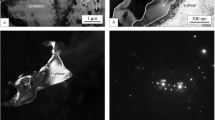
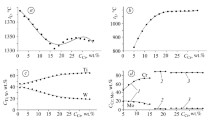
The use of x-ray spectroscopy is considered for studying the specific distribution of alloying elements in structural components of heat-resistant nickel alloys, namely, between secondary carbides, since the role of carbides in the formation of the properties of these alloys is complex. Thermodynamic processes of separation of excesses of phases are theoretically modeled using the CALPHAD method in the JMatPro software suite. Also, structures and distributions of chemical elements in carbides are studied as functions of the alloying level using an REM-106I scanning electron microscope. Phase reactions in typical carbides M23C6 and M6C in alloy ZhS6K tend to transform depending on the doping level by the given elements. Mathematical dependences of the infl uence of the alloying level on the carbide separation (dissolution) temperature and of changes in the alloy chemical composition on the contents of elements in the carbides are established. Carbide M6C gradually degenerates as the Cr content increases and disappears at 11 mass%. A topologically close-packed phase is formed in the structure with 3 mass% Mo in the alloy. Carbide M6C approaches the Mo-based monocarbide with 8 mass% Mo. Dependences of the carbide separation (dissolution) temperature on the amount of tungsten (W) in the alloy are calculated. The separation (dissolution) temperature of all carbides in the alloy increases as the W content in the alloy increases. A topologically closepacked phase separates in the alloy at a W concentration of 11 mass% and has negative effects on the properties of the studied system. The obtained dependences are experimentally confi rmed using x-ray spectroscopy on heatresistant Ni-based ZhS6K alloys. The stoichiometric formulas of the carbides are calculated. The theoretical and practical results are compared and found to be in agreement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Jiang, W.-Z. Zhang, Z.-F. Xu, H.-F. Huang, X.-X. Ye, B. Leng, L. Yan, Z.-J. Li, and X.-T. Zhou, Mater. Des., 112, 300–308 (2016); https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.09.075.
X. Dong, X. Zhang, K. Du, Y. Zhou, T. Jin, and H. Ye, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 28, 1031–1038 (2012); https://doi.org/10.1016/S1005-0302(12)60169-8.
Y. Zheng, S. Li, L. Zheng, and Y. Han, Superalloys, 61, 743–751 (2004).
B. Wu, L. Li, J. Wu, Z. Wang, Y. Wang, X. Chen, J. Dong, and J. Li, Int. J. Miner., Metall. Mater., 21, 58–64 (2014); doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-014-0865-1.
G. Achamma, M. S. Qureshi, and M. M. Malik, Zh. Prikl. Spektrosk., 86, No. 5, 746–750 (2019) [G. Achamma, M. S. Qureshi, and M. M. Malik, J. Appl. Spectrosc., 86, 831–835 (2019)].
N. Saunders, M. Fahrmann, and C. J. Small, in: Superalloys 2000, K. A. Green, T. M. Pollock, and R. D. Kissinger (Eds.), TMS, Warrendale (2000), pp. 803–811.
TU 1-92-177-91 Calibration charge blank of vacuum smelted cast heat-resistant alloys.
S. T. Kishkin, in: Ni-Based Cast Heat-Resistant Alloys [in Russian], S. T. Kishkin, G. B. Stroganov, and A. V. Logunov (Eds.), Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1987).
C. Sommitsch, R. Radis, A. Krumphals, M. Stockinger, and D. Huber, Microstructure Evolution in Metal Forming Processes, Woodhead Publ. Ltd. (2012), pp. 337–383; https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857096340.3.337.
A. Nowotnik, Rzeszow University of Technology, Rzeszow, Poland (2016), p. 155; https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-803581-8.02574-1.
H. Kitaguchi, Open Access Peer-Reviewed Chapter (2012), p. 210; doi: 10.5772/52011.
C.-N. Wei, H.-Y. Bor, and L. Chang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527, 3741–3747 (2010); doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.03.053.
B. G. Choi et al., Solid State Phenom., 124–126, 1505–1508 (2007); https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/SSP.124-126.1505.
R. Hu, G. Bai, J. Li, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 548, 83–88 (2012); doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.03.092.
X. Hu, Y. L. Zhu, L. Z. Zhou, et al., Philos. Mag. Lett., 95, No. 4, 237–244 (2015); doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09500839.2015.1039621.
Y. H. Rong, Y. X. Guo, and G. X. Hu, Metallography, 22, No. 1, 47–55 (1989); doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0026-0800(89)90021-9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S. V. Gaiduk is deceased
Translated from Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 87, No. 5, pp. 732–740, September–October, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glotka, A.A., Gaiduk, S.V. Distribution of Alloying Elements in the Structure of Heat-Resistant Nickel Alloys in Secondary Carbides. J Appl Spectrosc 87, 812–819 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-020-01075-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-020-01075-2