Abstract
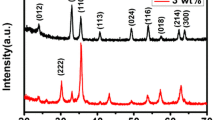
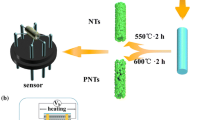
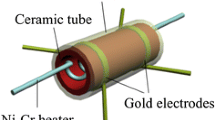
Hollow and porous α-Fe2O3 nanotubes were successfully synthesized by single nozzle electrospinning method followed by annealing treatment. The crystal structures and morphologies of the as-prepared materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy, respectively. The as-prepared materials were applied to construct gas sensor devices which gas sensing properties were further investigated. The obtained results revealed that porous α-Fe2O3 nanotube gas sensors exhibit a markedly enhanced gas sensing performance compared with hollow α-Fe2O3 nanotube gas sensors, which was about three times higher to 100 ppm acetone at 240 °C. Interestingly, hollow and porous α-Fe2O3 nanotube gas sensors both showed fast response–recovery time and good selectivity, but the porous ones possessed the shorter recovery time. The improved properties could be attributed to the unique morphology of porous nanotubes. Thus, further improvement of performance in metal-oxide-semiconductors materials could be realized by preparation the unique porous structures of nanotubes. Moreover, it is expected that porous metal-oxide-semiconductors nanotubes could be further design as promising candidates for gas sensing materials.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.-M. Li, Y.-J. Li, M.-Y. Lu, C.-I. Kuo, L.-J. Chen, Direct conversion of single-layer SnO nanoplates to multi-layer SnO2 nanoplates with enhanced ethanol sensing properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 2453–2456 (2009)
S. Benkara, S. Zerkout, H. Ghamri, Synthesis of Sn doped ZnO/TiO2 nanocomposite film and their application to H2 gas sensing properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 1271–1279 (2013)
L. Wang, J. Deng, Z. Lou, T. Zhang, Cross-linked p-type Co3O4 octahedral nanoparticles in 1D n-type TiO2 nanofibers for high-performance sensing devices. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 10022 (2014)
P. Song, Q. Wang, Z. Yang, Biomorphic synthesis and gas response of In2O3 microtubules using cotton fibers as templates. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 168, 421–428 (2012)
N.D. Cuong, D.Q. Khieu, T.T. Hoa, D.T. Quang, P.H. Viet, T.D. Lam, N.D. Hoa, N.V. Hieu, Facile synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles for high-performance CO gas sensor. Mater. Res. Bull. 68, 302–307 (2015)
P. Sun, C. Wang, X. Zhou, P. Cheng, K. Shimanoe, G. Lu, N. Yamazoe, Cu-doped α-Fe2O3 hierarchical microcubes: synthesis and gas sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 193, 616–622 (2014)
Y. Guo, G. Zhang, J. Liu, Y. Zhang, Hierarchically structured α-Fe2O3/Bi2WO6 composite for photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants under visible light irradiation. RSC Adv. 3, 2963 (2013)
N. Atar, Magnetic iron oxide and iron oxide@gold nanoparticle anchored nitrogen and sulfur-functionalized reduced graphene oxide electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation. RSC Adv. 5, 26402–26409 (2015)
O. Akyıldırım, H. Medetalibeyoğlu, S. Manap, M. Beytur, F.S. Tokalı, M.L. Yola, N. Atar, Electrochemical sensor based on graphene oxide/iron nanoparticles for the analysis of quercetin. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 10, 7743–7753 (2015)
W.X. Jin, S.Y. Ma, Z.Z. Tie, X.H. Jiang, W.Q. Li, J. Luo, X.L. Xu, T.T. Wang, Hydrothermal synthesis of monodisperse porous cube, cake and spheroid-like α-Fe2O3 particles and their high gas-sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 220, 243–254 (2015)
M.L. Yola, T. Eren, N. Atar, Molecularly imprinted electrochemical biosensor based on Fe@Au nanoparticles involved in 2-aminoethanethiol functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for sensitive determination of cefexime in human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 60, 277–285 (2014)
V.K. Gupta, M.L. Yola, T. Eren, F. Kartal, M.O. Çağlayan, N. Atar, Catalytic activity of Fe@Ag nanoparticle involved calcium alginate beads for the reduction of nitrophenols. J. Mol. Liq. 190, 133–138 (2014)
