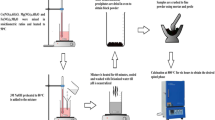
Abstract
Spinel ferrites (SFs) show high potential in different aspects of modern technology. Particularly, copper ferrite represents a promising electrode material for supercapacitors and lithium based batteries. This paper is devoted to synthesizing and characterizing nanostructured copper substituted cobalt ferrites using an eco-friendly sol–gel method. Energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) and FT-IR analyses confirm the chemical composition and the successful formation of the cubic phase of CuFe2O4, respectively. XRD analyses based on Williamson–Hall (W–H) method indicate that the average crystallite size drops from 25.1 to 12.1 nm dependent on the Cu2+ content in the samples. Further, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) reveals that the CoFe2O4 (CFO) has a honeycomb structure, which gradually disappears with the soaring of Cu2+ content in the samples and converts to a porous sponge-like shape structure. The investigated copper substituted CFO holds a high specific surface area equals to 102.5139 m2 g−1 which satisfies the contaminant adsorption applications. The measured DC resistivity (ρDC = 108 Ω m) is high enough to meet the requirements of transformer cores applications. Due to the difference in the magnetic moment between Cu2+ and Co2+ cations, the coercivity of the CFO significantly depends on the Cu2+ content; it has declined by more than 50% for the system Co0.25Cu0.75Fe2O4 in comparison to the pure CFO (Hc = 1617.30 Gauss).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.V. Humbe, J.S. Kounsalye, M.V. Shisode, K. Jadhav, Rietveld refinement, morphology and superparamagnetism of nanocrystalline Ni0. 70—xCuxZn0. 30Fe2O4 spinel ferrite. Ceram. Int. 44(5), 5466–5472 (2018)
T.R. Tatarchuk, M. Bououdina, N.D. Paliychuk, I.P. Yaremiy, V.V. Moklyak, Structural characterization and antistructure modeling of cobalt-substituted zinc ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 694, 777–791 (2017)
J. Patil, D. Nadargi, I.S. Mulla, S. Suryavanshi, Spinel MgFe 2 O 4 thick films: a colloidal approach for developing gas sensors. Mater. Lett. 213, 27–30 (2018)
S. Goh, C.H. Chia, S. Zakaria, M. Yusoff, C. Haw, S. Ahmadi, N. Huang, H. Lim, Hydrothermal preparation of high saturation magnetization and coercivity cobalt ferrite nanocrystals without subsequent calcination. Mater. Chem. Phys. 120(1), 31–35 (2010)
M. Sedlacik, V. Pavlinek, P. Peer, P. Filip, Tailoring the magnetic properties and magnetorheological behavior of spinel nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite by varying annealing temperature. Dalton Trans. 43(18), 6919–6924 (2014)
N.V. Long, Y. Yang, T. Teranishi, C.M. Thi, Y. Cao, M. Nogami, Synthesis and magnetism of hierarchical iron oxide particles. Mater. Des. 86, 797–808 (2015)
N.V. Long, Y. Yang, T. Teranishi, C.M. Thi, Y. Cao, M. Nogami, Biomedical applications of advanced multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 15(12), 10091–10107 (2015)
K.-H. Hellwege, L. Bornstein, Numerical Data and Functional Relationship in Science and Technology, Elastic, Piezoelectric, Pyroelectric, Piezooptic, Electrooptic Constants, and Nonlinear Dielectric Susceptibilities of Crystal (Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 1979)
I. Campbell, A. Fert, Ferromagnetic materials (EP Wolfarth, Amsterdam, 1982)
K. Khalaf, A. Al-Rawas, H. Widatallah, K. Al-Rashdi, A. Sellai, A. Gismelseed, M. Hashim, S. Jameel, M. Al-Ruqeishi, K. Al-Riyami, Influence of Zn2+ ions on the structural and electrical properties of Mg1—xZnxFeCrO4 spinels. J. Alloy. Compd. 657, 733–747 (2016)
W. Ponhan, S. Maensiri, Fabrication and magnetic properties of electrospun copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanofibers. Solid State Sci. 11(2), 479–484 (2009)
V. Lakhani, B. Zhao, L. Wang, U. Trivedi, K. Modi, Negative magnetization, magnetic anisotropy and magnetic ordering studies on Al3+-substituted copper ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 509(14), 4861–4867 (2011)
