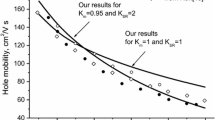
Abstract
Analytic expressions for the low-field mobility have been obtained in black phosphorus crystals and multilayer phosphorene. Acoustic and optical phonons, charged impurities and surface roughness are adopted as the scattering system. Theoretical considerations are based on a quantum kinetic equation and special form of the non-equilibrium distribution function (shifted Fermi distribution). Our calculations reveal that the hole mobility in black phosphorus crystals is limited by scattering with both acoustic and optical phonons over a wide temperature range of 10–400 K. The hole mobility in multilayer phosphorene is thus limited by impurity and optical phonon scattering in this temperature range.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qian, X., Wang, Y., Li, W., Lu, J., Li, J.: Modelling of stacked 2D materials and devices. 2D Mater 2(3), 032003 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1583/2/3/032003
Das, S., Demarteau, M., Roelofs, A.: Ambipolar phosphorene field effect transistor. ACS Nano 8(11), 11730 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn505868h
Gaddemane, G., Vandenberghe, W.G., Van de Put, M.L., Chen, S., Tiwari, S., Chen, E., Fischetti, M.V.: Theoretical studies of electronic transport in mono- and bi-layer phosphorene: a critical overview. arXiv:1801.08606v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] (2018)
Takagi, S., Toriumi, A., Iwase, M., Tango, H.: On the universality of inversion layer mobility in Si MOSFET’s: Part II-effects of surface orientation. IEEE Trans. ED 41(12), 2363 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1109/16.337450
Qiao, J., Kong, X., Hu, Z.-X., Yang, F., Ji, W.: High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun. 5, 4475 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5475
Wang, Y., Ding, Y.: Electronic structure and carrier mobilities of arsenene and antimonene nanoribbons: a first-principle study. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10, 254 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-0955-7
Jing, Y., Zhang, X., Zhou, Z.: Phosphorene: what can we know from computations? WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 6(1), 5 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/wcms.1234
Qiao, J., Kong, X., Hu, Z.-X., Yang, F., Ji, W.: High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun. 5, 4475 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5475
Fukuoka, S., Taen, T., Osada, T.: Electronic structure and the properties of phosphorene and few-layer black phosphorus. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 84, 121004 (2015). https://doi.org/10.7566/JPSJ.84.121004
Xu, Y., Zhang, H., Shao, H., Ni, G., Li, J., Lu, H., Zhang, R., Peng, B., Zhu, Y., Zhu, H., Soukoulis, C.M.: First-principles study on the electronic, optical, and transport properties of monolayer α- and β-GeSe. Phys. Rev. B 96, 245421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.96.245421
Boiko, I.I., Kozlovskiy, S.I.: Investigation of conductivity and piezoresistance of n-type silicon on basis of quantum kinetic equation and model distribution function. Sens. Actuators A 147, 17 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2008.03.002
Liu, H., Du, Y., Deng, Y., Ye, P.D.: Semiconducting black phosphorus: synthesis, transport properties and electronic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 2732 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00257A
Boiko, I.I.: Kinetics of Electron Gas Interacting with Fluctuating Potential. Naukova dumka, Kiev (1993). (in Russian)
Boiko, I.I. (ed.): Transport of Carriers in Semiconductors. V. Lashkaryov Institute of Semiconductor Physics, NAS of Ukraine, Kyiv (2009). (in Russian)
Knezevic, I., Ramayya, E.B., Vasileska, D., Goodnick, S.M.: Diffusive transport in quasi-2D and quasi-1D electron systems. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 6, 1725 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1166/jctn.2009.1240
Stroscio, M.A., Dutta, M.: Phonons in Nanostructures. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Kozlovskiy, S.I., Sharan, N.N.: Piezoresistance effect in n-type silicon: from bulk to nanowires. J. Comput. Electron. 13(2), 515 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-014-0563-2
Ando, Y., Cappy, A.: Ensemble Monte Carlo simulation for electron transport in quantum wire structures. J. Appl. Phys. 74, 3983 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.354441
Ferry, D.K., Goodnick, S.M., Bird, J.: Transport in Nanostructures, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2009)
Ando, T., Fowler, A.B., Stern, F.: Electronic properties of two-dimensional systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 54(2), 437 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.54.437
Jin, S., Fischetti, M.V., Tang, T.-W.: Modeling of surface-roughness scattering in ultrathin-body SOI MOSFETs. IEEE Trans. ED 54(9), 2191 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2007.902712
Narita, S., Terada, S., Mori, S., Muro, K., Akahama, Y., Endo, S.: Far-Infrared cyclotron resonance absorptions in black phosphorus single crystals. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 52, 3544 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.52.3544
Chang, J., Hobbs, C.: Theoretical study of phosphorene tunneling field effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 083509 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4913842
Jain, A., McGaughey, A.J.H.: Strongly anisotropic in-plane thermal transport in single-layer black phosphorene. Sci. Rep. 5, 8051 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08501
Asahina, H., Morita, A.: Band structure and optical properties of black phosphorus. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 17, 1839 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3719/17/11/006
Akahama, Y., Endo, S., Narita, S.: Electrical properties of black phosphorus single. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 52, 2148 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.52.2148
Zhang, Y., Rubio, A., Lay, G.L.: Emergent elemental two-dimensional materials beyond graphene. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 50(5), 053004 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aa4e8b
Lin, D., Liu, Y., Liang, Z., Lee, H.-W., Sun, J., Wang, H., Yan, K., Xie, J., Cui, Y.: Layered reduced graphene oxide with nanoscale interlayer gaps as a stable host for lithium metal anodes. Nat. Nanotech. 11, 626 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2016.32
Gillgren, N., Wickramaratne, D., Shi, Y., Espiritu, T., Yang, J., Hu, J., Wei, J., Liu, X., Mao, Z., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T., Bockrath, M., Barlas, Y., Lake, R.K., Lau, C.N.: Gate tunable quantum oscillations in air-stable and high mobility few-layer phosphorene heterostructures. 2D Mater (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1583/2/1/011001
Li, L., Ye, G.J., Tran, V., Fei, R., Chen, G., Wang, H., Wang, J., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T., Yang, L., Chen, X.H., Zhang, Y.: Quantum oscillations in a two-dimensional electron gas in black phosphorus thin films. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 608–613 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2015.91
Xia, F., Wang, H., Jia, Y.: Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nat. Commun. 5, 4458 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5458
Pirovano, A., Lacaita, A.L., Zandler, G., Oberhuber, R.: Explaining the dependences of the hole and electron mobilities in Si inversion layers. IEEE Trans ED 47(4), 718 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/16.830985
Das, S., Appenzeller, J.: Screening and interlayer coupling in multilayer MoS2. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 7(4), 268 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssr.201307015
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kovalenko, K.L., Kozlovskiy, S.I. & Sharan, N.N. A quantum kinetic approach for calculating low-field mobility in black phosphorus crystals and multilayer phosphorene. J Comput Electron 17, 1549–1556 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-018-1255-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-018-1255-0