Abstract
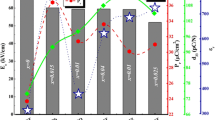
Effect of weak ferroelectric perovskite, bismuth magnesium zirconate [Bi(Mg0.5Zr0.5)O3] substitution in lead-free sodium bismuth titanate [(Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3] ceramics is studied. Influence of substitution on intrinsic and extrinsic contribution and impact on ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties are investigated. Improved spontaneous polarization (Ps), increased remnant polarization (Pr), decreased coercive field (Ec) and high piezoelectric coefficient (d33) are obtained for x = 0.01 mole fraction of Bi(Mg0.5Zr0.5)O3 substitution due to decrease in rhombohedral lattice distortion and homogeneous strain. Small rhombohedral lattice distortion (δr) and minimum homogeneous strain (δ) are the primary intrinsic parameters which favours the extrinsic parameters such as mobility of non-180° domain reorientation, domain switching and domain wall motion. Enhanced mobility softens the coercive field and increases remnant polarization to maximum. Reduced rhombohedral lattice distortion, low strain and enhanced mobility are the key factors for enhanced piezoelectric constant, highest remnant polarization and decreased coercive field in non-MPB (1 − x)(Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3–xBi(Mg0.5Zr0.5)O3 solid solutions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Rodel, W. Jo, K.T.P. Seifert, E. Anon, T. Granzow, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 1153 (2009)
G.H. Haertling, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 797 (1999)
P.K. Panda, J. Mater. Sci. 44, 5049 (2009)
M. Demartin Maeder, D. Damjanovic, N. Setter, J. Electroceram. 13, 385 (2004)
S.O. Leontsev, R.E. Eitel, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 11, 044302 (2010)
E. Aksel, J.L. Jones, Sensors 10, 1935 (2010)
T.R. Shrout, S.J. Zhang, J. Electroceram. 19, 111 (2007)
W. Jo, J.E. Daniels, J.L. Jones, X. Tan, P.A. Thomas, D. Damjanovic, J. Rödel, J. Appl. Phys. 109, 014110 (2011)
M. Chen, Q. Xu, B.H. Kim, B.K. Ahn, J.H. Ko, W.J. Kang, O.J. Nam, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 843 (2008)
F. Cordero, F. Craciun, F. Trequattrini, E. Mercadelli, C. Galassi, Phys. Rev. B 81, 144124 (2010)
I. Levin, I.M. Reaney, E.M. Anton, W. Jo, J. Rodel, J. Pokorny, L.A. Schmitt, H.J. Kleebe, M. Hinterstein, J.L. Jones, Phys. Rev. B 87, 024113 (2013)
A. Moosavi, M.A. Bahrevar, A.R. Aghaei, P. Ramos, M. Alguero, H. Amorın, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 47, 055304 (2014)
D. Rout, K.-S. Moon, S.-J.L. Kang, I.W. Kim, J. Appl. Phys. 108, 084102 (2010)
Y. Hiruma, Y. Imai, Y. Watanabe, H. Nagata, T. Takenaka, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 262904 (2008)
S. Kuharungrong, W. Schulze, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79(5), 1273–1280 (1996)
J.-K. Lee, K.S. Hong, C.K. Kim, S.-E. Park, J. Appl. Phys. 91, 4538 (2002)
G. Fan, W. Lu, X. Wang, F. Liang, J. Xiao, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 035403 (2008)
Yu. Huichun, Z.-G. Ye, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 112902 (2008)
L. Eric Cross, Ferroelectric Ceramics, Monte Verita (Birkhiiuser Verlag, Basel, 1993), pp. 1–84
W. Heywang, K. Lubitz, W. Wersing, Piezoelectricity Evolution and Future of a Technology, Springer Series in Materials Science (Springer, Berlin, 2008), p. 96
B.J. Chu, D.R. Chen, G.R. Li, Q.R. Yin, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 22, 2115 (2002)
Y. Watanabe, Y. Hiruma, H. Nagata, T. Takenaka, Ceram. Int. 34, 761764 (2008)
A. Herabut, A. Safari, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80(11), 29542958 (1997)
T. Takenaka, H. Nagata, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 36(9B), 60556057 (1997)
X. Wang, H. Chan, C.L. Choy, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 86(10), 18091811 (2003)
Y. Li, W. Chen, J. Zhou, Q. Xu, H. Sun, R. Xu, Mater. Sci. Eng., B 112, 59 (2004)
C. Zhou, X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. 43, 10161019 (2008)
C. Zhou, X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 19, 29–32 (2008)
Q. Wang, J. Chen, L. Fan, L. Liu, L. Fang, X. Xing, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 1171 (2013)
A. Ullah, M. Ishfaq, C.W. Ahn, A. Ullah, S.E. Awan, I.W. Kim, Ceram. Int. 41, 10557 (2015)
Y. Hiruma, K. Yoshii, H. Nagata, T. Takenaka, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 084121 (2008)
A. Maqbool, J. Rahman, A. Hussain, J.K. Park, T.G. Park, J.S. Song, M.H. Kim, IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 60, 012047 (2014)
D.E. Jain Ruth, M. Veera Gajendra Babu, S.M. Abdul Kader, B. Bagyalakshmi, D. Pathinettam Pandiyan, B. Sundarakannan, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 6757–6761 (2015)
D.E. Jain Ruth, S.M. Abdul Kader, M. Muneeswaran, N.V. Giridharan, D. Pathinettam Pandiyan, B. Sundarakannan, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2015). doi:10.1007/s10854-015-3768-7
J. Chen, J. Li, L. Fan, N. Zou, P. Gi et al., J. Appl. Phys. 112, 074101 (2012)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. A32, 751 (1976)
I. Grinberg, M.R. Suchomel, P.K. Davies, A.M. Rappe, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 094111 (2005)
G.O. Jones, P.A. Thomas, Acta Cryst. B58, 168–178 (2002)
T. Hahn, International Tables for Crystallography Volume A: Space-Group Symmetry, 5th edn. (Springer, Berlin, 2005), p. 16
B.N. Rao, R. Ranjan, Phys. Rev. B 86, 134103 (2012)
Y.S. Sung, J.M. Kim, J.H. Cho, T.K. Song, M.H. Kim, H.H. Chong, T.G. Park, D. Do, S.S. Kim, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 022901 (2010)
Y.S. Sung, J.M. Kim, J.H. Cho, T.K. Song, M.H. Kim, H.H. Chong, T.G. Park, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 202901 (2010)
A.G. Khatchaturyan, Philos. Mag. 90, 37–60 (2010)
J.L. Jones, M. Hoffman, J.E. Daniels, A.J. Studer, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 092901 (2006)
Acknowledgments
We thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi, India funding agency for the financial support under the Grant No. 03/(1238)/12/EMR-II.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain Ruth, D.E., Sundarakannan, B. Role of strain and lattice distortion on ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of bismuth magnesium zirconate substituted sodium bismuth titanate ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 3250–3257 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-4152-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-4152-3