Abstract
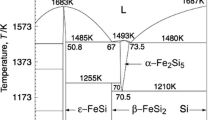
We investigated the influence of Cu addition to Co-doped β-FeSi2/Si thermoelectric material. We expected the addition of Cu to accelerate the eutectoid decomposition of α-Fe2Si5 phase resulting in a finer distribution of Si secondary phase. We added 1 mass% and 2 mass% of Cu followed by the annealing process in various conditions. We obtained a significant decrease of Si size, reaching less than 100 nm for composites with 2 mass% Cu, annealed at 650 °C-2 h. Within the same amount of Cu, Si size was clearly increased after annealed at 800 °C-4 h, suggesting that the phase transition is accelerated with the existence of Cu. The thermal conductivity value was greatly reduced for sample with 2 mass% Cu, compared with the experimental value of single β-FeSi2 and calculated value from the rule of mixture. This proves that the fine distribution of Si help suppress thermal conductivity despite the high value of the Si phase itself. However, the excessive amount of Cu (2 mass%) degenerated the electrical properties of β-FeSi2/Si. Nonetheless, the sample with 1 mass% Cu annealed at 800 °C for 4 h showed the highest ZT value of 0.1, indicating that it is essential to keep the balance of Cu amount and annealing conditions towards TE performance enhancement.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Zhang, L.-D. Zhao, Thermoelectric materials: energy conversion between heat and electricity. J. Mater. 1, 92–105 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2015.01.001
B. Ismail, W. Ahmed, Thermoelectric power generation using waste-heat energy as an alternative green technology. Recent Patents Electr. Eng. 2, 27–39 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2174/1874476110902010027
D.M. Rowe, CRC Handbook of Thermoelectrics (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1995), pp. 277–287
H. Anno, in Introduction to Thermoelectric Materials (Japanese). in Thermoelectr. Mater., (2005), p. 8
J.P. Fleurial, in International Union of Materials Research Society. Des. Discov. Highly Effic. Thermoelectr. Mater., (1998) pp. 2–3
J.X. Jiang, T. Sasakawa, K. Matsugi, G. Sasaki, O. Yanagisawa, Thermoelectric properties of β-FeSi2 with Si dispersoids formed by decomposition of α-Fe2Si5 based alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 391, 115–122 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.07.070
S. Kiatgamolchai, S. Nilpairach, J. Wanichsampan, A. Thueploy, The effects of elements with different melting points on ε-FeSi size in FeSi2 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 666, 237–242 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.01.068
T. Kojima, K. Masumoto, M.A. Okamoto, I. Nishida, Formation of β-FeSi2 from the sintered eutectic alloy FeSi–Fe2Si5 doped with cobalt. J. Less Common Met. 159, 299–305 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5088(90)90157-F
S. Kiatgamolchai, J. Parinyataramas, S. Nilpairach, A. Thueploy, J. Wanichsampan, M. Gao, Thermoelectric properties of β-FeSi2 prepared by the mechanical alloying technique and pressureless sintering. J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metall. 2, 119–127 (2006)
U. Ail, S. Gorsse, S. Perumal, M. Prakasam, A. Umarji, S. Vivès, P. Bellanger, R. Decourt, Thermal conductivity of β-FeSi2/Si endogenous composites formed by the eutectoid decomposition of α-Fe2Si5. J. Mater. Sci. 50, 6713–6718 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9225-4
S.K. Bux, R.G. Blair, P.K. Gogna, H. Lee, G. Chen, M.S. Dresselhaus, R.B. Kaner, J.-P. Fleurial, Nanostructured bulk silicon as an effective thermoelectric material. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 2445–2452 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200900250
N. Uchida, T. Kanayama, Japanese Patent No. 2010-207987, 2010–207987, n.d
F.L.B.M. Redzuan, I. Mikio, T. Masatoshi, Synthesis of Co-doped β-FeSi2/Si composites through eutectoid decomposition and its thermoelectric properties. J. Mater. Sci. 53, 7683–7690 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2066-1
I. Yamauchi, A. Suganuma, T. Okamoto, I. Ohnaka, Effect of copper addition on the -phase formation rate in FeSi2 thermoelectric materials. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 4603–4611 (1997)
