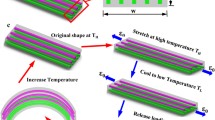
Abstract
Shape-memory polymers (SMPs) with complex deformation patterns have great potential for biomedical, smart robotics, and electronic device applications. However, after fabrication, the non-tunable and single permanent shape limits the development of SMPs. Here, we obtained a bilayer structure by depositing SMP on a taut pre-strain layer using 4D printing, which produces complex bidirectional spatial 3D shape transformation under the combined effect of the pre-strain layer and 3D printing layer. In addition, the effects of 3D printed layer thickness, aspect ratio, filling angle, filling rate, elongation of pre-strained layer, and deflection angle of pre-strained layer stretching direction and 3D printing long axis direction on the deformation of bilayer structure were investigated. The results show that by adjusting the above factors, the initial upward bending curvature of the bilayer structure, reverse downward deformation mode, and degree of bilayer structure under IR action was programmable. Thus, the adjustment of the permanent shape of the bilayer structure was achieved by using the above strategies. Meanwhile, with the presence of 3D printed layer SMP, the bilayer structure also has shape memory properties for complex shape memory. Therefore, this study further enriches the deformation modes of 4D printed SMPs to provide more complex and controllable permanent shape deformation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lendlein A, Jiang HY, Junger O, Langer R (2005) Light-induced shape-memory polymers. Nature 434(7035):879–882
Melly SK, Liu L, Liu Y, Leng J (2020) Active composites based on shape memory polymers: overview, fabrication methods, applications, and future prospects. J Mater Sci 55(25):10975–11051.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04761-w
Wang KJ, Jia YG, Zhu XX (2015) Biocompound-based multiple shape memory polymers reinforced by photo-cross-linking. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 1(9):855–863
Herath M, Epaarachchi J, Islam M, Fang L, Leng JS (2020) Light activated shape memory polymers and composites: a review. Eur Polym J 136:109912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.109912
Hager MD, Bode S, Weber C, Schubert US (2015) Shape memory polymers: past, present and future developments. Prog Polym Sci 49–50:3–33
Wang JY, Kunkel R, Luo JS, Li YH, Liu H, Bohnstedt BN, Liu YT, Lee CH (2019) Shape memory polyurethane with porous architectures for potential applications in intracranial aneurysm treatment. Polymers 11(4):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040631
Pekdemir ME, Oner E, Kok M, Qader IN (2021) Thermal behavior and shape memory properties of PCL blends film with PVC and PMMA polymers. Iran Polym J 30(6):633–641
Scalet G (2020) Two-way and multiple-way shape memory polymers for soft robotics: an overview. Actuators 9(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9010010
Wang KJ, Zhu XX (2018) Two-way reversible shape memory polymers containing polydopamine nanospheres: light actuation, robotic locomotion, and artificial muscles. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 4(8):3099–3106
Eisenhaure JD, Rhee SI, Ala’a M, Carlson A, Ferreira PM, Kim S (2015) The use of shape memory polymers for MEMS assembly. J Microelectromech Syst 25(1):69–77
Meng H, Mohamadian H, Stubblefield M, Jerro D, Ibekwe S, Pang S-S, Li G (2013) Various shape memory effects of stimuli-responsive shape memory polymers. Smart Mater Struct 22(9):093001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/22/9/093001
Rosales CAG, Duarte MFG, Kim H, Chavez L, Hodges D, Mandal P, Lin Y, Tseng T-L (2018) 3D printing of shape memory polymer (SMP)/carbon black (CB) nanocomposites with electro-responsive toughness enhancement. Mater Res Express 5(6):065704. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aacd53
Rousseau IA (2008) Challenges of shape memory polymers: a review of the progress toward overcoming SMP’s limitations. Polym Eng Sci 48(11):2075–2089
Hornat CC, Nijemeisland M, Senardi M, Yang Y, Pattyn C, van der Zwaag S, Urban MW (2020) Quantitative predictions of maximum strain storage in shape memory polymers (SMP). Polymer 186:122006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2019.122006
Khoo ZX, Teoh JEM, Liu Y, Chua CK, Yang S, An J, Leong KF, Yeong WY (2015) 3D printing of smart materials: a review on recent progresses in 4D printing. Virtual Phys Prototyp 10(3):103–122
