Abstract
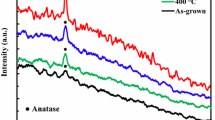
This work presents a study of the structural, morphological, and optical properties of titanium dioxide thin films prepared via plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition at the floating potential (Vf) or substrate bias (Vb) of − 10 and − 50 V, after being submitted to annealing processes varying the temperature from 450 to 850 °C. By tuning the annealing temperature and substrate bias voltage respectively, which could be helpful for the explanation about the thermal effect and the influence of ion bombardment on TiO2 films obtained from low-temperature plasma deposition. The results have shown that the TiO2 thin films grown at Vf and − 10 V persist in the anatase phase even after annealing at 850 °C. The phase transformation from anatase to rutile occurred in the case of − 50 V, and the crystallization enhancement has been identified as the annealing temperature increased. From scanning electron microscopy measurements, the formation of gradient columnar morphology was also perceived in the cases of Vf and − 10 V, with increasing annealing temperature at 850 °C, these structures disappear transforming into homogeneous columns with larger size at Vf and granular structure at − 10 V. In the case of − 50 V, a well-organized columnar morphology has been found in the as-deposited film, and it also can be modified into granular structure with the post-annealing effect at 850 °C but without thickness reduction. Spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE) study was used to determine the effect of annealing temperature on the thickness and on the optical constant of TiO2 thin films. SE shows that the band gap of TiO2 thin films was found to decrease when the annealing temperature increases. Meanwhile, the annealing temperature of 450 °C leads to a decrease of refractive indices of the films grown at Vf and − 10 V, but has no effect on the film of − 50 V. Then further increase of annealing temperature at 850 °C, an improvement of refractive indices can be identified for all the films deposited with various bias voltages.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Amassian, L. Desjardins, Martinu, Study of TiO2 film growth mechanisms in low-pressure plasma by in situ real-time spectroscopic ellipsometry. Thin Solid Films 447–448, 40 (2004)
R. Mechiakh, F. Meriche, R. Kremer, R. Bensaha, B. Boudine, A. Boudrioua, TiO2 thin films prepared by sol-gel method for waveguiding applications: correlation between the structural and optical properties. Opt. Mater. 30, 645 (2007)
J. Singh, S.A. Khan, J. Shah, R.K. Kotnala, S. Mohapatra, Nanostructured TiO2 thin films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering for photocatalytic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 422, 953–961 (2017)
G.D. Rajmohan, F.Z. Huang, R. d’Agostino, J. Plessis, X.J. Dai, Low temperature reactively sputtered crystalline TiO2 thin film as effective blocking layer for perovskite solar cells. Thin Solid Films 636, 307–313 (2017)
T. Dhandayuthapani, R. Sivakumar, R. Ilangovan, C. Gopalakrishnan, C. Sanjeeviraja, A. Sivanantharaja, High coloration efficiency, high reversibility and fast switching response of nebulized spray deposited anatase TiO2 thin films for electrochromic applications. Electrochim. Acta 255, 358–368 (2017)
F. Pan, H. Lin, H. Zhai, Z. Miao, Y. Zhang, K. Xu, B. Guan, H. Huang, H. Zhang, Pd-doped TiO2 film sensors prepared by premixed stagnation flames for CO and NH3 gas sensing, Sens. Actuators B 261, 451–459 (2018)
U. Diebold, The surface science of titanium dioxide. Surf. Sci. Rep. 48, 53–229 (2003)
L.J. Meng, V. Teixeira, H.N. Cui, F. Placido, Z. Xu, M.P. dos Santos, A study of the optical properties of titanium oxide films prepared by dc reactive magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 7970 (2006)
E.D. Palik, Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids, vol. II (Academic Press, San Diego, 1991), p. 795
