Abstract
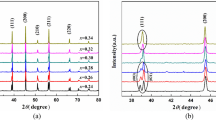
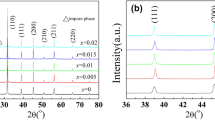
Lead-free and high-temperature piezoelectric ceramics of xBiFeO3–(1 − x)BaTiO3-1.0 mol% MnO2 (0.67 ≤ x ≤ 0.78) (xBF–(1 − x)BT-Mn) were fabricated by the conventional solid-state reaction method, and their high-temperature dielectric, piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties near the morphotropic phase boundary were studied systematically. XRD analysis revealed that xBF–(1 − x)BT-Mn ceramics exhibited pure perovskite structure, and the phase was driven by composition variation from the pseudo-cubic (0.67 ≤ x < 0.70) to rhombohedral (0.70 ≤ x ≤ 0.78). The dielectric constant ε r (1 kHz), dielectric loss tanδ (1 kHz), Curie temperature T C, depolarization temperature T d, piezoelectric constant d 33, remnant polarization P r (60 kV/cm) and room temperature planar electromechanical coupling factor k p of xBF–(1 − x)BT-Mn ceramics of x = 0.70 were 740, 0.045, 487, 430 °C, 35.5 μC/cm2, 177 pC/N and 0.37, respectively. The unipolar strain and high field strain coefficient d *33 of xBF–(1 − x)BT-Mn ceramics with x = 0.70 increased up to 0.26% and 652 pm/V at 180 °C. Temperature dependence of ε r, tanδ and k p of xBF–(1 − x)BT-Mn ceramics with x = 0.75 was stable from room temperature even up to 500 °C. These results indicated that xBF–(1 − x)BT-Mn ceramics were promising candidates for high-temperature lead-free piezoelectric applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quan ND, Huu Bac L, Thiet DV et al (2014) Current development in lead-free Bi0.5(Na,K)0.5TiO3-based piezoelectric materials. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2014:365391. doi:10.1155/2014/365391
Panda PK (2009) Review: environmental friendly lead-free piezoelectric materials. J Mater Sci 44(19):5049–5062. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3643-0
Zhou C, Feteira A, Shan X et al (2012) Remarkably high-temperature stable piezoelectric properties of Bi(Mg0.5Ti0.5)O3 modified BiFeO3–BaTiO3 ceramics. Appl Phys Lett 101(3):032901. doi:10.1063/1.4736724
Turner RC, Fuierer PA, Newnham RE et al (1994) Materials for high temperature acoustic and vibration sensors: a review. Appl Acoust 41(4):299–324
Rödel J, Jo W, Seifert KTP et al (2009) Perspective on the development of lead-free piezoceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 92(6):1153–1177
Wu J, Xiao D, Zhu J (2015) Potassium–sodium niobate lead-free piezoelectric materials: past, present, and future of phase boundaries. Chem Rev 115(7):2559–2595
Kumar MM, Palkar VR, Srinivas K et al (2000) Ferroelectricity in a pure BiFeO3 ceramic. Appl Phys Lett 76(19):2764–2766
Rojac T, Kosec M, Damjanovic D (2011) Large electric-field induced strain in BiFeO3 ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 94(12):4108–4111
Wang QQ, Wang Z, Liu XQ et al (2012) Improved structure stability and multiferroic characteristics in CaTiO3-modified BiFeO3 ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 95(2):670–675
Buscaglia MT, Mitoseriu L, Buscaglia V et al (2006) Preparation and characterisation of the magneto-electric xBiFeO3–(1 − x)BaTiO3 ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc 26(14):3027–3030
Kumar MM, Srinivas A, Suryanarayana SV (2000) Structure property relations in BiFeO3–BaTiO3 solid solutions. J Appl Phys 87(2):855–862
Wang TH, Tu CS, Ding Y et al (2011) Phase transition and ferroelectric properties of xBiFeO3–(1 − x) BaTiO3 ceramics. Curr Appl Phys 11(3):S240–S243
Leontsev SO, Eitel RE (2010) Progress in engineering high strain lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Sci Technol Adv Mat 11(4):044302. doi:10.1088/1468-6996/11/4/044302
Zhu WM, Ye ZG (2004) Effects of chemical modification on the electrical properties of 0.67BiFeO3–0.33PbTiO3 ferroelectric ceramics. Ceram Int 30(7):1435–1442
Ma Y, Chen XM (2009) Enhanced multiferroic characteristics in NaNbO3-modified BiFeO3 ceramics. J Appl Phys 105(5):4107. doi:10.1063/1.3081648
Kim JS, Cheon CI, Lee CH et al (2004) Weak ferromagnetism in the ferroelectric BiFeO3–ReFeO3–BaTiO3 Solid Solutions (Re = Dy, La). J Appl Phys 96(1):468–474
Singh A, Pandey V, Kotnala RK et al (2008) Direct evidence for multiferroic magnetoelectric coupling in 0.9BiFeO3–0.1BaTiO3. Phys Rev Lett 101(24):247602. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.247602
Chen J, Cheng J (2016) High electric-induced strain and temperature-dependent piezoelectric properties of 0.75BF–0.25BZT lead-free ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 99(2):536–542
Lee MH, Kim DJ, Park JS et al (2015) High-performance lead-free piezoceramics with high curie temperatures. Adv Mater 27(43):6976–6982
Leontsev SO, Eitel RE (2009) Dielectric and piezoelectric properties in Mn-modified (1 − x)BiFeO3–xBaTiO3 Ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 92(12):2957–2961
Li Q, Wei J, Cheng J et al (2017) High temperature dielectric, ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of Mn-modified BiFeO3–BaTiO3 lead-free ceramics. J Mater Sci 52(1):229–237
