAh g−1. After 1000 cycles, the capacity retention rate of the pristine LiMn2O4 (63.0%) has less than 74.3% of the Li1.05Cu0.05Mn1.90O4 sample. The lithium-ion diffusion coefficient indicates that the as-prepared Li1.05Cu0.05Mn1.90O4 electrode (1.58 × 10−10 cm2 s−1) at 600 °C displays better Li+ diffusion ability when compared with the pristine LiMn2O4 (8.06 × 10−11 cm2 s−1). Simultaneously, the apparent activation energy further demonstrates that the Li1.05Cu0.05Mn1.90O4 (22.84 kJ/mol) electrode has lower polarization when compared with the LiMn2O4 (34.95 kJ/mol) electrode. These results show that synergistic effect of the Li+ and Cu2+ enhances the cycle reversibility and kinetics properties in cycle of the electrode.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Li, D. Li, D. Song, X. Shi, X. Tang, H. Zhang, L. Zhang, Unravelling the structure and electrochemical performance of Li–Cr–Mn-O cathodes: from spinel to layered. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 8827–8835 (2018)
S.T. Myung, K. Amine, Y.K. Sun, Nanostructured cathode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 283, 219–236 (2015)
B. Chen, L. Ben, H. Yu, Y. Chen, X. Huang, Understanding surface structural stabilization of the high-temperature and high-voltage cycling performance of Al3+ modified LiMn2O4 cathode material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 550–559 (2018)
C.G. Han, C. Zhu, G. Saito, T. Akiyama, Improved electrochemical performance of LiMn2O4 surface-modified by a Mn4+ rich phase for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 209, 225–234 (2016)
Y. Ito, Y. Idemoto, Y. Tsunoda, N. Koura, Relation between crystal structures, electronic structures, and electrode performances of LiMn2−xMxO4 (M = Ni, Zn) as a cathode active material for 4 V secondary Li batteries. J. Power Sources 119–121, 733–737 (2003)
K. Suzuki, Y. Oumi, S. Takami, M. Kubo, A. Miyamoto, M. Kikuchi, Structural properties of LixMn2O4 as investigated by molecular dynamics and density functional theory. J. Appl. Phys. 39, 4318 (2000)
J. Mao, K. Dai, M. Xuan, G. Shao, R. Qiao, W. Yang, V.S. Battaglia, G. Liu, Effect of chromium and niobium doping on the morphology and electrochemical performance of high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 9116–9124 (2016)
R. Thirunakaran, T. Kim, W.S. Yoon, Zinc and aluminium: glutamic acid assisted dual-doped LiMn2O4 spinels via sol–gel method as cathode material for use in lithium rechargeable batteries. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technology 73, 62–71 (2014)
D.L. Fang, J.C. Li, X. Liu, P.F. Huang, T.R. Xu, M.C. Qian, C.H. Zheng, Synthesis of a Co–Ni doped LiMn2O4 spinel cathode material for high-power Li-ion batteries by a sol–gel mediated solid-state route. J. Alloys Compd. 640, 82–89 (2015)
M. Reynaud, P. Barpanda, G. Rousse, J.N. Chotard, B.C. Melot, N. Recham, J.M. Tarascon, Synthesis and crystal chemistry of the NaMSO4F family (M=Mg, Fe Co, Cu, Zn). Solid State Sci. 14, 15–20 (2012)
J. Liu, G. Li, Y. Yu, H. Bai, M. Shao, J. Guo, C. Su, X. Liu, W. Bai, Synthesis and electrochemical performance evaluations of polyhedra spinel LiAlxMn2-xO4 (x≦0.20) cathode materials prepared by a solution combustion technique. J. Alloys Compd. 728, 1315–1328 (2017)
H. Zhao, F. Li, X. Bai, T. Wu, Z. Wang, Y. Li, J. Su, Enhanced cycling stability of LiCuxMn1.95-xSi0.05O4 cathode material obtained by solid-state method. Materials 11, 1302 (2018)