N. Atar, T. Eren, M.L. Yola, H. Gerengi, S. Wang, Fe@Ag nanoparticles decorated reduced graphene oxide as ultrahigh capacity anode material for lithium-ion battery. Ionics 21, 3185–3192 (2015)
V.K. Gupta, N. Atar, M.L. Yola, Z. Üstündağ, L. Uzun, A novel magnetic Fe@Au core–shell nanoparticles anchored graphene oxide recyclable nanocatalyst for the reduction of nitrophenol compounds. Water Res. 48, 210–217 (2014)
R. Suresh, K. Giribabu, R. Manigandan, A. Vijayaraj, R. Prabu, A. Stephen, V. Narayanan, α-Fe2O3 nanoflowers: synthesis, characterization, electrochemical sensing and photocatalytic property. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 11, 645–652 (2013)
W. Zheng, X. Lu, W. Wang, Z. Li, H. Zhang, Y. Wang, Z. Wang, C. Wang, A highly sensitive and fast-responding sensor based on electrospun In2O3 nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 142, 61–65 (2009)
U. Cvelbar, Z. Chen, M.K. Sunkara, M. Mozetič, Spontaneous growth of superstructure α-Fe2O3 nanowire and nanobelt arrays in reactive oxygen plasma. Small 4, 1610–1614 (2008)
H.-y. Yang, X.-L. Cheng, X.-F. Zhang, Z.-k. Zheng, X.-F. Tang, Y.-M. Xu, S. Gao, H. Zhao, L.-H. Huo, A novel sensor for fast detection of triethylamine based on rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 205, 322–328 (2014)
C. Zhao, G. Zhang, W. Han, J. Fu, Y. He, Z. Zhang, E. Xie, Electrospun In2O3/α-Fe2O3 heterostructure nanotubes for highly sensitive gas sensor applications. CrystEngComm 15, 6491 (2013)
V. Kruefu, A. Wisitsoraat, A. Tuantranont, S. Phanichphant, Ultra-sensitive H2S sensors based on hydrothermal/impregnation-made Ru-functionalized WO3 nanorods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 215, 630–636 (2015)
M.-Y. Liao, C.-C. Huang, M.-C. Chang, S.-F. Lin, T.-Y. Liu, C.-H. Su, C.-S. Yeh, H.-P. Lin, Synthesis of magnetic hollow nanotubes based on the Kirkendall effect for MR contrast agent and colorimetric hydrogen peroxide sensor. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 7974 (2011)
C. Liu, X. Chi, X. Liu, S. Wang, Comparison of ethanol sensitivity based on cobalt–indium combined oxide nanotubes and nanofibers. J. Alloys Compd. 616, 208–212 (2014)
W.-S. Kim, B.-S. Lee, D.-H. Kim, H.-C. Kim, W.-R. Yu, S.-H. Hong, SnO2nanotubes fabricated using electrospinning and atomic layer deposition and their gas sensing performance. Nanotechnology 21, 245605 (2010)
L. Liu, C. Liu, S. Li, L. Wang, H. Shan, X. Zhang, H. Guan, Z. Liu, Honeycombed SnO2 with ultra sensitive properties to H2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 177, 893–897 (2013)
M. Hjiri, L. El Mir, S.G. Leonardi, A. Pistone, L. Mavilia, G. Neri, Al-doped ZnO for highly sensitive CO gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 196, 413–420 (2014)
Z. Wang, Z. Li, L. Liu, X. Xu, H. Zhang, W. Wang, W. Zheng, C. Wang, A novel alcohol detector based on ZrO2-doped SnO2 electrospun nanofibers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 634–637 (2010)
W. Zheng, Z. Li, H. Zhang, W. Wang, Y. Wang, C. Wang, Electrospinning route for α-Fe2O3 ceramic nanofibers and their gas sensing properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 1432–1436 (2009)
F. Tian, Y. Liu, K. Guo, Au nanoparticle modified flower-like ZnO structures with their enhanced properties for gas sensing. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 21, 140–145 (2014)
M. Wu, W. Zeng, Q. He, J. Zhang, Hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2 nanocorals, nanofragments and nanograss and their formaldehyde gas-sensing properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 1495–1501 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The work has been supported by the Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Department (No. 20140204027GX).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Zhang, J., Ni, M. et al. Comparison of gas sensing properties based on hollow and porous α-Fe2O3 nanotubes. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 11262–11267 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5247-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5247-1