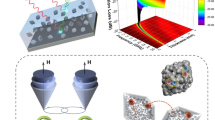
Abstract
The development of advanced microwave absorbing materials with high absorption intensity and broad bandwidth is crucial for applications in electromagnetic interference shielding and stealth technology. In this study, we propose a novel hybrid material composed of porous magnetic nanospindle@poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT)/MXene (Fe@P/MX), designed to achieve superior microwave absorption performance through impedance matching and electromagnetic loss mechanisms. The conductive PEDOT and MXene, combined with magnetic nanospindles, enable impedance matching and promote dielectric loss, which ultimately enhances microwave absorption. Additionally, the hybrid material contains multiple interfaces that induce interface polarization and strong absorption of electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic parameters of composites can be easily modulated by adjusting the content of PEDOT, thereby optimizing microwave absorption performance. The results demonstrate improved performance compared to existing materials, with the minimum reflection loss of − 60.6 dB at 17.0 GHz under the thickness of 1.6 mm. Besides, the effective absorption bandwidth extends to 5.4 GHz under the thickness of 1.9 mm. This core–shell hybrid material has significant potential for practical applications requiring efficient microwave absorption.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the fundings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Wongkasem N (2021) Electromagnetic pollution alert: microwave radiation and absorption in human organs and tissues. Electromagn Biol Med 40(2):236–253
Xia Y, Gao W, Gao C (2022) A review on graphene-based electromagnetic functional materials: electromagnetic wave shielding and absorption. Adv Func Mater 32(42):2204591
Guo Y, Ruan K, Wang G, Gu J (2023) Advances and mechanisms in polymer composites toward thermal conduction and electromagnetic wave absorption. Sci Bull 68(11):1195–1212
Wu Y, Chen L, Han Y et al (2023) Hierarchical construction of CNT networks in aramid papers for high-efficiency microwave absorption. Nano Res 16(5):7801–7809
Tong G, Wu W, Guan J, Qian H, Yuan J, Li W (2011) Synthesis and characterization of nanosized urchin-like α-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4: Microwave electromagnetic and absorbing properties. J Alloy Compd 509(11):4320–4326
Wu Z, Cheng H-W, Jin C et al (2022) Dimensional design and core–shell engineering of nanomaterials for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Mater 34(11):2107538
Wang J, Liu L, Jiao S, Ma K, Lv J, Yang J (2020) Hierarchical carbon fiber@MXene@MoS2 core-sheath synergistic microstructure for tunable and efficient microwave absorption. Adv Func Mater 30(45):2002595
Ni X, Hu X, Zhou S, Sun C, Bai X, Chen P (2011) Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) microspheres. Polym Adv Technol 22(5):532–537
Zhou W, Hu X, Sun C, Yan J, Zhou S, Chen P (2014) Microwave absorbing properties of Fe3O4–poly(3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) hybrids in low-frequency band. Polym Adv Technol 25(1):83–88
Qiao M, Tian Y, Wang J et al (2022) Magnetic-field-induced vapor-phase polymerization to achieve PEDOT-decorated porous Fe3O4 particles as excellent microwave absorbers. Ind Eng Chem Res 61(35):13072–13082
Yan L, Wang X, Zhao S et al (2017) Highly efficient microwave absorption of magnetic nanospindle-conductive polymer hybrids by molecular layer deposition. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(12):11116–11125
Li X, Huang Z, Shuck CE, Liang G, Gogotsi Y, Zhi C (2022) MXene chemistry, electrochemistry and energy storage applications. Nat Rev Chem 6(6):389–404
Zhou X, Wen J, Wang Z, Ma X, Wu H (2022) Broadband high-performance microwave absorption of the single-layer Ti3C2Tx MXene. J Mater Sci Technol 115:148–155
Dai Y, Wu X, Liu Z, Zhang H-B, Yu Z-Z (2020) Highly sensitive, robust and anisotropic MXene aerogels for efficient broadband microwave absorption. Compos B Eng 200:108263
Li X, Wen C, Yang L et al (2021) MXene/FeCo films with distinct and tunable electromagnetic wave absorption by morphology control and magnetic anisotropy. Carbon 175:509–518
Pan F, Yu L, Xiang Z et al (2021) Improved synergistic effect for achieving ultrathin microwave absorber of 1D Co nanochains/2D carbide MXene nanocomposite. Carbon 172:506–515
Yuan M, Zhou M, Fu H (2021) Synergistic microstructure of sandwich-like NiFe2O4@SiO2@MXene nanocomposites for enhancement of microwave absorption in the whole Ku-band. Compos B Eng 224:109178
Wu S, Liu H, Wang Q, Yin X, Hou L (2023) Hydrogen bonded interface self-assembled ZnFe2O4@PDA@Ti3C2TX MXene composites with three-dimensional core/shell/shell structure for ultrathin high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. J Alloy Compd 945:169372
Zhang Y, Ruan K, Zhou K, Gu J (2023) Controlled distributed Ti3C2Tx hollow microspheres on thermally conductive polyimide composite films for excellent electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Mater 35(16):2211642
Zhang P, Sun N, Soomro RA, Yue S, Zhu Q, Xu B (2021) Interface-engineered Fe3O4/MXene heterostructures for enhanced lithium-ion storage. ACS Appl Energy Mater 4(10):11844–11853
Xu W, Wang M, Li Z et al (2017) Chemical transformation of colloidal nanostructures with morphological preservation by surface-protection with capping ligands. Nano Lett 17(4):2713–2718
Qunyan L, Luyao S, Qifei C, Yunlu Z (2022) Synthesis and laccase immobilization of magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2@mesoporous SiO2 hollow microspheres. Chem Ind Eng Prog 41(10):5494–5500
Wang J, Jia Z, Liu X et al (2021) Construction of 1D heterostructure NiCo@C/ZnO nanorod with enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Letters 13(1):175
