Abstract
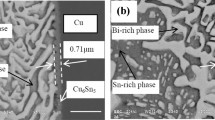
A solid-state reaction between the Sn–Ag–Cu solder and Ni metallization resulted in the formation of interfacial bilayer Cu6Sn5-based intermetallic compounds (IMCs) in a solder joint incorporating Au/Pd metallization. The layer near the Ni metallization was identified as (Cu,Ni,Au)6Sn5 containing 20.3 at.% of Ni and 1.7 at.% of Au, and the layer near the solder matrix was identified as (Cu,Au,Ni,Pd)6Sn5 containing 5.7 at.% of Au, 1.2 at.% of Ni, and 1.0 at.% of Pd. The electron diffraction analysis with high resolution transmission electron microscopy further characterized the interfacial bilayer IMCs as having the same hexagonal crystal structure with different crystal orientations. The kinetics study revealed that the (Cu,Ni,Au)6Sn5 in the interfacial bilayer reaction products was formed during the initial reflow process, while the (Cu,Au,Ni,Pd)6Sn5 layer was formed during subsequent solid-state aging. Predominant growth of the (Cu,Au,Ni,Pd)6Sn5 layer was observed during solid-state aging. In contrast, the growth of the initially formed (Cu,Ni,Au)6Sn5 layer was suppressed. The growth of the (Cu,Au,Ni,Pd)6Sn5 layer was governed by the dissolution of the (Au,Pd)Sn4 IMC that occurred during solid-state aging. The complete dissolution of (Au,Pd)Sn4 resulted in a reactant-limited chemical reaction from the conversion of (Au,Pd)Sn4 to (Cu,Au,Ni,Pd)6Sn5. The development of the interfacial bilayer IMCs in the solder joint incorporating Au/Pd metallization suppressed excessive IMC growth and unfavorable phase transformation during long-term solid-state aging. The detailed mechanism of the formation of the interfacial bilayer Cu6Sn5-based IMCs was investigated in this paper.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.N. Tu, Microelectron. Reliab. 51, 517 (2011)
H. Huebner, S. Penka, B. Barchmann, M. Eigner, W. Gruber, M. Nobis, S. Janka, G. Kristen, M. Schneegans, Microelectron. Eng. 83, 2155 (2006)
C.L. Liang, K.L. Lin, J.W. Peng, J. Electron. Mater. 45, 51 (2016)
C.W. Chen, T.C. Chiu, Y.T. Chiu, C.W. Lee, K.L. Lin, Intermetallics 85, 117 (2017)
Y.C. Chan, D. Yang, Prog. Mater. Sci. 55, 428 (2010)
K.N. Tu, A.M. Gusak, M. Li, J. Appl. Phys. 93, 1335 (2003)
Y. Tang, S.M. Luo, W.F. Huang, Y.C. Pan, G.Y. Li, J. Alloy. Compd. 719, 365 (2017)
Y. Tang, G.Y. Li, Y.C. Pan, J. Alloy. Compd. 554, 195 (2013)
Y. Tang, G.Y. Li, D.Q. Chen, Y.C. Pan, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 981 (2014)
Y. Tang, S.M. Luo, K.Q. Wang, G.Y. Li, J. Alloy. Compd. 684, 299 (2016)
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, J.K. Kivilahti, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 49, 1 (2005)
W.T. Chen, C.E. Ho, C.R. Kao, J. Mater. Res. 17, 263 (2002)
C.E. Ho, R.Y. Tsai, Y.L. Lin, C.R. Kao, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 584 (2002)
T.L. Shao, T.S. Chen, Y.M. Huang, C. Chen, J. Mater. Res. 19, 3654 (2004)
C.E. Ho, Y.W. Lin, S.C. Yang, C.R. Kao, D.S. Jiang, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1017 (2006)
J.W. Yoon, B.I. Noh, S.B. Jung, J. Electron. Mater. 40, 1950 (2011)
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, M. Paulasto-Kröckel, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 68, 1 (2010)
S.W. Fu, C.Y. Yu, T.K. Lee, K.C. Liu, J.G. Duh, Mater. Lett. 80, 103 (2012)
C.Y. Yu, T.K. Lee, M. Tsai, T.C. Liu, J.G. Duh, J. Electron. Mater. 39, 2544 (2010)
I.T. Wang, J.G. Duh, C.Y. Cheng, J. Wang, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 177, 278 (2012)
C.E. Ho, W.H. Wu, L.H. Hsu, C.S. Lin, J. Electron. Mater. 41, 11 (2012)
C.L. Liang, K.L. Lin, P.J. Cheng, Surf. Coat. Technol. 319, 55 (2017)
C.L. Liang, K.L. Lin, P.J. Cheng, J. Mater. Sci. 52, 11659 (2017)
H.K. Kim, K.N. Tu, P.A. Totta, Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 2204 (1996)
A.M. Minor, J.W. Morris Jr., Metall. Mater. Trans. A 31A, 798 (2000)
C.E. Ho, R. Zheng, G.L. Luo, A.H. Lin, C.R. Kao, J. Electron. Mater. 29, 1175 (2000)
J.H. Lee, J.H. Park, D.H. Shin, Y.H. Lee, Y.S. Kim, J. Electron. Mater. 30, 1138 (2001)
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, T. Mattila, J.K. Kivilahti, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 103 (2005)
M.O. Alam, Y.C. Chan, Chem. Mater. 17, 927 (2005)
C.E. Ho, L.C. Shiau, C.R. Kao, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 1264 (2002)
K. Nogita, T. Nishimura, Scr. Mater. 59, 191 (2008)
G. Zeng, S.D. McDonald, Q.F. Gu, S. Suenaga, Y. Zhang, J.H. Chen, K. Nogita, Intermetallics 43, 85 (2013)
U. Schwingenschlögl, C.D. Paola, K. Nogita, C.M. Gourlay, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 061908 (2010)
K. Nogita, C.M. Gourlay, S.D. McDonald, Y.Q. Wu, J. Read, Q.F. Gu, Scr. Mater. 65, 922 (2011)
Y.D. Jeon, S. Nieland, A. Ostmann, H. Reichl, K.W. Paik, J. Electron. Mater. 32, 548 (2003)
Y.D. Jeon, K.W. Paik, A. Ostmann, H. Reichl, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 80 (2005)
L.Y. Hsiao, G.Y. Jang, K.J. Wang, J.G. Duh, J. Electron. Mater. 36, 1476 (2007)
C. Yu, J.Y. Liu, H. Lu, P.L. Li, J.M. Chen, Intermetallics 15, 1471 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China under MOST104-2221-E-006-028-MY3. We also wish to express our deep appreciation to the ASE group, Kaohsiung for supplying the specimens and for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, CL., Lin, KL. & Cheng, PJ. The interfacial bilayer Cu6Sn5 formed in a Sn–Ag–Cu flip-chip solder joint incorporating Au/Pd metallization during solid-state aging. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 15233–15240 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9665-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9665-0