Abstract
Resistive random access memory (RRAM) technology promises superior performance and scalability while employing well-developed fabrication processes. Conductance in insulating oxides employed in RRAM devices can be strongly affected by atomic-level changes that makes cell switching properties extremely sensitive to operation conditions inducing local structural modifications. This opens an opportunity to condition the memory cell stack by forming a conductive filament capable of high frequency, low energy switching. Certain materials with pre-existing conductive paths, in particular some polycrystalline oxides, like hafnia, are shown to respond well to this approach. For this class of materials, the concept of ultra-fast pulse technique as an ultimate method for assessing RRAM switching capabilities in circuitry operations is discussed. Hafnia-based cells demonstrate compliance-free (1R) forming with no current overshoot, low operation currents, and reduced variability.



After Ref. [15]


After Ref. [25]

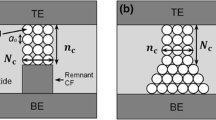
From [28]

After [28]


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawa, A.: Resistive switching in transition metal oxides. Mater. Today 11, 28–36 (2008)
Bersuker, G., Gilmer, D.C., Veksler, D., Yum, J., Park, H., Lian, S., Vandelli, L., Padovani, A., Larcher, L., McKenna, K., Shluger, A., Iglesias, V., Porti, M., Nafria, M., Taylor, W., Kirsch, P.D., Jammy, R.: Metal oxide RRAM switching mechanism based on conductive filament microscopic properties. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), pp. 19.6.1–19.6.4 (2010)
Kalantarian, A., Bersuker, G., Gilmer, D.C., Veksler, D., Butcher, B., Padovani, A., Pirrotta, O., Larcher, L., Geer, R., Nishi, Y., Kirsch, P.: Controlling uniformity of RRAM characteristics through the forming process. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), pp. 6C.4.1–6C.4.5 (2012)
Bersuker, G., Gilmer, D.C.: Metal oxide resistive random access memory (RRAM) technology. In: Advances in Non-volatile Memory and Storage Technology. In: Nishi, Y. (ed.) Woodhead Publishing, pp. 288–340 (2014). ISBN 9780857098030
Vandelli, L., Padovani, A., Larcher, L., Broglia, G., Ori, G., Montorsi, M., Bersuker, G., Pavan, P.: Comprehensive physical modeling of forming and switching operations in HfO\(_2\) RRAM devices. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), pp. 17.5.1–17.5.4 (2011)
Butcher, B., Bersuker, G., Vandelli, L., Padovani, A., Larcher, L., Kalantarian, A., Geer, R., Gilmer, D.C.: Modeling the effects of different forming conditions on RRAM conductive filament stability. In: 2013 5th IEEE International Memory Workshop (IMW), pp. 52–55 (2013)
Shrestha, P.R., Nminibapiel, D., Kim, J.H., Campbell, J.P., Cheung, K.P., Deora, S., Bersuker, G., Baumgart, H.: Energy control paradigm for compliance-free reliable operation of RRAM. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, pp. MY.10.1–MY.10.4 (2014)
Nminibapiel, D.M., Veksler, D., Shrestha, P.R., Kim, J.H., Campbell, J.P., Ryan, J.T., Baumgart, H., Cheung, K.P.: Characteristics of resistive memory read fluctuations in endurance cycling. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 38(3), 326–329 (2017)
Magyari-Kope, B., Zhao, L., Kamiya, K., Yang, M.Y., Niwa, M., Shiraishi, K., Nishi, Y.: The interplay between electronic and ionic transport in the resistive switching process of random access memory devices. ECS Trans. 64, 153–158 (2014)
Bradley, S.R., Shluger, A.L., Bersuker, G.: Electron-injection-assisted generation of oxygen vacancies in monoclinic HfO\(_{2}\). Phys. Rev. Appl. 4, 064008 (2015)
Ayvazian, T., Bersuker, G., Lingley, Z.R., Brodie, M.J., Foran, B.J.: Conductive paths through polycrystalline BaTiO\(_3\): scanning probe microscopy study. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 072904 (2016)
Padovani, A., Larcher, L., Pirrotta, O., Vandelli, L., Bersuker, G.: Microscopic modeling of HfO\(_x\) RRAM operations: from forming to switching. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 62, 1998–2006 (2015)
McKenna, K., Shluger, A.: The interaction of oxygen vacancies with grain boundaries in monoclinic HfO\(_{2}\). Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 222111 (2009)
McKenna, K.P., Shluger, A.L.: Electronic properties of defects in polycrystalline dielectric materials. Microelectron. Eng. 86, 1751–1755 (2009)
Lanza, M., Zhang, K., Porti, M., Nafría, M., Shen, Z.Y., Liu, L.F., Kang, J.F., Gilmer, D., Bersuker, G.: Grain boundaries as preferential sites for resistive switching in the HfO\(_2\) resistive random access memory structures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 123508 (2012)
Lanza, M., Bersuker, G., Porti, M., Miranda, E., Nafr’ıa, M., Aymerich, X.: Resistive switching in hafnium dioxide layers: local phenomenon at grain boundaries. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 193502 (2012)