Wen C, Li X, Zhang R et al (2022) High-density anisotropy magnetism enhanced microwave absorption performance in Ti3C2Tx MXene@Ni microspheres. ACS Nano 16(1):1150–1159
Zhou W, Hu X, Bai X et al (2011) Synthesis and electromagnetic, microwave absorbing properties of core–shell Fe3O4–Poly(3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) microspheres. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(10):3839–3845
Liu P, Yao Z, Ng VMH, Zhou J, Kong LB, Yue K (2018) Facile synthesis of ultrasmall Fe3O4 nanoparticles on MXenes for high microwave absorption performance. Compos A Appl Sci Manuf 115:371–382
Li Y, Gao Y, Fan B, Guan L, Zhao B, Zhang R (2021) Tailoring microwave electromagnetic responses in Ti3C2Tx MXene with Fe3O4 nanoparticle decoration via a solvothermal method. The J Phys Chem C 125(36):19914–19924
Sui J, Li W, Pan Q (2015) Vesicle-templating PEDOT hollow microspheres and their electrocatalytic activity towards ascorbic acid. J Func Polym 28(4):380–385
Li N, Huang G-W, Li Y-Q et al (2017) Enhanced microwave absorption performance of coated carbon nanotubes by optimizing the Fe3O4 nanocoating structure. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(3):2973–2983
Zhong S, Yu M, Liang X, Dong Y, Liu J, Wang C (2022) Microwave absorption performance and multiple loss mechanisms of three-dimensional porous Fe4N@Fe3O4@Fe/carbon composite. J Mater Sci 57:16649–16664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07663-1
Han Y, He M, Hu J et al (2023) Hierarchical design of FeCo-based microchains for enhanced microwave absorption in C band. Nano Res 16(1):1773–1778
Liu P, Gao S, Wang Y, Huang Y, Zhou F, Liu P (2021) Magnetic porous N-doped carbon composites with adjusted composition and porous microstructure for lightweight microwave absorbers. Carbon 173:655–666
Ling X, Wang K, Zhang W, Wu Y, Jin Q, Zhang D (2022) Bio-inspired, bimetal ZIF-derived hollow carbon/MXene microstructure aim for superior microwave absorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 625:317–327
Wang K, Chu W, Li H, Chen Y, Cai Y, Liu H (2021) Ferromagnetic Ti3CNCl2-decorated RGO aerogel: from 3D interconnecting conductive network construction to ultra-broadband microwave absorber with thermal insulation property. J Coll Interface Sci 604:402–414
Tao J, Zhou J, Yao Z et al (2021) Multi-shell hollow porous carbon nanoparticles with excellent microwave absorption properties. Carbon 172:542–555
Ma H, Wang Y, Wang B et al (2023) Synthetic 3D flower-like 1T/2H MoS2@CoFe2O4 composites with enhanced microwave absorption performances. J Mater Sci 58(3):1183–1199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-08051-5
Meng X, Liu Y, Han G, Yang W, Yu Y (2020) Three-dimensional (Fe3O4/ZnO)@ C Double-core@ shell porous nanocomposites with enhanced broadband microwave absorption. Carbon 162:356–364
Wang X, Pan F, Xiang Z et al (2020) Magnetic vortex core-shell Fe3O4@ C nanorings with enhanced microwave absorption performance. Carbon 157:130–139
Ding J, Cheng L (2021) Core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2@PANI composite: preparation, characterization, and applications in microwave absorption. J Alloy Compd 881:160574
Tong Z, Liao Z, Liu Y et al (2021) Hierarchical Fe3O4/Fe@ C@ MoS2 core-shell nanofibers for efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 179:646–654
Meng X, Lei W, Yang W, Liu Y, Yu Y (2021) Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with ultra-thin carbon layer for polarization-controlled microwave absorption performance. J Coll Interface Sci 600:382–389
Liu X, Zhao X, Yan J, Huang Y, Li T, Liu P (2021) Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance of core-shell Fe3O4@poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) microspheres/reduced graphene oxide composite. Carbon 178:273–284
Yang Z, Li M, Zhang Y et al (2020) Constructing uniform Fe3O4@C@MnO2 microspheres with yolk-shell interior toward enhancement in microwave absorption. J Alloy Compd 817:152795
Gao S, Zhang Y, He J et al (2023) Coal gasification fine slag residual carbon decorated with hollow-spherical Fe3O4 nanoparticles for microwave absorption. Ceram Int 49(11):17554–17565
Ma M, Li W, Tong Z et al (2020) Facile synthesis of the one-dimensional flower-like yolk-shell Fe3O4@SiO2@NiO nanochains composites for high-performance microwave absorption. J Alloy Compd 843:155199
Li J, Ji H, Xu Y, Zhang J, Yan Y (2020) Three-dimensional graphene supported Fe3O4 coated by polypyrrole toward enhanced stability and microwave absorbing properties. J Market Res 9(1):762–772
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Top Young Talents of Ten Thousand Talents Plan, National Natural Science Foundation of China (51971133, 51902200, 52072241, and 62375186), the Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (22511100400, 19JC1410400, 19ZR1425100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing—original draft, Visualization; XL: Formal analysis, Writing—review& editing; QD: Formal analysis, Visualization; QL: Conceptualization, Supervision; YW: Funding acquisition, Resources; QJ: Funding acquisition, Resources; WZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision; Writing—review& editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that there is not any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Ethical approval
There are no human subjects in this article.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Mohammad Naraghi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Ling, X., Dong, Q. et al. Design and synthesis of core–shell porous magnetic nanospindle@poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/MXene composite for efficient microwave absorption. J Mater Sci 58, 15100–15115 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08957-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08957-8