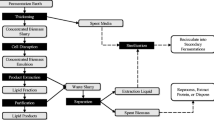
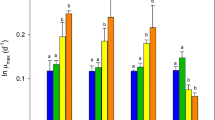
Abstract
In response to the rapid expansion of the worldwide population, there is an urgent need for the development of new, more environmentally-conscious, food sources. In this context, microalgae, such as Euglena, are of interest due to their capacity for large-scale cultivation and flexible bioproduct output. Media recycling techniques have been proposed as waste- and cost-reducing measures for large-scale algal cultivation. Culture dynamics and phytohormone production during novel fermentation conditions can enhance growth and biomass production; yet, little is known about the impacts on growth regulating phytohormones such as cytokinins (CKs) and abscisic acid (ABA) under these conditions. Using Euglena gracilis, an organic culture medium was recycled at 25, 50 and 75% inclusion rates through multiple growth cycles to evaluate impacts on biomass production and phytohormone profiles. A 25% recycled inclusion rate resulted in biomass accumulation similar to the control over one growth cycle. Subsequent recycled rates and growth cycling reduced E. gracilis biomass accumulation relative to the control, even with cell counts continuing to increase throughout, highlighting that the recycled medium inclusion and the number of repeated culture cycles impacts the biomass output of E. gracilis. Phytohormone analysis indicated that E. gracilis synthesized CKs via the tRNA-degradation pathway with increased hormone levels corresponding to higher recycle rates; ABA increased in the supernatant at higher recycle rates but was not detected in any pellet fractions. This research expands upon the roles of CKs and ABA as signaling molecules and adds guidance for building a suite of conditions specific for industrial product development.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acién FG, Fernández JM, Magán JJ, Molina E (2012) Production cost of a real microalgae production plant and strategies to reduce it. Biotechnol Adv 30:1344–1353
Aldholmi M, Ahmad R, Carretero-Molina D, Pérez-Victoria I, Martín J, Reyes F, Genilloud O, Gourbeyre L, T. Gefflaut T, Carlsson H, Maklakov A, O’Neill E, Field RA, Wilkinson B, O’Connell M, Ganesan A, (2022) Euglenatides, potent antiproliferative cyclic peptides isolated from the freshwater photosynthetic microalga Euglena gracilis. Angew Chem Int 61:e202203175
Aoki MM, Kisiala AB, Rahman T, Morrison EN, Emery RJN (2021) Cytokinins are pervasive among common in vitro culture media: An analysis of their forms, concentrations and potential sources. J Biotechnol 334:43–46
Aoki MM, Kisiala AB, Li S, Stock NL, Brunetti CR, Huber RJ, Emery RJN (2019a) Cytokinin Detection during the Dictyostelium discoideum life cycle: Profiles are dynamic and affect cell growth and spore germination. Biomolecules 9:702
Aoki MM, Seegobin M, Kisiala A, Noble A, Brunetti C, Emery RJN (2019) Phytohormone metabolism in human cells: Cytokinins are taken up and interconverted in HeLa cell culture. FASEB Bioadv 1:320–331
Bajguz A, Piotrowska A (2009) Conjugates of auxin and cytokinin. Phytochemistry 70:957–969
Bürkle L, Cedzich A, Döpke C, Stransky H, Okumoto S, Gillissen B, Kühn C, Frommer WB (2003) Transport of cytokinins mediated by purine transporters of the PUP family expressed in phloem, hydathodes, and pollen of Arabidopsis. Plant J 34:13–26
Chen F (1996) High cell density culture of microalgae in heterotrophic growth. Trends Biotech 14:421–426
Chi W, Zheng L, He C, Han B, Zheng M, Gao W, Sun C, Zhou G, Gao X (2017) Quorum sensing of microalgae associated marine Ponticoccus sp. PD-2 and its algicidal function regulation. AMB Express 7:59
Cook J R (1968) The cultivation and growth of Euglena. In: Buetow DE (ed.), The Biology of Euglena. I: General Biology and Ultrastructure. Academic Press, New York, pp 243–314
