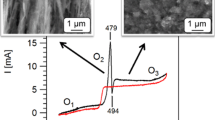
Abstract
The electrodeposition process of vanadium from LiCl–KCl base electrolytes was investigated by means of cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic electrolyses and micro analytical analysis of the deposits. It is demonstrated that the valence state of the vanadium ions has a critical influence on the feasibility of performing a reproducible and stable coating process aiming to obtain compact vanadium films. When the electrolyte contained predominantly trivalent vanadium ions, the process was unstable and the deposit consisted of dendrites. In contrast, making use of a comproportionation reaction of metallic vanadium and VCl3 to divalent vanadium ions led to a stable deposition behaviour and allowed to obtain thick deposits with high current efficiencies. The disadvantageous behaviour of melts with mostly trivalent ions is explained by the fact that deposition is interfered by the reduction of trivalent to divalent ions under limiting current conditions.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baroch EF (2000) Vanadium and vanadium alloys. Kirk-Othmer encyclopedia of chemical technology. Wiley, New York
Muroga T (2016) Vanadium for nuclear systems. Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering, Elsevier, Amsterdam
Moskalyk RR, Alfantazi AM (2003) Processing of vanadium: a review. Miner Eng 16(9):793–805
Peters M, Leyens C (2002) Titan und Titanlegierungen. Wiley, Weinheim
Lei KPV, Sullivan TA (1971) Electrorefining of vanadium prepared by carbothermic reduction of V2O5. Metall Trans 2:2312–2134
Baker DH, Ramsdell JD (1960) Electrolytic vanadium and its properties. J Electrochem Soc 107(12):985–989
Tripathy PK, Sehra JC, Bose DK, Singh RP (1996) Electrodeposition of vanadium from a molten salt bath. J Appl Electrochem 26(8):887–890
Kazakova OS, Kuznetsov SA (2012) Electrochemical behavior and electrorefining of vanadium in melts containing titanium salts. ECS Trans 50(11):181–190
Polovov IB, Tray ME, Chernyshov MV, Volkovich VA, Vasin BD, Rebrin OI (2014) Electrode processes in vanadium-containing chloride melts. In: Gaune-Escard M, Haarberg GM (eds) Molten salt chemistry and technology. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 257–281
Gruen D, McBeth R (1962) Absorbtion spectra of the II, III, IV and V oxidation states of vanadium in LiCl-KCl eutectic octahedral-tetrahedral transformations of V (II) and V (III). J Phys Chem 66(1):57–65
Chernyshov MV, Polovov IB, Volkovich VA, Vasin BD, Rebrin OI, Vonogradov KV, Griffiths TR (2010) Electronic absorption spectra of vanadium species in halide melts. ECS Trans 33(7):287–296
Wei D, Okido M, Oki T (1994) Characteristics of titanium deposits by electrolysis in molten chloride-fluoride mixture. J Appl Electrochem 24(9):923–929
Gillesberg B, Barner JHV, Bjerrum NJ, Lantelme F (1999) Niobium plating processes in alkali chloride melts. J Appl Electrochem 29(8):939–949
Gussone J, Hausmann J (2011) Deposition of titanium on SiC fibres from chloride melts. J Appl Electrochem 41(6):657–662
Chen Z, Li S, Wang Y, Li W, Wei C, Kong W, Jia X, Pei Q, Zhang W (2016) Electrochemical deposition of magnesium on SiC fibers from the LiCl-KCl-MgCl2 molten salt. J Electrochem Soc 9(163):522–525
Milicevic K, Friedrich B, Gussone J, Haubrich J (2017) Anodic dissolution of vanadium in molten LiCl–KCl–TiCl2. J Appl Electrochem 47(5):573–581
Berghoute Y, Salmi A, Lantelme F (1994) Internal reference systems for fused electrolytes. J Electroanal Chem 365(1–2):171–177
Plambeck JA (1967) Electromotive force series in molten salts., J Chem Eng Data 12(1):77–82
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2001) Electrochemical methods, fundamentals and applications, 2 edn. Wiley, New York
Mamantov G, Manning DL, Dale JM (1965) Reversible deposition of metals on solid electrodes by voltammetry with linearly varying potential. J Electroanal Chem 9(4):253–259
Berzins T, Delahay P (1953) Oscillographic polarographic waves for the reversible deposition of metals on solid electrodes. J Am Chem Soc 75(3):555–559
Wranglén G (1960) Dendrites and growth layers in the electrocrystallization of metals., Electrochim Acta 2(1–3):130–143
Cordner GDP, Worner HW (1951) Electrolytic preparation of titanium. Aust J Appl Sci 2:358–367
Kühnl H, Ehrlich P, Uihlein RD (1960) Die Abscheidung von Titanmetall durch Schmelzelektrolyse mit löslicher Anode. Z anorg allg Chem 306(5–6):246–259
Polovov IB, Vasin BD, Abakumov AV, Rebrin OI, Chernyshov MV, Volkovich VA, Griffiths TR (2007) Thermodynamics of the formation of vanadium(II) complexes in chloride melts. ECS Trans 3(35):589–597
Acknowledgements
We thank the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgesellschaft, DFG) for financially supporting the project (HA 4397/6-1, FR 1713/23-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gussone, J., Vijay, C.R.Y., Haubrich, J. et al. Effect of vanadium ion valence state on the deposition behaviour in molten salt electrolysis. J Appl Electrochem 48, 427–434 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1165-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1165-7