Abstract
Purpose
Contact with cardiac tissue is an important determinant of lesion efficacy during atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation. The Sensei X™ robotic navigation system (RNS) (Hansen Medical, Mountain View, CA, USA) has been validated for contact force (CF) sensing expressed in grams (g). The Thermocool® SmartTouch™ catheter enables the measurement of catheter tip CF and direction inside the heart. We aimed to investigate the catheter CF with and without RNS during pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) procedures.
Methods
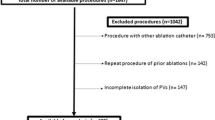
Eighty patients with symptomatic AF (56 males, age 63 ± 18) were enrolled in this study. Fifty-seven patients had paroxysmal AF and 23 early persistent AF. All procedures were performed with the Thermocool® SmartTouch™ ablation catheter. Forty patients were randomized to perform PVI with the Sensei X™ RNS (group 1), while in the other 40 patients (group 2), PVI was performed without the RNS.
Results
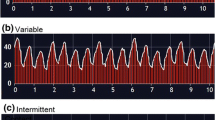
AF ablation was performed successfully in all patients without complications, while contact force was kept in the established 10–40 g range. A significantly higher CF was documented on the PVs in group 1 compared to group 2. The 1-year freedom from AF recurrence was higher in group 1 compared to group 2 (90 vs. 65 %, p = 0.04). Moreover, a significant reduction of fluoroscopy time was noted in the RNS group (13 ± 10 vs. 20 ± 10 min, respectively, p = 0.05).
Conclusions
The Sensei X™ RNS permits a significantly higher CF during transcatheter AF ablation with a low rate of AF recurrence at clinical follow-up.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camm, A. J., Lip, G. Y., De Caterina, R., Savelieva, I., Atar, D., Hohnloser, S. H., et al. (2012). ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG). 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. European Heart Journal, 33, 2719–2747.
Calkins, H., Kuck, K. H., Cappato, R., Brugada, J., Camm, A. J., Chen, S. A., et al. (2012). 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design. Heart Rhythm, 9, 632–696.
Di Biase, L., Paoletti Perini, A., Mohanty, P., Goldenberg, A. S., Grifoni, G., Santangeli, P., et al. (2014). Visual, Tactile and Contact Force Feedback: which one is more important for catheter ablation? Results from an in vitro experimental study. Heart Rhythm, 11(3), 506–513.
Kumar, S., Chan, M., Lee, J., Wong, M. C., Yudi, M., Morton, J. B., et al. (2014). Catheter-tissue contact force determines atrial electrogram characteristics before and lesion efficacy after antral pulmonary vein isolation in humans. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 25(2), 122–129.
Olson, M. D., Phreaner, N., Schuller, J. L., Nguyen, D. T., Katz, D. F., Aleong, R. G., et al. (2013). Effect of catheter movement and contact during application of radiofrequency energy on ablation lesion characteristics. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 38(2), 123–129.
Haldar, S., Jarman, J. W., Panikker, S., Jones, D. G., Salukhe, T., Gupta, D., et al. (2013). Contact force sensing technology identifies sites of inadequate contact and reduces acute pulmonary vein reconnection: a prospective case control study. International Journal of Cardiology, 168, 1160–1166.
Martinek, M., Lemes, C., Sigmund, E., Derndorfer, M., Aichinger, J., Winter, S., et al. (2012). Clinical impact of an open-irrigated radiofrequency catheter with direct force measurement on atrial fibrillation ablation. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 35, 1312–1318.
Okumura, Y., Johnson, S. B., Bunch, T. J., Henz, B. D., O’Brien, C. J., & Packer, D. L. (2008). A systematical analysis of in vivo contact forces on virtual catheter tip/tissue surface contact during cardiac mapping and intervention. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 19, 632–640.
Bai, R., DI Biase, L., Valderrabano, M., Lorgat, F., Micochova, H., Tilz, R., et al. (2012). Worldwide experience with the robotic navigation system in catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: methodology, efficacy and safety. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 23, 820–826.
Duncan, E. R., Finlay, M., Page, S. P., Hunter, R., Goromonzi, F., Richmond, L., et al. (2012). Improved electrogram attenuation during ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation with the Hansen robotic system. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 35(6), 730–738.