M. Ito, H. Nagai, D. Harimoto, S. Katsuyama, K. Majima, Effects of Cu addition on the thermoelectric properties of hot-pressed??-FeSi2 with SiC dispersion. J. Alloys Compd. 322, 226–232 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(01)01171-9
I. Yamauchi, S. Ueyama, I. Ohnaka, fl-FeSi2 Phase formation from a unidirectionally solidified rod-type eutectic structure composed of both e and E phases. Mater. Sci. Eng. 208, 108–115 (1996)
M. Li, S.J. Zinkle, Physical and mechanical properties of copper and copper alloys. Compr. Nucl. Mater. 4, 667–690 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-056033-5.00122-1
M.H. Lee, J. Rhyee, Thermoelectric properties of p-type PbTe/Ag2Te bulk composites by extrinsic phase mixing Thermoelectric properties of p -type PbTe/Ag 2 Te bulk composites by extrinsic phase mixing. AIV Adv. 5, 127223 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4938565
V.C. Srivastava, S.N. Ojha, Microstructure and electrical conductivity of Al-SiC p composites produced by spray forming process. Bull. Mater. Sci. 28(2), 125–130 (2005)
H. Zou, D.M. Rowe, G. Min, Growth of p- and n-type bismuth telluride thin films by co-evaporation. J. Cryst. Growth 222, 82–87 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(00)00922-2
X.W. Wang, H. Lee, Y.C. Lan, G.H. Zhu, G. Joshi, D.Z. Wang, J. Yang, A.J. Muto, M.Y. Tang, J. Klatsky, S. Song, M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, Z.F. Ren, Enhanced thermoelectric figure of merit in nanostructured n -type silicon germanium bulk alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 1–4 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3027060
Y. Noda, H. Kon, Y. Furukawa, N. Otsuka, I.A. Nishida, K. Masumoto, Preparation and thermoelectric properties of Mg2Si1-xGex (x = 0.0 ~ 0.4) Solid Solution Semiconductors. Mater. Trans. 33, 845 (1992). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans1989.33.845
M. Thesberg, H. Kosina, N. Neophytou, On the Lorenz number of multiband materials. Phys. Rev. B 95, 1–14 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.95.125206
H. Kim, Z.M. Gibbs, Y. Tang, H. Wang, G.J. Snyder, H. Kim, Z.M. Gibbs, Y. Tang, H. Wang, G.J. Snyder, Characterization of Lorenz number with Seebeck coefficient measurement. APL Mater. 041506, 1–6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4908244
M. Otsuka, R. Homma, Y. Hasegawa, Estimation of phonon and carrier thermal conductivities for bulk thermoelectric materials using transport properties. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 2752–2764 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4955-x
Y. Xiao, C. Chang, X. Zhang, Y. Pei, F. Li, B. Yuan, Thermoelectric transport properties of Ag m Pb 100 Bi m Se 100 + 2 m system. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 2712–2717 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-4081-1
P. Golinelli, L. Varani, L. Reggiani, Generalization of thermal conductivity and lorenz number to hot-carrier conditions in nondegenerate semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 1115–1118 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.1115
E. Arushanov, K.G. Lisunov, Transport properties of β-FeSi2. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 54, 2 (2015). https://doi.org/10.7567/jjap.54.07ja02
M. Ito, H. Nagai, E. Oda, S. Katsuyama, K. Majima, Effects of P doping on the thermoelectric properties of β-FeSi2. J. Appl. Phys. 91, 2138–2142 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1436302
M. Ito, K. Takemoto, Synthesis of thermoelectric Fe0.98Co0.02Si2 with fine Ag dispersion by mechanical milling with AgO powder. Mater. Trans. 49, 1714–1719 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.e-mra2008808
J. Jiang, K. Matsugi, G. Sasaki, O. Yanagisawa, Resistivity study of eutectoid decomposition kinetics of α-Fe2Si5 alloy. Mater. Trans. 46, 720–725 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.46.720
Funding
This research did not receive any specific Grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Redzuan, F.L.B.M., Ito, M. & Takeda, M. Effects of Cu addition to n-type β-FeSi2/Si composite on the Si precipitation and its thermoelectric properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 12234–12243 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01582-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01582-9