Abstract
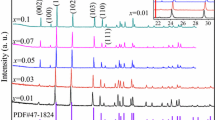
Eu3+ ions activated BaLaMgSbO6 phosphors were successfully synthesized by the solid-state reaction method using NH4Cl as the flux. The BaCl2 was selected to substitute BaCO3 as the starting material to attest that NH4Cl not only reacted with BaCO3 but also reacted with other starting materials. The analysis of TG/DSC was used to probe the role of NH4Cl flux in the process of synthesizing BaLaMgSbO6 powders. The crystal structure was investigated by XRD and Rietveld refinement, and the morphology by SEM. The phosphors had monoclinic double perovskite structure with the space group P21, as well as the rock-salt ordering of B-site. The luminescence properties, including the photoluminescence excitation and emission spectra, and the color coordinates were investigated. Also, the relationship between the crystalline size and the emission intensity were discussed. With increasing the calcination temperature, both the crystalline size and the emission intensity monotonously increased. The relative intensity ratio of red/orange emission was used to measure the degree of distortion from the inversion symmetry of the local environment of the Eu3+ ions in BaLaMgSbO6.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Cheng, Z. Xia, M.S. Molokeev, X. Jing, Dalton Trans. 44(41), 18078–18089 (2015)
Z. Lei, D. Meng, Z. Gao, X. Zhang, Q. Yang, Y. Wang, J. Mater, Sci.-Mater. 27(2), 1840–1846 (2015)
R. Cao, Q. Xiong, W. Luo, D. Wu, X. Fen, X. Yu, Ceram. Int. 41(5), (2015) 7191–7196
F. Liu, Y. Fang, J. Hou, N. Zhang, Z. Ma, Ceram. Int. 40(2), 3237–3241 (2014)
H. Sun, Q. Zhang, X. Wang, T. Zhang, Mater. Lett. 131, 164–166 (2014)
H. Yu, D. Deng, L. Chen, D. Chen, J. Zhong, H. Zhao, S. Xu, Ceram. Int. 41(3), 3800–3805 (2015)
R. Yu, M. Li, N. Xie, T. Wang, N. Xue, H. Guo, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98(12), 3849–3855 (2015)
Y. Zhang, W. Gong, J. Yu, Y. Lin, G. Ning, RSC Adv. 5(117), 96272–96280 (2015)
Y. Liu, Y. Wang, L. Wang, Y.-Y. Gu, S.-H. Yu, Z.-G. Lu, R. Sun, RSC Adv. 4(9), 4754–4762 (2014)
S.K. Gupta, M. Sahu, P.S. Ghosh, D. Tyagi, M.K. Saxena, R.M. Kadam, Dalton Trans. 44, 18957–18969 (2015)
X. Yin, J. Yao, Y. Wang, C. Zhao, F. Huang, J. Lumin. 132(7), 1701–1704 (2012)
Y.-F. Wu, Y.-T. Nien, Y.-J. Wang, I.-G. Chen, J. McKittrick, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95(4), 1360–1366 (2012)
X.G. Zhang, J.L. Zhang, Y.B. Chen, M.L. Gong, Ceram. Int. 42(12) 13919–13924 (2016)
G. Zhu, Y.R. Shi, M. Mikami, Y. Shimomura, Y.H. Wang, Mater. Res. Bull 50, 405–408 (2014)
C. Huang, L. Chen, Q. Zhang, S. Chang, B. Zhang, A. Chang, H. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. 27(7) 7560–7565 (2016)
H.D. Nguyen, S.J. Kim, I.H. Yeo, S.I. Mho, J. Electrochem. Soc. 159(3), J54-J60 (2012)
X.W. Cao, Y.G. Liu, Z.H. Huang, M.H. Fang, X.W. Wu, Ceram. Int. 41(10), 14184–14189 (2015)
X. Yin, Y. Wang, F. Huang, Y. Xia, D. Wan, J. Yao, J. Solid State Chem 184(12), 3324–3328 (2011)
N. Xiao, J. Shen, T.J. Xiao, B. Wu, X.B. Luo, L. Li, Z.Q. Wang, X.J. Zhou, Mater. Res. Bull 70, 684–690 (2015)
L. Zhang, Z. Lu, P. Han, J. Lu, N. Xu, L. Wang, Q. Zhang, J. McKittrick, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95(12), 3871–3877 (2012)
P. Zhang, X. Chen, Z. Zhang, M. Fei, L. Chen, J. Lumin 169, 733–738 (2016)
G. Li, J. Chen, Z. Mao, W. Song, T. Sun, D. Wang, Ceram. Int. 42(1), 1756–1761 (2016)
P. Han, X. Jiang, Adv. Powder Technol. 26(3), 977–982 (2015)
Q. Liu, X. Li, B. Zhang, L. Wang, Q. Zhang, L. Zhang, Ceram. Int. 42(14), 15294–15300 (2016)
R. Yu, C. Wang, J. Chen, Y. Wu, H. Li, H. Ma, ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 3(3), R33–R37 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the generous financial support from Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (51402133, 51202111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Wang, L., Li, X. et al. The evolution and role of NH4Cl flux used to synthesize double perovskite BaLaMgSbO6: a potential red phosphor for white LEDs. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 5352–5359 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6194-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6194-6