Lorgat, F., Pudney, E., van Deventer, H., & Chitsaz, S. (2012). Robotically controlled ablation for atrial fibrillation: the first real-world experience in Africa with the Hansen robotic system. Cardiovascular Journal of Africa, 23(5), 274–280.
Willems, S., Steven, D., Servatius, H., Hoffmann, B. A., Drewitz, I., Müllerleile, K., et al. (2010). Persistence of pulmonary vein isolation after robotic remote-navigated ablation for atrial fibrillation and its relation to clinical outcome. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 21, 1079–1084.
Di Biase, L., Wang, Y., Horton, R., Gallinghouse, G. J., Mohanty, P., Sanchez, J., et al. (2009). Ablation of atrial fibrillation utilizing robotic catheter navigation in comparison to manual navigation and ablation: single-center experience. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 20, 1328–1335.
Wazni, O. M., Barrett, C., Martin, D. O., Shaheen, N., Tarakji, K., Baranowski, B., et al. (2009). Experience with the hansen robotic system for atrial fibrillation ablation-lessons learned and techniques modified: Hansen in the real world. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 20(11), 1193–1196.
Di Biase, L., Natale, A., Barrett, C., Tan, C., Elayi, C. S., Ching, C. K., et al. (2009). Relationship between catheter forces, lesion characteristics, “popping”, and char formation: experience with Robotic Navigation System. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 20, 436–440.
Society, B. H. R. (2014). Standard for Interventional Electrophysiology Study and Catheter Ablation in Adults.
Kuck, K. H., Reddy, V. Y., Schmidt, B., Natale, A., Neuzil, P., Saoudi, N., et al. (2012). A novel radiofrequency ablation catheter using contact force sensing: Toccata study. Heart Rhythm, 9(1), 18–23.
Reddy, V. Y., Shah, D. C., Kautzenr, J., Schmidt, B., Saoudi, N., Herrera, C., et al. (2012). The relationship between contact force and clinical outcome during radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in the TOCCATA study. Heart Rhythm, 9(11), 1789–1795.
Mizuno, H., Vergara, P., Maccabelli, G., Trevisi, N., Eng, S. C., Brombin, C., et al. (2013). Contact force monitoring for cardiac mapping in patients with ventricular tachycardia. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 24, 519–524.
Dello Russo, A., Fassini, G., Casella, M., Bologna, F., Al-Nono, O., Colombo, D., et al. (2014). Simultaneous assessment of contact pressure and local electrical coupling index using robotic navigation. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 40, 23–31.
Nakagawa, H., Kautzner, J., Natale, A., Peichl, P., Cihak, R., Wichterle, D., et al. (2013). Locations of high contact force during left atrial mapping in atrial fibrillation patients: electrogram amplitude and impedance are poor predictors of electrode-tissue contact force for ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology, 6(4), 746–753.
Steven, D., Servatius, H., Rostock, T., Hoffman, B., Drewitz, I., Mullerleile, K., et al. (2010). Reduced fluoroscopy during atrial fibrillation ablation: benefits of robotic guided navigation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 21, 6–12.
Ullah, W., McLean, A., Hunter, R. J., Baker, V., Richmond, L., Cantor, E. J., et al. (2014). Randomized trial comparing robotic to manual ablation for atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 11, 1862–1869.
Ullah, W., Hunter, R. J., Haldar, S., McLean, A., Dhinoja, M., Sporton, S., et al. (2014). Comparison of robotic and manual persistent AF ablation using catheter contact force sensing: an international multicenter registry study. PACE, 37, 1427–1435.
Casella, M., Pelargonio, G., Dello Russo, A., Riva, S., Bartoletti, S., Santangeli, P., et al. (2011). "Near-zero" fluoroscopic exposure in supraventricular arrhythmia ablation using the EnSite NavX™ mapping system: personal experience and review of the literature. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 31, 109–118.
Ait-Ali, L., Andreassi, M. G., Foffa, I., Spadoni, I., Vano, E., & Picano, E. (2010). Cumulative patient effective dose and acute radiation-induced chromosomal DNA damage in children with congenital heart disease. Heart, 96, 269–274.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dello Russo, A., Fassini, G., Conti, S. et al. Analysis of catheter contact force during atrial fibrillation ablation using the robotic navigation system: results from a randomized study. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 46, 97–103 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-016-0102-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-016-0102-0