Cowan AK, Rose PD (1991) Abscisic acid metabolism in salt-stressed cells of Dunaliella salina: Possible interrelationship with β-carotene accumulation. Plant Physiol 97:798–803
Discart V, Bilad MR, Marbelia L, Vankelecom IFJ (2014) Bioresource Technology Impact of changes in broth composition on Chlorella vulgaris cultivation in a membrane photobioreactor (MPBR) with permeate recycle. Bioresour Technol 152:321–328
Ebenezer TE, Low RS, O'Neill EC, Huang I, DeSimone A, Farrow SC, Field RA, Ginger ML, Guerrero SA, Hammond M, Hampl V, Horst G, Ishikawa T, Karnkowska A, Linton EW, Myler P, Nakazawa M, Cardol P, Sánchez-Thomas R, Saville BJ, Shah MR, Simpson AGB, Sur A, Suzuki K, Tyler KM, Zimba PV, Hall N, Field MC (2022) Euglena International Network (EIN): Driving euglenoid biotechnology for the benefit of a challenged world. Biol Open 11:bio059561
Emery RJN, Ma Q, Atkins CA (2000) The forms and sources of cytokinins in developing white lupine seeds and fruits. Plant Physiol 123:1593–1604
Farooq W, Suh WI, Park MS, Yang J (2014) Water use and its recycling in microalgae cultivation for biofuel application. Bioresour Technol 184:73–81
Farooq W (2021) Sustainable production of microalgae biomass for biofuel and chemicals through recycling of water and nutrient within the biorefinery context: A review. GCB Bioenergy 13:914–940
Fernández FGA, Reis A, Wijffels RH, Barbosa M, Verdelho V, Llamas B (2021) The role of microalgae in the bioeconomy. New Biotech 61:99–107
Fret J, Roef L, Blust R, Diels L, Tavernier S, Vyverman W, Michiels M (2017) Reuse of rejuvenated media during laboratory and pilot-scale cultivation of Nannochloropsis sp. Algal Res 27:265–273
Gambello MJ, Iglewski BH (1991) Cloning and characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasR gene, a transcriptional activator of elastase expression. J Bacteriol 173:3000–3009
Gajdosová S, Spíchal L, Kamínek M, Hoyerová K, Novák O, Dobrev PI, Galuszka P, Klíma P, Gaudinová A, Zizková E, Hanus J, Dancák M, Trávnícek B, Pesek B, Krupicka M, Vanková R, Strnad M, Motyka V (2011) Distribution, biological activities, metabolism, and the conceivable function of cis-zeatin-type cytokinins in plants. J Exp Bot 62:2827–2840
Gibb M, Kisiala AB, Morrison EN, Emery RJN (2020) The origins and roles of methylthiolated cytokinins: Evidence from among life Kingdoms. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:605672
Gissibl A, Sun A, Care A, Nevalainen H, Sunna A (2019) Bioproducts from Euglena gracilis: Synthesis and applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:108
Han X, Zeng H, Bartocci P, Fantozzi F, Yan Y (2018) Phytohormones and effects on growth and metabolites of microalgae: A review. Fermentation 4:25
Hartung W (2010) The evolution of abscisic acid (ABA) and ABA function in lower plants, fungi and lichen. Funct Plant Biol 37:806–812
Hayashi M, Toda K, Ishiko H, Komatsu R, Kitaoka S (1994) Effects of shifting pH in the stationary phase of growth on the chemical composition of Euglena gracilis. Biosci Biotech Biochem 58:1964–1967
Hirose N, Makita N, Yamaya T, Sakakibara H (2005) Functional characterization and expression analysis of a gene, OsENT2, encoding an equilibrative nucleoside trans-porter in rice suggest a function in cytokinin transport. Plant Physiol 138:196–206
Hirsch R, Hartung W, Gimmler H (1989) Abscisic acid content of algae under stress. Bot Acta 102:326–334
Hlavova M, Turoczy Z, Bisova K (2015) Improving microalgae for biotechnology — From genetics to synthetic biology. Biotechnol Adv 33:1194–1203
Hnain AK, Cockburn LM, Lefebvre DD (2011) Microbiological processes for waste conversion to bioenergy products: Approaches and directions. Environ Rev 19:214–237
Jirásková D, Poulíčková A, Novák O, Sedláková K, Hradecká V, Strnad M (2009) High-throughput screening technology for monitoring phytohormone production in microalgae. J Phycol 45:108–118