Maurya D, Thota H, Garg A et al (2008) Magnetic studies of multiferroic Bi1−x Sm x FeO3 ceramics synthesized by mechanical activation assisted processes. J Phys-Condens Mat 21(2):026007. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/21/2/026007
Yang H, Zhou C, Liu X et al (2013) Piezoelectric properties, and temperature stabilities of Mn-and Cu-modified BiFeO3–BaTiO3 high temperature ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc 33(6):1177–1183
Liu XH, Xu Z, Wei XY et al (2008) Ferroelectric and ferromagnetic properties of 0.7BiFe1−x Cr x O3–0.3BaTiO3 solid solutions. J Am Ceram Soc 91(11):3731–3734
Zhou Q, Zhou C, Yang H et al (2014) Piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties of Ga modified BiFeO3–BaTiO3 lead free ceramics with high curie temperature. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 25(1):196–201
Wu YJ, Chen XK, Zhang J et al (2012) Magnetic enhancement across a ferroelectric–antiferroelectric phase boundary in Bi1–xNdxFeO3. J Appl Phys 111(5):053927. doi:10.1063/1.3693531
Cen Z, Zhou C, Yang H et al (2013) Remarkably high-temperature stability of Bi(Fe1−x Al x )O3–BaTiO3 solid solution with near-zero temperature coefficient of piezoelectric properties. J Am Ceram Soc 96(7):2252–2256
Behera C, Choudhary RNP, Das PR (2014) Structural and electrical properties of La-modified BiFeO3–BaTiO3 composites. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 25(5):2086–2095
Zhou X, Zhou C, Zhou Q et al (2014) Investigation of structural and electrical properties of B-site complex Ion (Mg1/3Nb2/3)4+-modified high-curie-temperature BiFeO3–BaTiO3 ceramics. J Electron Mater 43(3):755–760
Tong K, Zhou C, Wang J et al (2017) Enhanced piezoelectricity and high-temperature sensitivity of Zn-modified BF–BT ceramics by in situ and ex situ measuring. Ceram Int 43(4):3734–3740
Ariizumi T, Zushi J, Kojima S et al (2012) Effects of Mn additive on dielectric and piezoelectric properties of (Na0.5K0.5)NbO3–BaZrO3–(Bi0.5K0.5)TiO3 ternary system. Jpn J Appl Phys 51(7S):07GC01. doi:10.1143/JJAP.51.07GC01
Zhang H, Jo W, Wang K et al (2014) Compositional dependence of dielectric and ferroelectric properties in BiFeO3–BaTiO3 solid solutions. Ceram Int 40(3):4759–4765
Zheng Q, Luo L, Lam KH et al (2014) Enhanced ferroelectricity, piezoelectricity, and ferromagnetism in Nd-modified BiFeO3–BaTiO3 lead-free ceramics. J Appl Phys 116(18):184101. doi:10.1063/1.4901198
Lin Y, Yu J (2014) Ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of high temperature perovskite-type 0.69BiFeO3–0.02Bi(Mg1/2Ti1/2)O3–0.29BaTiO3 ceramics. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 25(12):5462–5466
Rojac T, Kosec M, Budic B et al (2010) Strong ferroelectric domain-wall pinning in BiFeO3 ceramics. J Appl Phys 108(7):074107. doi:10.1063/1.3490249
Lin Y, Zhang L, Yu J (2015) Stable piezoelectric property of modified BiFeO3–BaTiO3 lead-free piezoceramics. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 26(11):8432–8441
Zheng W, Yu J (2016) Residual tensile stresses and piezoelectric properties in BiFeO3–Bi (Zn1/2Ti1/2)O3–PbTiO3 ternary solid solution perovskite ceramics. AIP Adv 6(8):085314. doi:10.1063/1.4961641
Zhang S, Eitel RE, Randall CA et al (2005) Manganese-modified BiScO3–PbTiO3 piezoelectric ceramic for high-temperature shear mode sensor. Appl Phys Lett 86(26):262904. doi:10.1063/1.1968419
Wei YX, Wang XT, Zhu JT, Wang XL, Jia JJ (2013) Dielectric, ferroelectric, and piezoelectric properties of BiFeO3–BaTiO3 ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 96(10):3163–3168
Song TH, Eitel RE, Shrout TR et al (2004) Dielectric and piezoelectric properties in the BiScO3–PbTiO3–PbO·SnO2 ternary system. Jpn J Appl Phys 43(8R):5392. doi:10.1143/JJAP.43.5392
Wang D, Khesro A, Murakami S et al (2016) Temperature dependent, large electromechanical strain in Nd-doped BiFeO3–BaTiO3 lead-free ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc 37:1857–1860
Chen J, Dong Y, Cheng J (2015) Reduced dielectric loss and strain hysteresis in (0.97-x) BiScO3−x PbTiO3–0.03Pb (Mn1/3Nb2/3)O3 piezoelectric ceramics. Ceram Int 41(8):9828–9833
Chen J, Jin G, Wang CM et al (2014) Reduced dielectric loss and strain hysteresis in Fe and Mn comodified high-temperature BiScO3–PbTiO3 ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 97(12):3890–3896
Kungl H, Fett T, Wagner S et al (2007) Nonlinearity of strain and strain hysteresis in morphotropic LaSr-doped lead zirconate titanate under unipolar cycling with high electric fields. J Appl Phys 101:044101. doi:10.1063/1.2434836
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51302163, 51672169).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Fu, D., Cheng, J. et al. Temperature dependence of the dielectric and piezoelectric properties of xBiFeO3–(1 − x)BaTiO3 ceramics near the morphotropic phase boundary. J Mater Sci 52, 10726–10737 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1280-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1280-6