K.R. Murali, T. Saravanan, M. Jayachandran, Synthesis and characterization of copper substituted lithium manganate spinels. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 19, 533–537 (2007)
B. Ebin, S. Gürmen, G. Lindbergh, Electrochemical properties of nanocrystalline LiCuxMn2−xO4 (x=0.2–0.6) particles prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 136, 424–430 (2012)
P. Angelopoulou, F. Paloukis, G. Słowik, G. Wójcik, G. Avgouropoulos, Combustion-synthesized LixMn2O4 based spinel nanorods as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J. Chem. Eng. 311, 191–202 (2017)
J. Hao, H. Bai, J. Liu, F. Yang, Q. Li, C. Su, J. Guo, Synthesis and electrochemical properties of spinel Li(Li0.05Cu0.05Mn1.90)O4 by a flameless combustion method. J Alloys Compd. 668, 200–205 (2016)
N.V. Kosova, E.T. Devyatkina, Synthesis of nanosized materials for lithium-ion batteries by mechanical activation: studies of their structure and properties. Russ. J. Electrochem. 48, 320–329 (2012)
H. Gu, G. Wang, C. Zhu, Y. Hu, X. Zhang, W. Wen, X. Yang, B. Wang, X. Gao, X. Zhan, J. Li, Z.F. Ma, Q. He, Correlating cycle performance improvement and structural alleviation in LiMn2-xMxO4 spinel cathode materials: a systematic study on the effects of metal-ion doping. Electrochim. Acta 298, 806–817 (2019)
H. Zhao, F. Li, X. Liu, C. Cheng, Z. Zhang, Y. Wu, W. Xiong, B. Chen, Effects of equimolar Mg (II) and Si (IV) co-doping on the electrochemical properties of spinel LiMn2−2xMgxSixO4 prepared by citric acid assisted sol–gel method. Electrochim. Acta 151, 263–269 (2015)
X. Ding, H. Zhou, G. Liu, Z. Yin, Y. Jiang, X. Wang, Electrochemical evaluation of LiAl0.05Ni0.05Mn1.9O4 cathode material synthesized via electrospinning method. J. Alloys Compd. 632, 147–151 (2015)
T.F. Yi, Y. Xie, Y.R. Zhu, R.S. Zhu, M.F. Ye, High rate micron-sized niobium-doped LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 as ultra high power positive-electrode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 211, 59–65 (2012)
R.H. Zeng, W.S. Li, L.D. Sheng, Q.M. Huang, L.Z. Zhao, Insertion/removal kinetics of lithium ion in spinel LiCuxMn2-xO4. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 17, 1312–1318 (2007)
X.Y. Feng, C. Shen, H.F. Xiang, H.K. Liu, Y.C. Wu, C.H. Chen, High rate capability of 5 V LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material synthesized via a microwave assist method. J. Alloys Compd. 695, 227–232 (2017)
X.T. Yin, W.D. Zhou, J. Li, P. Lv, Q. Wang, D. Wang, F.Y. Wu, D. Dastan, H. Garmestani, Z. Shi, Ş. Ţălu, Tin dioxide nanoparticles with high sensitivity and selectivity for gas sensors at sub-ppm level of hydrogen gas detection. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 14687–14694 (2019)
A.V. Potapenko, S.A. Kirillov, Enhancing high-rate electrochemical properties of LiMn2O4 in a LiMn2O4/LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 core/shell composite. Electrochim. Acta 258, 9–16 (2017)
D. Dastan, Nanostructured anatase titania thin films prepared by sol-gel dip coating technique. J. At. Mol. Condens. Nano Phys. 2, 109–114 (2015)
D. Dastan, Effect of preparation methods on the properties of titania nanoparticles: solvothermal versus sol–gel. Appl. Phys. A 123(11), 699 (2017)