Kim S, Wirasnita R, Lee D, Yu J, Lee T (2021) Enhancement of growth and paramylon production of Euglena gracilis by upcycling of spent tomato byproduct as an alternative medium. Appl Sci 11:8182
Kiseleva AA, Tarachovskaya ER, Shishova MF (2012) Biosynthesis of phytohormones in algae. Russ J Plant Physiol 59:595–610
Kisiala A, Kambhampati S, Stock NL, Aoki M, Emery RJN (2019) Quantification of cytokinins using high-resolution accurate-mass orbitrap mass spectrometry and parallel reaction monitoring (PRM). Anal Chem 91:15049–15056
Kisiala A, Laffont C, Emery RJ, Frugier F (2013) Bioactive cytokinins are selectively secreted by Sinorhizobium meliloti nodulating and nonnodulating strains. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 26:1225–1231
Ko D, Kang J, Kiba T, Park J, Kojima M, Do J, Kim KY, Kwon M, Endler A, Song WY, Martinoia E, Sakakibara H, Lee Y (2014) Arabidopsis ABCG14 is essential for the root-to-shoot translocation of cytokinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:7150–7155
Leedale GF (1964) Pellicle structure in Euglena. Brit Phycol Bull 2:291–306
Liu L, Pohnert G, Wei D (2016) Extracellular metabolites from industrial microalgae and their biotechnological potential. Mar Drugs 14:191
Loftus SE, Johnson ZI (2017) Cross-study analysis of factors affecting algae cultivation in recycled medium for biofuel production. Algal Res 24:154–166
Lowrey J, Armenta RE, Brooks MS (2016) Nutrient and media recycling in heterotrophic microalgae cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:1061–1075
Lu Y, Tarkowská D, Turečková V, Luo T, Xin Y, Li J, Wang Q, Jiao N, Strnad M, Xu J (2014) Antagonistic roles of abscisic acid and cytokinin during response to nitrogen depletion in oleaginous microalga Nannochloropsis oceanica expand the evolutionary breadth of phytohormone function. Plant J 80:52–68
Lu Y, Xu J (2015) Phytohormones in microalgae: a new opportunity for microalgal biotechnology? Trends Plant Sci 20:273–282
Mathieu-Rivet E, Mati-Baouche N, Walet-Balieu ML, Lerouge P, Bardor M (2020) N- and O-glycosylation pathways in the microalgae polyphyletic group. Front Plant Sci 11:609993
Morrison EN, Emery RJ, Saville BJ (2015) Phytohormone involvement in the Ustilago maydis- Zea mays Pathosystem: Relationships between abscisic acid and cytokinin levels and strain virulence in infected cob tissue. PLoS One 10:e0130945
Morrison EN, Emery RJN, Saville BJ (2017) Fungal derived cytokinins are necessary for normal Ustilago maydis infection of maize. Plant Pathol 66:726–742
Nambara E, Marion-Poll A (2005) Abscisic acid biosynthesis and catabolism. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:165–185
Nguyen HN, Nguyen TQ, Kisiala AB, Emery RJN (2021) Beyond transport: cytokinin ribosides are translocated and active in regulating the development and environmental responses of plants. Planta 254:45
Nguyen NH, Nguyen QT, Dang DH, Emery RJN (2023) Phytohormones enhance heavy metal responses in Euglena gracilis: Evidence from uptake of Ni, Pb and Cd and linkages to hormonomic and metabolomic dynamics. Environ Pollut 320:121094
Noble A, Kisiala A, Galer A, Clysdale D, Emery RJN (2014) Euglena gracilis (Euglenophyceae) produces abscisic acid and cytokinins and responds to their exogenous application singly and in combination with other growth regulators. Eur J Phycol 49:244–254
O’Neill EC, Trick M, Hill L, Rejzek M, Dusi RG, Hamilton CJ, Zimba PV, Henrissat B, Field RA (2015) The transcriptome of Euglena gracilis reveals unexpected metabolic capabilities for carbohydrate and natural product biochemistry. Mol Biosyst 11:2808–2820
Ord G, Cameron I, Fensom D (1977) The effect of pH and ABA on the hydraulic conductivity of Nitella membranes. Can J Bot 55:1–4