N. Moumen, M. Pileni, New syntheses of cobalt ferrite particles in the range 2–5 nm: comparison of the magnetic properties of the nanosized particles in dispersed fluid or in powder form. Chem. Mater. 8(5), 1128–1134 (1996)
C. Pham-Huu, N. Keller, C. Estournes, G. Ehret, J. Greneche, M. Ledoux, Microstructural investigation and magnetic properties of CoFe 2 O 4 nanowires synthesized inside carbon nanotubes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 5(17), 3716–3723 (2003)
H. Deng, X. Li, Q. Peng, X. Wang, J. Chen, Y. Li, Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew. Chem. 117(18), 2842–2845 (2005)
M. Sajjia, M. Oubaha, M. Hasanuzzaman, A.G. Olabi, Developments of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by the sol–gel process. Ceram. Int. 40(1), 1147–1154 (2014)
A. Samavati, A. Ismail, Antibacterial properties of copper-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Particuology 30, 158–163 (2017)
B.C. Sekhar, G. Rao, O. Caltun, B.D. Lakshmi, B.P. Rao, P.S. Rao, Magnetic and magnetostrictive properties of Cu substituted Co-ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 398, 59–63 (2016)
M. Orojloo, P. Zolgharnein, M. Solimannejad, S. Amani, Synthesis and characterization of cobalt (II), nickel (II), copper (II) and zinc (II) complexes derived from two Schiff base ligands: Spectroscopic, thermal, magnetic moment, electrochemical and antimicrobial studies. Inorg. Chim. Acta 467, 227–237 (2017)
M.A. Maksoud, G.S. El-Sayyad, A. Ashour, A.I. El-Batal, M.S. Abd-Elmonem, H.A. Hendawy, E. Abdel-Khalek, S. Labib, E. Abdeltwab, M. El-Okr, Synthesis and characterization of metals-substituted cobalt ferrite [Co (1 – x)] MxFe2O4;(M = Zn, Cu, Mn; x = 0, 05)] nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents and sensors for Anagrelide determination in biological samples. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 92, 644–656 (2018)
A. Ashour, A.I. El-Batal, M.A. Maksoud, G.S. El-Sayyad, S. Labib, E. Abdeltwab, M. El-Okr, Antimicrobial activity of metal-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel technique. Particuology 40, 141–151 (2018)
A.A. Reheem, A. Atta, M.A. Maksoud, Low energy ion beam induced changes in structural and thermal properties of polycarbonate. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 127, 269–275 (2016)
P. Belavi, G. Chavan, L. Naik, R. Somashekar, R. Kotnala, Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of cadmium substituted nickel–copper ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 132(1), 138–144 (2012)
K. Ramakrishna, C. Srinivas, S. Meena, B. Tirupanyam, P. Bhatt, S. Yusuf, C. Prajapat, D. Potukuchi, D. Sastry, Investigation of cation distribution and magnetocrystalline anisotropy of Ni x Cu 0.1 Zn 0.9 – x Fe 2 O 4 nanoferrites: Role of constant mole percent of Cu 2 + dopant in place of Zn 2+. Ceram. Int. 43(11), 7984–7991 (2017)
M.K. Abbas, M.A. Khan, F. Mushtaq, M.F. Warsi, M. Sher, I. Shakir, M.F.A. Aboud, Impact of Dy on structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Li-Tb-nanoferrites synthesized by micro-emulsion method. Ceram. Int. 43(7), 5524–5533 (2017)
A.V. Humbe, A.C. Nawle, A. Shinde, K. Jadhav, Impact of Jahn Teller ion on magnetic and semiconducting behaviour of Ni-Zn spinel ferrite synthesized by nitrate-citrate route. J. Alloy. Compd. 691, 343–354 (2017)
M. Hashim, S.E. Shirsath, S. Kumar, R. Kumar, A.S. Roy, J. Shah, R. Kotnala, Preparation and characterization chemistry of nano-crystalline Ni–Cu–Zn ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 549, 348–357 (2013)
V.J. Angadi, B. Rudraswamy, K. Sadhana, S.R. Murthy, K. Praveena, Effect of Sm3+–Gd3+ on structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrites synthesized via combustion route. J. Alloy. Compd. 656, 5–12 (2016)
M. Amer, T. Meaz, A. Hashhash, S. Attalah, A. Ghoneim, Structural properties and magnetic interactions in Sr-doped Mg–Mn nanoparticle ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 162, 442–451 (2015)
E.R. Kumar, P.S.P. Reddy, G.S. Devi, S. Sathiyaraj, Structural, dielectric and gas sensing behavior of Mn substituted spinel MFe2O4 (M = Zn, Cu, Ni, and Co) ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 398, 281–288 (2016)