Calka, P., Sowinska, M., Bertaud, T., Walczyk, D., Dabrowski, J., Zaumseil, P., Walczyk, C., Gloskovskii, A., Cartoixa, X., Sune, J., Schroeder, T.: Engineering of the chemical reactivity of the Ti/HfO\(_2\) interface for RRAM: experiment and theory. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 5056–5060 (2014)
Young-Fisher, K.G., Bersuker, G., Butcher, B., Padovani, A., Larcher, L., Veksler, D., Gilmer, D.C.: Leakage current-forming voltage relation and oxygen gettering in HfO\(_x\) RRAM devices. Electron Device Lett. 34, 750–752 (2013)
Bradley, S.R., Bersuker, G., Shluger, A.L.: Modeling of oxygen vacancy aggregates in monoclinic HfO\(_2\): Can they contribute to conductive filament formation? J. Phys. Condens. Matter 27, 415401 (2015)
McKenna, K.P.: Optimal stoichiometry for nucleation and growth of conductive filaments in HfO\(_x\). Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 22, 025001 (2014)
Butcher, B., Bersuker, G., Gilmer, D.C., Larcher, L., Padovani, A., Vandelli, L., Geer, R., Kirsch, P.D.: Connecting the physical and electrical properties of Hafnia-based RRAM. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, pp. 22.2.1–22.2.4 (2013)
Waser, R., Dittmann, R., Staikov, G., Szot, K.: Redox based resistive switching memories nanoionic mechanisms, prospects, and challenges. Adv. Mater. 21, 2632–2663 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200900375
Wong, H.-S.P., Lee, H.-Y., Yu, S., Yu, S., Chen, Y.-S., Wu, Y., Chen, P.-S., Lee, B., Chen, F.T., Tsai, M.-J.: Metal-oxide RRAM. Proc. IEEE 100, 1951–1970 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2012.2190369
Yu, S.M., Guan, X., Wong, H.-S., et al.: On the stochastic nature of resistive switching in metal oxide RRAM: physical modeling, Monte Carlo simulation, and experimental characterization. In: IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEDM.2011.6131572
Veksler, D., Bersuker, G., Chakrabarti, B., Vogel, E., Deora, S., Matthews, K., Gilmer, D.C., Li, H.F., Gausepohl, S., Kirsch, P.D.: Methodology for the statistical evaluation of the effect of random telegraph noise (RTN) on RRAM characteristics. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), pp. 9.6.1–9.6.4 (2012)
Veksler, D., Bersuker, G., Vandelli, L., Padovani, A., Larcher, L., Muraviev, A., Chakrabarti, B., Vogel, E., Gilmer, D.C., Kirsch, P.D.: Random telegraph noise (RTN) in scaled RRAM devices. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), pp. MY.10.1–MY.10.4 (2013)
Kwon, J., Sharma, A., Chen, C.-Y., Fantini, A., Jurczak, M., Picard, Y., Bain, J., Skowronski, M.: Transient thermometry and HRTEM analysis of RRAM thermal dynamics during switching and failure. In: 2016 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), pp. 7B-3
Nminibapiel, D.M., et al.: Impact of RRAM read fluctuations on the program-verify approach. Electron Device Lett. 38, 736–739 (2017)
Fantini, A., Gorine, G., Degraeve, R., Goux, L., Chen, C.Y., Redolfi, A., Clima, S., Cabrini, A., Torelli, G., Jurczak, M.: Intrinsic program instability in HfO\(_2\) RRAM and consequences on program algorithms. In: IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), pp. 7.5.1–7.5.4 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEDM.2015.7409648
Wang, C., Wu, H., Gao, B., Dai, L., Deng, N., Sekar, D.C., Lu, Z., Kellam, M., Bronner, G., Qian, H.: Relaxation effect in RRAM arrays: demonstration and characteristics. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 37, 182–185 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2015.2508034
Clima, S., Chen, Y.Y., Fantini, A., Goux, L., Degraeve, R., Govoreanu, B., Pourtois, G., Jurczak, M.: Intrinsic tailing of resistive states distribution in amorphous HfO\(_x\) and TaO\(_x\) based resistive random access memories. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 37, 769–771 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2015.2448731
Ambrogio, S., Balatti, S., McCaffrey, V., Wang, D.C., Ielmini, D.: Noise-induced resistance broadening in resistive switching memory—Part II: array statistics. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 62, 3812–3819 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2015.2477135
Pan, Y., Cai, Y., Liu, Y., Fang, Y., Yu, M., Tan, S., Huang, R.: Microscopic origin of read current noise in TaO\(_x\)-based resistive switching memory by ultra-low temperature measurement. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 153504 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4945790
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bersuker, G., Veksler, D., Nminibapiel, D.M. et al. Toward reliable RRAM performance: macro- and micro-analysis of operation processes. J Comput Electron 16, 1085–1094 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-017-1105-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-017-1105-5