Gao B, Yang Q, Zhao X, Jin G, Ma Y, Xu F (2016) 4D Bioprinting for Biomedical Applications. Trends Biotechnol 34(9):746–756
de Marco C, Pane S, Nelson BJ (2018) 4D printing and robotics. Sci Robot 3(18). https://doi.org/10.1126/scirobotics.aau0449
Choi, J., Kwon, O. C., Jo, W., Lee, H. J., & Moon, M. W. (2015). 4D printing technology: a review. 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing, 2(4), 159–167
Chu H, Yang W, Sun L, Cai S, Yang R, Liang W, Yu H, Liu L (2020) 4D printing: a review on recent progresses. Micromachines 11(9):796. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11090796
Bajpai A, Baigent A, Raghav S, Bradaigh CO, Koutsos V, Radacsi N (2020) 4D printing: materials, technologies, and future applications in the biomedical field. Sustainability 12(24):10628. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410628
Kuang X, Roach DJ, Wu J, Hamel CM, Ding Z, Wang T, Dunn ML, Qi HJ (2019) Advances in 4D printing: materials and applications. Adv Funct Mater 29(2):1805290. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201805290
Gladman AS, Matsumoto EA, Nuzzo RG, Mahadevan L, Lewis JA (2016) Biomimetic 4D printing. Nat Mater 15(4):413–418
Li Y, Zhang F, Liu Y, Leng J (2020) 4D printed shape memory polymers and their structures for biomedical applications. Sci China-Technol Sci 63(4):545–560
Invernizzi M, Turri S, Levi M, Suriano R (2018) 4D printed thermally activated self-healing and shape memory polycaprolactone-based polymers. Eur Polymer J 101:169–176
Ly ST, Kim JY (2017) 4D Printing - fused deposition modeling printing with thermal-responsive shape memory polymers. Int J Precis Eng Manufact-Green Technol 4(3):267–272
Naficy S, Gately R, Gorkin R, Xin H, Spinks GM (2017) 4D printing of reversible shape morphing hydrogel structures. Macromol Mater Eng 302(1):1600212
Zarek M, Layani M, Eliazar S, Mansour N, Cooperstein I, Shukrun E, Szlar A, Cohn D, Magdassi S (2016) 4D printing shape memory polymers for dynamic jewellery and fashionwear. Virtual Phys Prototyp 11(4):263–270
Monzon MD, Paz R, Pei E, Ortega F, Suarez LA, Ortega Z, Aleman ME, Plucinski T, Clow N (2017) 4D printing: processability and measurement of recovery force in shape memory polymers. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 89(5–8):1827–1836
Ge Q, Dunn CK, Qi HJ, Dunn ML (2014) Active origami by 4D printing. Smart Mater Struct 23(9):094007
Teoh JEM, An J, Chua CK, Lv M, Krishnasamy V, Liu Y (2017) Hierarchically self-morphing structure through 4D printing. Virtual Phys Prototyp 12(1):61–68
Wang J, Wang Z, Song Z, Ren L, Liu Q, Ren L (2019) Biomimetic shape-color double-responsive 4D printing. Adv Mater Technol 4(9):1900293. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.201900293
Lee AY, Zhou A, An J, Chua CK, Zhang Y (2020) Contactless reversible 4D-printing for 3D-to-3D shape morphing. Virtual Phys Prototyp 15(4):481–495
Zhang Q, Zhang K, Hu G (2016) Smart three-dimensional lightweight structure triggered from a thin composite sheet via 3D printing technique. Sci Rep 6(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22431v
Kacergis L, Mitkus R, Sinapius M (2019) Influence of fused deposition modeling process parameters on the transformation of 4D printed morphing structures. Smart Mater Struct 28(10):105042. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/ab3d18
Pekdemir ME, Kok M, Qader IN, Aydogdu Y (2022) Preparation and physicochemical properties of mwcnt doped polyvinyl chloride/poly (epsilon-caprolactone) blend. J Polym Res 29(4):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-02947-1
Haruna H, Pekdemir ME, Tukur A, Coskun M (2020) Characterization, thermal and electrical properties of aminated PVC/oxidized MWCNT composites doped with nanographite. J Therm Anal Calorim 139(6):3887–3895
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52005211), the Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan Project (No. YDZJ202101ZYTS071), and National key R & D projects (No. 2018YFF01012402), and Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Mineral Processing (BGRIMM-KJSKL-2021-25).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Handling Editor: Jaime Grunlan.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Ji, D., Yang, X. et al. 4D printing of bilayer structures with programmable shape-shifting behavior. J Mater Sci 57, 21309–21323 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07981-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07981-4