Ördög V, Stirk WA, Lenobel R, Bancifova M, Strnad M, van Staden J, Szigeti J, Nemeth L (2004) Screening microalgae for some potentially useful agricultural and pharmaceutical secondary metabolites. J Appl Phycol 16:309–314
Perez-Garcia O, Escalante FME, De-Bashan LE, Bashan Y (2011) Heterotrophic cultures of microalgae: Metabolism and potential products. Water Res 45:11–36
Pils B, Heyl A (2009) Unraveling the evolution of cytokinin signaling. Plant Physiol 151:782–791
Proust H, Hoffmann B, Xie X, Yoneyama K, Schaefer DG, Yoneyama K, Nogué F, Rameau C (2011) Strigolactones regulate protonema branching and act as a quorum sensing-like signal in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Development 138:1531–1539
Rodolfi L, Zittelli GC, Barsanti L, Rosati G, Tredici MR (2003) Growth medium recycling in Nannochloropsis sp. mass cultivation. Biomol Eng 20:243–248
Romanenko EA, Kosakovskaya IV, Romanenko PA (2015) Phytohormones of microalgae: Biological role and involvement in the regulation of physiological processes. Pt I. Auxins, abscisic acid, ethylene. Int J Algae 17:275–289
Romanov GA, Schmülling T (2022) On the biological activity of cytokinin free bases and their ribosides. Planta 255:27
Rösch C, Skarka J, Wegerer N (2012) Materials flow modeling of nutrient recycling in biodiesel production from microalgae. Bioresour Technol 107:191–199
Ruiz J, Olivieri G, de Vree J, Bosma R, Willems P, Reith JH, Eppink MHM, Kleinegris DMM, Wijffels RH, Barbosa MJ (2016) Towards industrial products from microalgae. Energy Environ Sci 9:3036–3043
Sakakibara H (2006) Cytokinins: Activity, biosynthesis, and translocation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:431–439
Sakakibara H (2021) Cytokinin biosynthesis and transport for systemic nitrogen signaling. Plant J 105:421–430
Santner A, Calderon-Villalobos LI, Estelle M (2009) Plant hormones are versatile chemical regulators of plant growth. Nat Chem Biol 5:301–307
Satiat-Jeunemaitre B, Hawes C (1993) Insights into the secretory pathway and vesicular transport in plant cells. Biol Cell 79:7–15
Schäfer M, Brütting C, Meza-Canales ID, Großkinsky DK, Vankova R, Baldwin IT, Meldau S (2015) The role of cis-zeatin-type cytokinins in plant growth regulation and mediating responses to environmental interactions. J Exp Bot 66:4873–4884
Schwender J, Gemünden C, Lichtenthaler HK (2001) Chlorophyta exclusively use the 1-deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate/2-C-methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway for the biosynthesis of isoprenoids. Planta 212:416–423
Seegobin M, Kisiala A, Noble A, Kaplan D, Brunetti C, Emery RJN (2018) Canis familiaris tissues are characterized by different profiles of cytokinins typical of the tRNA degradation pathway. FASEB J 32:6575–6581
Spíchal L (2012) Cytokinins - Recent news and views of evolutionally old molecules. Funct Plant Biol 39:267–284
Stirk W, Novák O, Strnad M, van Staden J (2003) Cytokinins in macroalgae. Plant Growth Regul 41:13–24
Stirk WA, van Staden J (2010) Flow of cytokinins through the environment. Plant Growth Regul 62:101–116
Stirk WA, Ördög V, Novák O, Rolčík J, Strnad M, Bálint P, van Staden J (2013) Auxin and cytokinin relationships in 24 microalgal strains. J Phycol 49:459–467
Swaminathan S, Bock RM (1977) Isolation and identification of cytokinins from Euglena gracilis transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry 16:1355–1360
Swaminathan S, Bock RM, Skoog F (1977) Subcellular localization of cytokinins in transfer ribonucleic acid. Plant Physiol 59:558–563
Takezawa D, Komatsu K, Sakata Y (2011) ABA in bryophytes: how a universal growth regulator in life became a plant hormone? J Plant Res 124:437–453
Tominaga N, Takahata M, Tominaga H (1993) Effects of NaCl and KNO3 concentrations on the abscisic acid content of Dunaliella sp. (Chlorophyta). Hydrobiologia 267:163–168
