Abstract
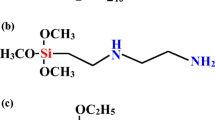
The facile approach of non-covalent surface treatment utilizing poly(ethyleneimine) (PEI) polymer was applied to modify graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs). The effects of surface modification and various GNPs–PEI loadings to cure characteristic, mechanical, physical, and morphological properties of natural rubber (NR)/ethylene–propylene–diene–monomer (EPDM) blend nanocomposites were studied and compared to the unfilled NR/EPDM blend and blends filled with unmodified GNPs at similar loadings. We found that the modification of GNPs surface significantly influences the properties of NR/EPDM blends. The addition of GNPs significantly improved the blend’s processability, offering approximately a 104.30 % increase in tensile strength obtained with the addition of 5.00 wt% GNPs–PEI. A reduced swelling index of Q f/Q g in parallel with an increase in modified GNPs–PEI content revealed enhancements in terms of rubber–filler interactions between the NR/EPDM matrix and GNPs. These findings were further supported by X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, thermogravimetry analysis, and fracture morphology by scanning electron microscope.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soldano C, Mahmood A, Dujardin E (2010) Production, properties and potential of graphene. Carbon 48:2127–2150
Zhang YY, Wang CM, Cheng Y, Xiang Y (2011) Mechanical properties of bilayer graphene sheets coupled by sp3 bonding. Carbon 49:4511–4517
Li W, Tang X-Z, Zhang H-B, Jiang Z-G, Yu Z-Z, Du X-S, Mai Y-W (2011) Simultaneous surface functionalization and reduction of graphene oxide with octadecylamine for electrically conductive polystyrene composites. Carbon 49:4724–4730
Wu H, Drzal LT (2012) Graphene nanoplatelet paper as a light-weight composite with excellent electrical and thermal conductivity and good gas barrier properties. Carbon 50:1135–1145
Cao Y, Feng J, Wu P (2010) Preparation of organically dispersible graphene nanosheet powders through a lyophilization method and their poly(lactic acid) composites. Carbon 48:3834–3839
Raza MA, Westwood AVK, Stirling C (2012) Effect of processing technique on the transport and mechanical properties of graphite nanoplatelet/rubbery epoxy composites for thermal interface applications. Mater Chem Phys 132:63–73
Sridhar V, Lee I, Chun HH, Park H (2013) Graphene reinforced biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) nano-composites. eXPRESS Polym Lett 7:320–328
Fang M, Wang K, Lu H, Yang Y, Nutt S (2009) Covalent polymer functionalization of graphene nanosheets and mechanical properties of composites. J Mater Chem 19:7098–7105
Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Piner RD, Kohlhaas KA, Kleinhammes A, Jia Y, Wu Y, Nguyen ST, Ruoff RS (2007) Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 45:1558–1565
Kuilla T, Bhadra S, Yao D, Kim NH, Bose S, Lee JH (2010) Recent advances in graphene based polymer composites. Prog Polym Sci 35:1350–1375
Ma J, Meng Q, Zaman I, Zhu S, Michelmore A, Kawashima N, Wang CH, Kuan HC (2014) Development of polymer composites using modified, high-structural integrity graphene platelets. Compos Sci Technol 91:82–90
Mady MM, Mohammed WA, El-Guendy NM, Elsayed AA (2011) Interaction of DNA and polyethylenimine: Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) studies. Int J Phys Sci 6:7328–7334
Shan C, Wang L, Han D, Li F, Zhang Q, Zhang X, Niu L (2013) Polyethyleneimine-functionalized graphene and its layer-by-layer assembly with Prussian blue. Thin Solids Films 534:572–576
Wang F, Liu P, Nie T, Wei H, Cui Z (2013) Characterization of a polyamine microsphere and its adsorption for protein. Int J Mol Sci 14:17–29
Wootthikanokkhan J, Tunjongnawin P (2003) Investigation of the effect of mixing schemes on cross-link distribution and tensile properties of natural–acrylic rubber blends. Polym Test 22:305–312
Bitinis N, Verdejo R, Maya EM, Espuche E, Cassagnau P, Lopez-Manchado MA (2012) Physicochemical properties of organoclay filled polylactic acid/natural rubber blend bionanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 72:305–313
Kongsinlark A, Rempel GL, Prasassarakich P (2012) Synthesis of monodispersed polyisoprene–silica nanoparticles via differential microemulsion polymerization and mechanical properties of polyisoprene nanocomposite. Chem Eng J 193–194:215–226
Sirisinha C, Saeoui P, Guaysomboon J (2004) Oil and thermal aging resistance in compatibilized and thermally stabilized chlorinated polyethylene/natural rubber blends. Polym 45:4909–4916