M.T. Rahman, M. Vargas, C. Ramana, Structural characteristics, electrical conduction and dielectric properties of gadolinium substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 617, 547–562 (2014)
A. Ditta, M.A. Khan, M. Junaid, R.A. Khalil, M.F. Warsi, Structural, magnetic and spectral properties of Gd and Dy co-doped dielectrically modified Co-Ni (Ni0. 4Co0. 6Fe2O4) ferrites. Phys. B 507, 27–34 (2017)
A. Ramakrishna, N. Murali, S. Margarette, T.W. Mammo, N.K. Joythi, B. Sailaja, C.C.S. Kumari, K. Samatha, V. Veeraiah, Studies on structural, magnetic, and DC electrical resistivity properties of Co0. 5M0. 37Cu0. 13Fe2O4 (M = Ni, Zn and Mg) ferrite nanoparticle systems, Adv. Powder Technol. 29, 2601–2607 (2018)
M. Amer, A. Matsuda, G. Kawamura, R. El-Shater, T. Meaz, F. Fakhry, Characterization and structural and magnetic studies of as-synthesized Fe2 + CrxFe (2 – x) O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 439, 373–383 (2017)
M. Amer, T. Meaz, A. Mostafa, H. El-Ghazally, Structural and physical properties of the nano-crystalline Al-substituted Cr–Cu ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 343, 286–292 (2013)
R.H. Kadam, S.T. Alone, M.L. Mane, A.R. Biradar, S.E. Shirsath, Phase evaluation of Li + substituted CoFe2O4 nanoparticles, their characterizations and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 355, 70–75 (2014)
C.C. Naik, S. Gaonkar, I. Furtado, A. Salker, Effect of Cu 2 + substitution on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of cobalt ferrite with its enhanced antimicrobial property. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29(17), 14746–14761 (2018)
S. Singhal, J. Singh, S. Barthwal, K. Chandra, Preparation and characterization of nanosize nickel-substituted cobalt ferrites (Co 1 – xNixFe 2 O 4). J. Solid State Chem. 178(10), 3183–3189 (2005)
J. Balavijayalakshmi, N. Suriyanarayanan, R. Jayapraksah, Influence of copper on the magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nano particles. Mater. Lett. 81, 52–54 (2012)
M. Gabal, Y. Al Angari, M. Kadi, Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni1 – xCuxFe2O4 prepared through oxalates precursors. Polyhedron 30(6), 1185–1190 (2011)
K.R. Babu, K.R. Rao, B.R. Babu, Cu2+-modified physical properties of Cobalt-Nickel ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 434, 118–125 (2017)
K.V. Babu, G.S. Kumar, K. Jalaiah, P.T. Shibeshi, Effects of copper substitution on the microstructural, electrical and magnetic properties of Ni0. 7Co0. 3-xCuxFe2O4 ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 118, 172–185 (2018)
R. Devan, Y. Kolekar, B. Chougule, Effect of cobalt substitution on the properties of nickel–copper ferrite. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 18(43), 9809 (2006)
M. Kurian, A. Appukkuttan, A.K. Paul, D.S. Nair, Influence of synthesis conditions on the surface properties of cobalt copper nanoferrites. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 54(2), 199–204 (2018)
M.N. Akhtar, A. Rahman, A. Sulong, M.A. Khan, Structural, spectral, dielectric and magnetic properties of Ni0. 5 MgxZn0. 5-xFe2O4 nanosized ferrites for microwave absorption and high frequency applications. Ceram. Int. 43(5), 4357–4365 (2017)
D. Jnaneshwara, D. Avadhani, B.D. Prasad, H. Nagabhushana, B. Nagabhushana, S. Sharma, S. Prashantha, C. Shivakumara, Role of Cu2 + ions substitution in magnetic and conductivity behavior of nano-CoFe2O4. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 132, 256–262 (2014)
K. Ramakrishna, C. Srinivas, S. Meena, B. Tirupanyam, P. Bhatt, S. Yusuf, C. Prajapat, D. Potukuchi, D. Sastry, Investigation of cation distribution and magnetocrystalline anisotropy of NixCu0. 1Zn0. 9 – xFe2O4 nanoferrites: Role of constant mole percent of Cu2 + dopant in place of Zn2+. Ceram. Int. 43(11), 7984–7991 (2017)
K.H. Maria, S. Choudhury, M.A. Hakim, Structural phase transformation and hysteresis behavior of Cu-Zn ferrites. Int. Nano Lett. 3(1), 42 (2013)