Vigani M, Parisi C, Rodriguez-Cerezo E, Barbosa MJ, Sijtsma L, Ploeg M, Enzing C (2015) Food and feed products from micro-algae: Market opportunities and challenges for the EU. Trends Food Sci Technol 42:81–92
Wang Y, Seppänen-Laakso T, Rischer H, Wiebe MG (2018) Euglena gracilis growth and cell composition under different temperature, light and trophic conditions. PLoS One 13:e0195329
Xu JM, Xiong JQ (2023) Boosting the yields of microalgal biomass and high-value added products by phytohormones: A mechanistic insight using transcriptomics. J Cleaner Production 393:136175
Xinyi E, Crofcheck C, Crocker M (2016) Application of recycled media and algae-based anaerobic digestate in Scenedesmus cultivation. J Renew Sustain Energy 8:013116
Yokoya NA, Stirk WA, van Staden J, Novak O, Tureckova V, Pencik A, Strnad M (2010) Endogenous cytokinins, auxins, and abscisic acid in red algae from Brazil. J Phycol 46:1198–1205
Yoshioka K, Suzuki K, Osanai T (2020) Effect of pH on metabolite excretion and cell morphology of Euglena gracilis under dark, anaerobic conditions. Algal Res 51:102084
Yu X, Chen L, Zhang W (2015) Chemicals to enhance microalgal growth and accumulation of high-value bioproducts. Front Microbiol 6:56
Zhou J, Lyu Y, Richlen M, Anderson DM, Cai Z (2016) Quorum sensing is a language of chemical signals and plays an ecological role in algal-bacterial interactions. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci 35:81–105
Zhu J, Hong DD, Wakisaka M (2019) Phytic acid extracted from rice bran as a growth promoter for Euglena gracilis. Open Chem 17:57–63
Žižková E, Kubeš M, Dobrev PI, Přibyl P, Šimura J, Zahajská L, Záveská Drábková L, Novák O, Motyka V (2017) Control of cytokinin and auxin homeostasis in cyanobacteria and algae. Ann Bot 119:151–166
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada Discovery Grant (NSERC RGPIN-05436) and NSERC College-University Idea to Innovation Grant Program (CUI2I 470778-14). The authors thank Canadian Foundation for Innovation: Leaders Opportunity Fund and Ontario Research Fund: Research Infrastructure for funding instrumentation, including the Thermo Fisher QExactive Orbitrap, in the Water Quality Centre at Trent University.
Funding
Financial support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada Discovery Grant (NSERC RGPIN-05436) to RJNE, ENM and TS and NSERC College-University Idea to Innovation Grant Program (CUI2I 470778–14) to RJNE, ABK and AMK is gratefully acknowledged. Partial funding to AMK was provided by Noblegen Inc. The authors thank Canadian Foundation for Innovation: Leaders Opportunity Fund and Ontario Research Fund: Research Infrastructure for funding instrumentation, including the Thermo Fisher QExactive Orbitrap, in the Water Quality Centre at Trent University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AMK: Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing Original Draft; ENM: Data analysis, Figure and Table creation, Writing-review and Editing; TS: Writing Draft; ABK: Formal analysis; KHR: Investigation; AN: Funding acquisition; RJN: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Noblegen Inc. is a commercial, for-profit organization that is using E. gracilis in future food products and biosolutions. Partial funding for this research was provided by Noblegen Inc. KHR is an employee of Noblegen Inc. AN is the CEO and founder of Noblegen Inc. and is a shareholder.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kuhne, A.M., Morrison, E.N., Sultana, T. et al. Cultivation of heterotrophic Euglena gracilis: The effects of recycled media on culture growth and associations with growth regulating phytohormone profiles. J Appl Phycol 35, 2161–2175 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-023-03062-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-023-03062-4