Alipour A, Naderi G, Bakhshandeh GH, Vali H, Shokoohi S (2011) Elastomer nanocomposites based on NR/EPDM/organoclay: morphology and properties. Int Polym Proc XXVI 48–55:2011
Arayapranee W, Rempel GL (2007) Properties of NR/EPDM blends with or without methyl methacrylate–butadiene–styrene (MBS) as a compatibilizer. Int J Mater Struct Reliab 5:1–12
Botros SH, El Sayed AM (2001) Swelling behavior of NR/EPDM rubber blends under compression strain. J Appl Polym Sci 82:3052–3057
Motaung TE, Luyt AS, Thomas S (2011) Morphology and properties of NR/EPDM rubber blends filled with small amounts of titania nanoparticles. Polym Compos 32:1289–1296
Nabil H, Ismail H, Azura AR (2013) Compounding, mechanical and morphological properties of carbon-black-filled natural rubber/recycled ethylene propylene diene monomer (NR/R-EPDM) blends. Polym Test 32:385–393
Sae-oui P, Sirisinha C, Thepsuwan U, Thapthong P (2007) Influence of accelerator type on properties of NR/EPDM blends. Polym Test 26:1062–1067
Shehata AB, Afifi H, Darwish NA, Mounir A (2006) Evaluation of the effect of polymeric compounds as compatibilizers for NR/EPDM blend. Polym Plast Technol Eng 45:165–170
Zaharescu T, Meltzer V, Vilcu R (1998) DSC studies on specific heat capacity of irradiated ethylene–propylene elastomers-II. EPDM. Polym Degrad Stab 61:383–387
Arayapranee W, Rempel GL (2008) A comparative study of the cure characteristics, processability, mechanical properties, ageing, and morphology of rice husk ash, silica and carbon black filled 75:25 NR/EPDM blends. J Appl Polym Sci 109:932–941
Zaharescu T, Meltzer V, Vilcu R (2000) Thermal properties of EPDM/NR blends. Polym Degrad Stab 70:341–345
Sadayuki N, Tatsuo S (2007) Development of EPDM grades with good processability characteristics—specialized polymer design for anti-vibration rubber. Sumitomo Kagaku 2007-I:1–9
Zhang H, Datta RN, Talma AG, Noordermeer JWM (2010) Maleic-anhydride grafted EPM as compatibilising agent in NR/BR/EPDM blends. Eur Polym J 46:754–766
El-Sabbagh SH (2003) Compatibility study of natural rubber and ethylene–propylene diene rubber blends. Polym Test 22:93–100
Ahmed K, Sirajuddin Nizami S, Raza NZ, Shirin K (2012) Cure characteristics, mechanical and swelling properties of marble sludge filled EPDM modified chloroprene rubber blends. Adv Mater Phys Chem 02:90–97
Halimatuddahliana Ismail H (2007) Thermoplastic elastomer based on PP/EPDM/ENR25 and PP/EPDM/NR blends. Polym Plast Technol Eng 43:357–368
Ismail H, Mathialagan M (2012) Comparative study on the effect of partial replacement of silica or calcium carbonate by bentonite on the properties of EPDM composites. Polym Test 31:199–208
Samaržija-Jovanović S, Jovanović V, Marković G, Konstantinović S, Marinović-Cincović M (2011) Nanocomposites based on silica-reinforced ethylene–propylene–diene–monomer/acrylonitrile–butadiene rubber blends. Compos B 42:1244–1250
Abd Razak J, Ahmad SH, Ratnam CT, Shueb MI, Mahamood MA, Yaakub J, Shamsuri SR, Mohamad N (2014) The effects of covalent treated graphene nanoplatelets surface modification to cure characteristic, mechanical, physical and morphological properties of NR/EPDM rubber blend nanocomposites. Adv Environ Biol 8:3289–3298
Abd Razak J, Ahmad SH, Ratnam CT, Mahamood MA, Lau KT, Ab Maulod HE, Munawar RF, Mohamad N (2015) Non-covalent polymeric wrapping of IGEPAL C0890 for graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs-C0890) filled NR/EPDM rubber blend nanocomposites. Appl Mech Mater 761:385–390
Abd Razak J, Ahmad SH, Ratnam CT, Mahamood MA, Yaakub J, Mohamad N (2015) Graphene nanoplatelets-filled NR/EPDM rubber blend: effects of GNPs loading on blend processability, mechanical properties and fracture morphology. Polym Res J 9:43–56
Ganguli S, Roy AK, Anderson DP (2008) Improved thermal conductivity for chemically functionalized exfoliated graphite/epoxy composites. Carbon 46:806–817
Abd Razak J, Ahmad SH, Ratnam CT, Mahamood MA, Yaakub J, Mohamad N (2015) Effects of EPDM-g-MAH compatibilizer and internal mixer processing parameters on the properties of NR/EPDM blends: an analysis using response surface methodology. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/app.42199
Abd Razak J, Ahmad SH, Ratnam CT, Mahamood MA, Yaakub J, Mohamad N (2014) NR/EPDM elastomeric rubber blend miscibility evaluation by two-level fractional factorial design of experiment. AIP Conf Proc 1614:82–89
Ghoneim AM, Ismail MN (1999) Studies on EPDM/NR blends. I. Dielectric and mechanical properties. Polym Plast Technol Eng 38:979–995
Jovanović V, Samaržija-Jovanović S, Budinski-Simendić J, Marković G, Marinović-Cincović M (2013) Composites based on carbon black reinforced NBR/EPDM rubber blends. Compos B 45:333–340
