Abstract
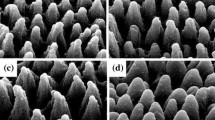
The high infrared absorption of silicon could be achieved by doping silicon with chalcogens via femtosecond laser. In the paper, the samples of Se-doped silicon with different thickness of Si film were prepared with the aid of femtosecond laser. The effect of the thickness of silicon film on optical and the electrical properties of se-doped silicon is investigated. All the samples were thermally annealed at 500 °C for 1 h, and the absorptance of all the samples was found with a certain degree of reduction. With the increase of thickness of silicon film, the results of visible-near infrared spectrum showed that the infrared absorptance increased first and then decreased. In particular, the optical absorption, sheet carrier density and responsivity for samples prepared with the silicon film that was 300 nm thick were greater than that of the samples prepared with the Si films of other thickness. The experiment demonstrated that it is significant to select the silicon film of appropriate thickness in the fabrication of Se doped silicon.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Masini, L. Colace, G. Assanto, Mater. Sci. Eng. 89, 2 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0921-5107(01)00781-4
A. Datas, C. Algora, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 94, 2137 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2010.06.042
A. Luque, A. Marti, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 5014 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.5014
Z.-Y. Zhao, P.-Z. Yang, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 17499 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cp01522c
K. Sánchez, I. Aguilera, P. Palacios, P. Wahnón, Phys. Rev. B 79, 165203 (2009)
B.K. Nayak, M.C. Gupta, Appl. Phys. A 89, 663 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-4268-2
M. Halbwax, T. Sarnet, P. Delaporte et al., Thin Solid Films 516, 6791 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2007.12.117
A.Y. Vorobyev, C. Guo, Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 7291 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.03.106
K. Liu, S. Qu, X. Zhang et al., Appl. Phys. A 114, 765 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7682-7
I. Umezu, J.M. Warrender, S. Charnvanichborikarn et al., J. Appl. Phys. 113, 213501. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4804935
A. Kurek, S.T. Barry, (2011) Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 12, 045001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/12/4/045001
M.J. Smith, Y.-T. Lin, M.-J. Sher, M.T. Winkler, E. Mazur, S. Gradecak, J. Appl. Phys. 110, 053524 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3633528
L. Du, Z. Wu, Y. Su et al., Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 54: 51 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2016.06.019
T. Zhang, P. Zhang, S. Li, W. Li, Z. Wu, Y. Jiang, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8, 351 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276x-8-351
M.J. Smith, M. Winkler, M.-J. Sher, Y.-T. Lin, E. Mazur, S. Gradecak, Appl. Phys. A 105, 795 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-011-6651-2
H.M. van Driel, J.E. Sipe, J.F. Young, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 1955 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.49.1955
M.A. Sheehy, B.R. Tull, C.M. Friend, E. Mazur, (2007) Mater. Sci. Eng. B 137, 289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2006.10.002
L.-P. Cao, Z.-D. Chen, C.-L. Zhang, J.-H. Yao, (2015) Front. Phys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-015-0491-z
X. Li, L. Chang, R. Qiu, C. Wen, Z. Li, S. Hu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 8002 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.04.155
M.T. Winkler, D. Recht, M.-J. Sher, A.J. Said, E. Mazur, M.J. Aziz, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 178701 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.178701
Funding
This study was funded by National Science Funds for Creative Research Groups of China (61421002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Wu, Z., Du, L. et al. Effect of the thickness of Si film on Si/Se film doped silicon prepared by femtosecond laser. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 4526–4532 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8401-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8401-5