M.V. Sofianou, V. Psycharis, N. Boukos, T. Vaimakis, J. Yu, R. Dillert, D. Bahnemann, C. Trapalis, Tuning the photocatalytic selectivity of TiO2 anatase nanoplates by altering the exposed crystal facets content., Appl. Catal. B 142–143, 761 (2013)
J.Y. Zhang, I.W. Boyd, B.J. O’Sullivan, P.K. Hurley, P.V. Kelly, J.P. Senateur, Nanocrystalline TiO2 films studied by optical, XRD and FTIR spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 303, 134 (2002)
D.A.H. Hanaor, C.C. Sorrell, Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 855 (2011)
T.B. Ghosh, S. Dhabal, A.K. Datta, On crystallite size dependence of phase stability of nanocrystalline TiO2. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 4577 (2003)
M. Hirano, N. Nakahara, K. Ota, O. Tanaike, N. Inagaki, Photoactivity and phase stability of ZrO2-doped anatase-type TiO2 directly formed as nanometer-sized particles by hydrolysis under hydrothermal conditions. J. Solid State Chem. 170, 39 (2003)
G. Li, L. Li, J. Boerio-Goates, B.F. Woodfield, High purity anatase TiO2 nanocrystals: near room-temperature synthesis, grain growth kinetics, and surface hydration chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 8659 (2005)
J. Kim, K.C. Song, S. Foncillas, S. Pratsinis, Dopants for synthesis of stable bimodally porous titania. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 2863 (2001)
V.G. Sevastyanov, E.P. Simonenko, N.P. Simonenko, A.S. Mokrushin, V.A. Nikolaev, N.T. Kuznetsov, Sol-gel made titanium dioxide nanostructured thin films as gas-sensing materials for the detection of oxygen. Mendeleev Commun. 28, 164–166 (2018)
A.E.J. González, S.G. Santiago, Structural and optoelectronic characterization of TiO2 films prepared using the sol–gel technique. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 22, 709–716 (2007)
O. Wiranwetchayan, S. Promnopas, T. Thongtem, A. Chaipanich, S. Thongtem, Effect of alcohol solvents on TiO2 films prepared by sol–gel method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 326, 310–315 (2017)
M. Horprathum, P. Eiamchai, P. Chindaudom, N. Nuntawong, V. Patthanasettakul, P. Limnonthakul, P. Limsuwan, Characterization of inhomogeneity in TiO2 thin films prepared by pulsed dc reactive magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 520, 272–279 (2011)
N. Martin, D. Baretti, C. Rousselot, J.-Y. Rauch, The effect of bias power on some properties of titanium and titanium oxide films prepared by R.F. magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 107, 172–182 (1998)
H. Yao, M. Chiu, W. Wu, F. Shieu, Influence of RF bias on the characteristics of TiO2 thin films prepared by DC sputtering. J. Electrochem. Soc. 153, F237–F243 (2006)
D. Li, A. Goullet, M. Carette, A. Granier, J.P. Landesman, Effect of growth interruptions on TiO2 films deposited by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 182, 409–417 (2016)
L. Martinu, D. Poitras, Plasma deposition of optical films and coatings: a review. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 18, 2619–2645 (2000)
A. Borras, J. Cotrino, A.R. Gonzalez-Elipe, Type of plasmas and microstructures of TiO2 thin films prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 154, P152-P157 (2007)
M. Nakamura, D. Korzec, T. Aoki, J. Engemann, Y. Hatanaka, Characterization of TiOx film prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition using a multi-jet hollow cathode plasma source., Appl. Surf. Sci. 175–176, 697–702 (2001)
A. Sobczyk-Guzenda, M. Gazicki-Lipman, H. Szymanowski, J. Kowalski, P. Wojciechowski, T. Halamus, A. Tracz, Characterization of thin TiO2 films prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition for optical and photocatalytic applications. Thin Solid Films 517, 5409–5414 (2009)
D. Li, M. Carette, A. Granier, J.P. Landesman, A. Goullet, Effect of ion bombardment on the structural and optical properties of TiO2 thin films deposited from oxygen/titanium tetraisopropoxide inductively coupled plasma. Thin Solid Films 589, 783–791 (2015)