G. Mustafa, M. Islam, W. Zhang, Y. Jamil, A.W. Anwar, M. Hussain, M. Ahmad, Investigation of structural and magnetic properties of Ce 3+-substituted nanosized Co–Cr ferrites for a variety of applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 618, 428–436 (2015)
M. Dar, D. Varshney, Effect of d-block element Co2 + substitution on structural, Mössbauer and dielectric properties of spinel copper ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 436, 101–112 (2017)
Q. Wei, F. Xiong, S. Tan, L. Huang, E.H. Lan, B. Dunn, L. Mai, Porous one-dimensional nanomaterials: design, fabrication and applications in electrochemical energy storage. Adv. Mater. 29(20), 1602300 (2017)
F. Dehghani, S. Hashemian, A. Shibani, Effect of calcination temperature for capability of MFe2O4 (M = Co, Ni and Zn) ferrite spinel for adsorption of bromophenol red. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 48, 36–42 (2017)
K. Ahalya, N. Suriyanarayanan, V. Ranjithkumar, Effect of cobalt substitution on structural and magnetic properties and chromium adsorption of manganese ferrite nano particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 372, 208–213 (2014)
T. Tatarchuk, N. Paliychuk, M. Bououdina, B. Al-Najar, M. Pacia, W. Macyk, A. Shyichuk, Effect of cobalt substitution on structural, elastic, magnetic and optical properties of zinc ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 731, 1256–1266 (2018)
S. Patange, S.E. Shirsath, K. Lohar, S. Algude, S. Kamble, N. Kulkarni, D. Mane, K. Jadhav, Infrared spectral and elastic moduli study of NiFe 2 – x Cr x O 4 nanocrystalline ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 325, 107–111 (2013)
M. Amer, Structural and magnetic studies of the Co 1 + x Ti x Fe 2 (1 – x) O 4 ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 771–778 (2017)
E. El-Ghazzawy, M. Amer, Structural, elastic and magnetic studies of the as-synthesized Co 1 – x Sr x Fe 2 O 4 nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 690, 293–303 (2017)
W. Wooster, Physical properties and atomic arrangements in crystals. Rep. Prog. Phys. 16(1), 62 (1953)
K. Modi, M. Rangolia, M. Chhantbar, H. Joshi, Study of infrared spectroscopy and elastic properties of fine and coarse grained nickel–cadmium ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. 41(22), 7308–7318 (2006)
V. Patil, S.E. Shirsath, S. More, S. Shukla, K. Jadhav, Effect of zinc substitution on structural and elastic properties of cobalt ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 488(1), 199–203 (2009)
M. Amer, A. Matsuda, G. Kawamura, R. El-Shater, T. Meaz, F. Fakhry, Characterization and structural and magnetic studies of as-synthesized Fe 2 + CrxFe (2 – x) O 4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 439, 373–383 (2017)
R.A. Pawar, S.M. Patange, Q.Y. Tamboli, V. Ramanathan, S.E. Shirsath, Spectroscopic, elastic and dielectric properties of Ho3 + substituted Co-Zn ferrites synthesized by sol-gel method. Ceram. Int. 42(14), 16096–16102 (2016)
M.A. Maksoud, G.S. El-Sayyad, A. Ashour, A.I. El-Batal, M.A. Elsayed, M. Gobara, A.M. El-Khawaga, E. Abdel-Khalek, M. El-Okr, Antibacterial, antibiofilm, and photocatalytic activities of metals-substituted spinel cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Microbial pathogenesis 127, 144–158 (2019)
S. Algude, S. Patange, S.E. Shirsath, D. Mane, K. Jadhav, Elastic behaviour of Cr 3 + substituted Co–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 350, 39–41 (2014)
S.E. Shirsath, S. Patange, R. Kadam, M. Mane, K. Jadhav, Structure refinement, cation site location, spectral and elastic properties of Zn 2 + substituted NiFe 2 O 4. J. Mol. Struct. 1024, 77–83 (2012)
R. Pawar, S. Desai, S. Patange, S. Jadhav, K. Jadhav, Inter-atomic bonding and dielectric polarization in Gd 3 + incorporated Co-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Phys. B 510, 74–79 (2017)
N. Abu-Elsaad, Elastic properties of germanium substituted lithium ferrite. J. Mol. Struct. 1075, 546–550 (2014)
