Abstract
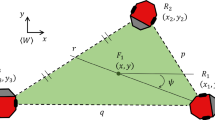
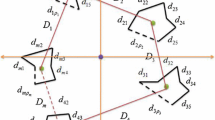
Cluster space control is a method of multirobot formation keeping that considers a group of robots to be a single entity, defining state variables to represent characteristics of the group, such as position, orientation, and shape. This technique, however, suffers from singularities when a minimal state representation is used. This paper presents three alternative implementations of this control approach that eliminate singularities through changes in the control architecture or through redundant formation definitions. These proposed solutions rely on quaternions, dual quaternions, and control implementations that produce singularity-free trajectories while maintaining a cluster level abstraction that allows for simple specification and monitoring. A key component of this work is a novel concept of representing formation shape parameters with dual quaternions. Simulation results show the feasibility of the proposed solutions and illustrate their differences and limitations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu, C.-H., Nagpal, R.: Biologically-inspired control for multi-agent self-adaptive tasks. In: AAAI (2010)
Lin, Z., Ding, W., Yan, G., Yu, C., Giua, A.: Leader–follower formation via complex laplacian. Automatica (2013)
Tan, K.-H., Lewis, M.A.: Virtual structures for high-precision cooperative mobile robotic control. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IROS, vol. 1, pp. 132–139 (Nov 1996)
Ani Hsieh, M., Kumar, V., Chaimowicz, L.: Decentralized controllers for shape generation with robotic swarms. Robotica 26(05), 691–701 (2008)
Mas, I., Kitts, C.: Dynamic control of mobile multirobot systems The cluster space formulation. Access, IEEE 2, 558–570 (2014)
Mas, I., Li, S., Acain, J., Kitts, C.: Entrapment/escorting and patrolling missions in multi-robot cluster space control, pp. 5855–5861 (2009)
Mas, I., Kitts, C.: Object manipulation using cooperative mobile multi-robot systems. Lecture Notes in Engineering and Computer Science: Proceedings of The World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science 2012, WCECS 2012, 324–329 (2012)
Kitts, C.A., Mas, I.: Cluster space specification and control of mobile multirobot systems. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 14(2), 207–218 (April 2009)
Huizenga, F.: Singularity avoidance for the cluster space control of mobile multi-robot systems. Santa Clara University, Master’s thesis (May 2012)
Belta, C., Kumar, V.: Motion generation for formations of robots: a geometric approach. In: Proceedings 2001 ICRA. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2001, vol. 2, pp. 1245–1250. IEEE (2001)
Fierro, R., Das, A., Spletzer, J., Esposito, J., Kumar, V., Ostrowski, J., Pappas, G., Taylor, C., Hur, Y., Alur, R., Lee, I., Grudic, G., Southall, B.: A framework and architecture for multi-robot coordination. The International Journal of Robotics Research 21(10-11), 977–995 (2002)
Chaimowicz, L., Sugar, T., Kumar, V.: Mario Fernando Montenegro Campos. An architecture for tightly coupled multi-robot cooperation. In: Proceedings 2001 ICRA, IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2001, vol. 3, pp. 2992–2997. IEEE (2001)
Maithripala, D.H.S., Berg, J.M., Maithripala, D.H.A., Jayasuriya, S.: A geometric virtual structure approach to decentralized formation control. In: American Control Conference (ACC) 2014, pp. 5736–5741. IEEE (2014)
Chaimowicz, L., Kumar, V.: Aerial shepherds: Coordination among uavs and swarms of robots. In: Distributed Autonomous Robotic Systems 6, pp. 243–252. Springer (2007)
Jia, Q., Li, G., Lu, J.: Formation control and attitude cooperative control of multiple rigid body systems. In: Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications 2006 ISDA’06, vol. 2, pp. 82–86. IEEE (2006)
Wang, P.K.C., Hadaegh, F.Y., Lau, K: Synchronized formation rotation and attitude control of multiple free-flying spacecraft. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 22(1), 28–35 (1999)
Wang, X., Han, D., Changbin, Y., Zheng, Z.: The geometric structure of unit dual quaternion with application in kinematic control. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 389(2), 1352–1364 (2012)
Dooley, J.R., McCarthy, J.: On the geometric analysis of optimum trajectories for cooperating robots using dual quaternion coordinates. In: Proceedings., 1993 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 1993, vol. 1, pp. 1031–1036 (1993)
Han, D.-P., Wei, Q., Li, Z.-X.: Kinematic control of free rigid bodies using dual quaternions. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 5(3), 319–324 (2008)
Wang, X., Yu, C., Lin, Z.: A dual quaternion solution to attitude and position control for rigid-body coordination. IEEE Trans. Robot. 28(5), 1162–1170 (2012)
Dong, H., Qinglei, H., Ma, G.: Dual-quaternion based fault-tolerant control for spacecraft formation flying with finite-time convergence ISA transactions (2016)
Jinjie, W., Liu, K., Gao, Y., Zhang, B.: 6dof quasi-optimal integral sliding mode control for satellite formation flying using dual quaternion. In: Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), 2013 25th Chinese, pp. 1764–1769 (2013)
Yinqiu, W., Yu, F., Yu, C.: Distributed attitude and position consensus for networked rigid bodies based on unit dual quaternion. In: Control Conference (CCC), 2015 34th Chinese, pp. 7368–7373. IEEE (2015)
Kristiansen, R., Nicklasson, P.J., Gravdahl, J.T.: Quaternion-based backstepping control of relative attitude in a spacecraft formation. In: 2006 45th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 5724–5729. IEEE (2006)
Adorno, B.V., Fraisse, P., Druon, S.: Dual position control strategies using the cooperative dual task-space framework. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), p. 2010 (2010)
Meyer, J., Sendobry, A., Kohlbrecher, S., Klingauf, U., Von Stryk, O.: Comprehensive simulation of quadrotor uavs using ros and gazebo. In: Simulation, Modeling, and Programming for Autonomous Robots, pp. 400–411. Springer (2012)
Furrer, F., Burri, M., Achtelik, M., Roland Siegwart.: Robot Operating System (ROS): The Complete Reference (Volume 1), chapter RotorS—A Modular Gazebo MAV Simulator Framework, pp. 595–625. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work has been sponsored through USAIT Grant W911NF-14-1-0008, ITBACyT 2013-17, and Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica, FONCYT PICT 2014-2055.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mas, I., Kitts, C. Quaternions and Dual Quaternions: Singularity-Free Multirobot Formation Control. J Intell Robot Syst 87, 643–660 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-016-0445-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-016-0445-x