Johnson PS (2001) Rubber processing: an introduction. Carl Hanser, Munich
Pasbakhsh P, Ismail H, Ahmad Fauzi MN, Abu Bakar A (2009) Influence of maleic anhydride grafted ethylene propylene diene monomer (MAH-g-EPDM) on the properties of EPDM nanocomposites reinforced by halloysite nanotubes. Polym Test 28:548–559
Ismail H, Shaari SM, Othman N (2011) The effect of chitosan loading on the curing characteristics, mechanical and morphological properties of chitosan-filled natural rubber (NR), epoxidised natural rubber (ENR) and styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) compounds. Polym Test 30:784–790
Vijayalekshmi V (2009) Studies on natural rubber/clay nanocomposites: effect of maleic anhydride grafting of rubber. PhD Thesis, Cochin University of Science and Technology
Podstawka E, Ozaki Y, Proniewicz LM (2004) Part I: Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy investigation of amino acids and their homodipeptides adsorbed on colloidal silver. Appl Spectrosc 58:570–580
Stuart BH (2004) Infrared spectroscopy: fundamental and applications. Analytical techniques in the sciences. Wiley, London. doi:10.1002/0470011149
Geng Y, Liu MY, Li J, Shi XM, Kim JK (2008) Effects of surfactant treatment on mechanical and electrical properties of CNT/epoxy nanocomposites. Compos A 39:1876–1883
Sirqueira AS, Soares BG (2007) Compatibilization of natural rubber/EPDM blends by anhydride- and mercapto-functionalized copolymers. J Macromol Sci Part B Phys 46:639–650
Konar BB, Roy SK, Pariya TK (2010) Study on the effect of nano and active particles of alumina on natural rubber–alumina composites in the presence of epoxidized natural rubber as compatibilizer. J Macromol Sci Part A Pure Appl Chem 47:416–422
Tavakoli M, Katbab AA, Nazockdast H (2011) Effectiveness of maleic anhydride grafted EPDM rubber (EPDM-g-MAH) as compatibilizer in NR/organoclay nanocomposites prepared by melt compounding. J Macromol Sci Part B Phys 50:1270–1284
Basfar AA, Abdel-Aziz MM, Mofti S (2002) Influence of different curing systems on the physico-mechanical properties and stability of SBR and NR rubbers. Radiat Phys Chem 63:81–87
Zhang HB, Zheng WG, Yan Q, Jiang ZG, Yu ZZ (2012) The effect of surface chemistry of graphene on rheological and electrical properties of polymethylmethacrylate composites. Carbon 50:5117–5125
Guo J, Ren L, Wang R, Zhang C, Yang Y, Liu T (2011) Water dispersible graphene noncovalently functionalized with tryptophan and its poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite. Compos B 42:2130–2135
George SC, Thomas S (2001) Transport phenomena through polymeric systems. Prog Polym Sci 26:985–1017
Kumnuantip C, Sombatsompop N (2003) Dynamic mechanical properties and swelling behaviour of NR/reclaimed rubber blends. Mater Lett 57:3167–3174
Mohamad N, Yaakub J, Abd Razak J, Yaakob MY, Shueb MI, Muchtar A (2014) Effects of epoxidized natural rubber (ENR-50) and processing parameters on the properties of NR/EPDM blends using response surface methodology. J Appl Polym Sci 40713:1–8
Cerezo FT, Preston CML, Shanks RA (2007) Morphology, thermal stability, and mechanical behavior of [poly(propylene)-grafted maleic anhydride]-layered expanded graphite oxide composites. Macromol Mater Eng 292:155–168
Ramanathan T, Abdala AA, Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Herrera-Alonso M, Piner RD, Adamson DH, Schniepp HC, Chen X, Ruoff RS, Nguyen ST, Aksay IA, Prud’Homme RK, Brinson RC (2008) Functionalized graphene sheets for polymer nanocomposites. Nat Nanotechnol 3:327–331
Acknowledgements
We greatly acknowledge the research funding from Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) code FRGS/2012/FKP/TK04/02/1/F00132—Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM) for sponsoring this work. Our special gratitude to the Ministry of Education, Malaysia (MOE), Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM), the Carbon Research Technology Research Group, Advanced Manufacturing Centre of Excellence Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka, and the Malaysian Nuclear Agency (MNA) for the financial, technical, and supervisory support which made this work possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abd Razak, J., Haji Ahmad, S., Ratnam, C.T. et al. Effects of poly(ethyleneimine) adsorption on graphene nanoplatelets to the properties of NR/EPDM rubber blend nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 50, 6365–6381 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9188-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9188-5