J. Liu, G. Li, H. Bai, M. Shao, C. Su, J. Guo, X. Liu, W. Bai, Enhanced cycle and rate performances of Li(Li0.05Al0.05Mn1.90)O4 cathode material prepared via a solution combustion method for lithium-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 307, 79–89 (2017)
L. Chen, W. Zhai, L. Chen, D. Li, X. Ma, Q. Ai, X. Xu, G. Hou, L. Zhang, J. Feng, P. Si, L. Ci, Nanostructured LiMn2O4 composite as high-rate cathode for high performance aqueous Li-ion hybrid supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 392, 116–122 (2018)
D. Capsoni, M. Bini, G. Chiodelli, V. Massarotti, C.B. Azzoni, M. Cristina Mozzati, A. Comin, Inhibition of Jahn-Teller cooperative distortion in LiMn2O4 spinel by transition metal ion doping. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 3, 2162–2166 (2001)
S. Chen, Z. Chen, C. Cao, Mesoporous spinel LiMn2O4 cathode material by a soft-templating route. Electrochim. Acta 199, 51–58 (2016)
X. Li, Z. Shao, K. Liu, G. Liu, B. Xu, Synthesis and electrochemical characterizations of LiMn2O4 prepared by high temperature ball milling combustion method with citric acid as fuel. J. Electroanalyt. Chem. 818, 204–209 (2018)
Q. Zhu, S. Zheng, X. Lu, Y. Wan, Q. Chen, J. Yang, L.Z. Zhang, Z. Lu, Improved cycle performance of LiMn2O4 cathode material for aqueous rechargeable lithium battery by LaF3 coating. J. Alloys Compd. 654, 384–391 (2016)
J.L. Wang, Z.H. Li, J. Yang, J.J. Tang, J.J. Yu, W.B. Nie, G.T. Lei, Q.Z. Xiao, Effect of Al-doping on the electrochemical properties of a three-dimensionally porous lithium manganese oxide for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 75, 115–122 (2012)
S.L. Chou, J.Z. Wang, J.Z. Sun, D. Wexler, F.M. Liu, H.K. Dou, S.X. Dou, High capacity, safety, and enhanced cyclability of lithium metal battery using a V2O5 nanomaterial cathode and room temperature ionic liquid electrolyte. Chem. Mater. 20, 7044–7051 (2008)
D. Dastan, S.W. Gosavi, N.B. Chaure, Studies on electrical properties of hybrid polymeric gate dielectrics for field effect transistors. Macromol. Symp. 347, 81–86 (2015)
S.L. Chou, J.Z. Wang, H.K. Liu, S.X. Dou, Rapid synthesis of Li4Ti5O12 microspheres as anode materials and its binder effect for lithium-ion battery. J. Phys. Chem. 115, 16220–16227 (2011)
H. Ma, S. Zhang, W. Ji, Z. Tao, J. Chen, α-CuV2O6 nanowires: hydrothermal synthesis and primary lithium battery application. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 5361–5367 (2008)
X. Zhu, J. Yang, D. Dastan, H. Garmestani, R. Fan, Z. Shi, Fabrication of core-shell structured Ni@BaTiO3 scaffolds for polymer composites with ultrahigh dielectric constant and low loss. Composites Part A Appl Sci. Manuf. 125, 105521 (2019)
X.T. Yin, W.D. Zhou, J. Li, Q. Wang, F.Y. Wu, D. Dastan, D. Wang, H. Garmestani, X.M. Wang, Ş. Ţălu, A highly sensitivity and selectivity Pt-SnO2 nanoparticles for sensing applications at extremely low level hydrogen gas detection. J. Alloys Compd. 805, 229–236 (2019)
Acknowledgements
Linqiao Liang and Mingwu Xiang contributed equally to this work. This work was financially supported by the project for the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51972282, 51462036, U1602273).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, L., Xiang, M., Bai, W. et al. Electrochemical properties and kinetics of Li–Cu co-doping LiMn2O4 cathode materials. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 286–297 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02502-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02502-7