I. Ahmad, S.M. Shah, M.N. Ashiq, F. Nawaz, A. Shah, M. Siddiq, I. Fahim, S. Khan, Fabrication of Nd3 + and Mn2 + ions co-doped spinal strontium nanoferrites for high frequency device applications. J. Electron. Mater. 45(10), 4979–4988 (2016)
T.W. Mammo, N. Murali, Y.M. Sileshi, T. Arunamani, Studies of structural, morphological, electrical, and magnetic properties of Mg-substituted Co-ferrite materials synthesized using sol-gel autocombustion method. Phys. B 523, 24–30 (2017)
A. Mostafa, E. Abdel-Khalek, W. Daoush, S. Moustfa, Study of some co-precipitated manganite perovskite samples-doped iron. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320(24), 3356–3360 (2008)
C. Venkataraju, G. Sathishkumar, K. Sivakumar, Effect of nickel on the electrical properties of nanostructured MnZn ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 498(2), 203–206 (2010)
L. Van Uitert, Dc resistivity in the nickel and nickel zinc ferrite system. J. Chem. Phys. 23(10), 1883–1887 (1955)
K. Ramarao, B.R. Babu, B.K. Babu, V. Veeraiah, S. Ramarao, K. Rajasekhar, A.V. Rao, Composition dependence of structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Co substituted magnesium ferrite. Phys. B 528, 18–23 (2018)
M. El-Saadawy, Diffusion coefficient of vacancies and jump length of electrons in Co1 – xZnxFe2O4 ferrites. J. Adv. Ceram. 1(2), 144–149 (2012)
O. Hemeda, M. El-Saadawy, Effect of gamma irradiation on the structural properties and diffusion coefficient in Co–Zn ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 256(1–3), 63–68 (2003)
A. Tawfik, S. Olofa, The diffusion coefficient of vacancies and jump length of electrons in zinc doped manganese ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 174(1–2), 133–136 (1997)
M.T. Farid, I. Ahmad, M. Kanwal, G. Murtaza, M. Hussain, S.A. Khan, I. Ali, Synthesis, electrical and magnetic properties of Pr-substituted mn ferrites for high-frequency applications. J. Electron. Mater. 46(3), 1826–1835 (2017)
M.T. Farid, I. Ahmad, M. Kanwal, I. Ali, Effect of praseodymium ions on manganese based spinel ferrites, Chin. J. Phys. 55, 813–824 (2017)
P.P. Naik, R. Tangsali, Enduring effect of rare earth (Nd3+) doping and γ-radiation on electrical properties of nanoparticle manganese zinc ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 723, 266–275 (2017)
M. Raghasudha, D. Ravinder, P. Veerasomaiah, Electrical resistivity studies of Cr doped Mg nano-ferrites. Mater. Discov. 2, 50–54 (2015)
M. El-Saadawy, Diffusion coefficient of vacancies and jump length of electrons in Co 1 – x Zn x Fe 2 O 4 ferrites. J. Adv. Ceram. 1(2), 144–149 (2012)
X. Guoxi, X. Yuebin, Effects on magnetic properties of different metal ions substitution cobalt ferrites synthesis by sol–gel auto-combustion route using used batteries. Mater. Lett. 164, 444–448 (2016)
H. Bayrakdar, O. Yalçın, S. Vural, K. Esmer, Effect of different doping on the structural, morphological and magnetic properties for Cu doped nanoscale spinel type ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 343, 86–91 (2013)
R. Sharma, P. Thakur, M. Kumar, N. Thakur, N. Negi, P. Sharma, V. Sharma, Improvement in magnetic behaviour of cobalt doped magnesium zinc nano-ferrites via co-precipitation route. J. Alloy. Compd. 684, 569–581 (2016)
K.M. Batoo, D. Salah, G. Kumar, A. Kumar, M. Singh, M.A. El-sadek, F.A. Mir, A. Imran, D.A. Jameel, Hyperfine interaction and tuning of magnetic anisotropy of Cu doped CoFe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 411, 91–97 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Materials Science Unit, Radiation Physics Department, National Center for Radiation Research and Technology, Egypt, for financing and supporting this study under the project Synthesizing and Characterizations of Nanostructured Magnetic Materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maksoud, M.I.A.A., El-ghandour, A., El-Sayyad, G.S. et al. Tunable structures of copper substituted cobalt nanoferrites with prospective electrical and magnetic applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 4908–4919 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00785-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00785-4