A. Dussan, A. Bohórquez, H.P. Quiroz, Effect of annealing process in TiO2 thin films: structural, morphological, and optical properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 424, 111–114 (2017)
J.B. Naceur, M. Gaidi, F. Bousbih, R. Mechiakh, R. Chtourou, Annealing effects on microstructural and optical properties of nanostructured-TiO2 thin films prepared by sol-gel technique. Curr. Appl. Phys. 12, 422–428 (2012)
B. Drevillon, J. Perrin, R. Marbit, A. Violet, J.L. Dalby, Fast polarization modulated ellipsometer using a microprocessor system for digital Fourier analysis. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 53, 969 (1982)
B. Santara, P.K. Giri, K. Imakita, M. Fujii, Microscopic origin of lattice contraction and expansion in undoped rutile TiO2 nanostructures. J. Phys. D 47, 215302 (2014)
A. Dorian, H. Hanaor, C.C. Sorrell, Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 855–874 (2011)
C.L. Wang, W.S. Hwang, H.L. Ch, H.J. Lin, H.H. Ko, M.C. Wang, Kinetics of anatase transition to rutile TiO2 from titanium dioxide precursor powders synthesized by a sol-gel process. Ceram. Int. 42, 13136–13143 (2016)
D. Reyes-Coronado, G. Rodríguez-Gattorno, M.E. Espinosa-Pesqueira, C. Cab, R. de Coss, G. Oskam, Phase-pure TiO2 nanoparticles: anatase, brookite and rutile. Nanotechnology 19, 145605 (2008)
D. Li, A. Goullet, M. Carette, A. Granier, Y. Zhang, J.P. Landesman, Structural and optical properties of RF-biased PECVD TiO2 thin films deposited in an O2/TTIP helicon reactor. Vacuum 131, 231–239 (2016)
D. Li, S. Elisabeth, A. Granier, M. Carette, A. Goullet, J.P. Landesman, Structural and optical properties of PECVD TiO2–SiO2 mixed oxide films for optical applications. Plasma Process. Polym. 13, 918–928 (2016)
X. Ding, X. Liu, Correlation between anatase-to-rutile transformation and grain growth in nanocrystalline titania powders. J. Mater. Res. 13, 2556 (1998)
J.H. Anderson Jr., G.A. Parks, Electrical conductivity of silica gel in the presence of adsorbed water. J. Phys. Chem. 72, 3662–3668 (1968)
G. Socrates, Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts (Wiley, Chichester, 2001)
C. Pecharroman, F. Gracia, J.P. Holgado, M. Ocana, A.R. Gonzalez-Elipe, J. Bassas, J. Santiso, A. Figueras, Determination of texture by infrared spectroscopy in titanium oxide–anatase thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 4634–4645 (2003)
Y. Leprince-Wang, D. Souche, K. Yu-Zhang, S. Fisson, G. Vuye, J. Rivory, Relations between the optical properties and the microstructure of TiO2 thin films prepared by ion-assisted deposition. Thin Solid Films 359, 171 (2000)
H. Long, G. Yang, A. Chen, Y. Li, P. Lu, Growth and characteristics of laser deposited anatase and rutile TiO2 films on Si substrates. Thin Solid Films 517, 745–749 (2008)
A. Sonnenfeld, P. Rudolf, von Rohr, Effect of substrate temperature and RF biasing on the optical properties of titania-like thin films obtained by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Plasma Process. Polym. 6, S722 (2009)
L. Miao, P. Jin, K. Kaneko, A. Terai, N. Nabatova-Gabain, S. Tanemura, Preparation and characterization of polycrystalline anatase and rutile TiO2 thin films by rf magnetron sputtering., Appl. Surf. Sci. 212–213, 255–263 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51602279), Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds (1601048B), Jiangsu Overseas Visiting Scholar Program for University Prominent Young & Middle-aged Teachers and Presidents, Program for High-end Talents in Yangzhou University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Dai, S., Goullet, A. et al. Annealing and biasing effects on the structural and optical properties of PECVD-grown TiO2 films from TTIP/O2 plasma. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 13254–13264 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9449-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9449-6