Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate long-term outcomes of infliximab (IFX) treatment in patients with Behçet's disease (BD)-associated uveitis.
Patients and methods
We retrospectively analyzed the cases of patients with BD-associated uveitis treated with IFX for > 5 years. We compared the numbers of ocular inflammatory attacks, ocular disease activities, and visual acuity before and after the initiation of IFX treatment.
Results
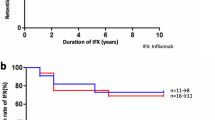
The 24 patients were 20 men and 4 women. Their mean age at the initiation of IFX treatment was 37.3 ± 9.2 years. The mean term from the initiation of IFX treatment was 10.3 ± 2.4 years. The average number of ocular inflammatory attacks was 5.4 ± 2.1 per 12 months before the IFX treatment and significantly lower at 0.83 ± 0.96 per 12 months after the initiation of IFX treatment (p < 0.05). We used a scoring system for BD-associated uveitis named the Behçet's disease ocular attack score 24 (BOS24) to estimate the changes in ocular disease activities between before and after initiation of IFX treatment. The average score decreased significantly from 7.58 ± 2.77 to 2.55 ± 2.74 after the initiation of IFX treatment (p < 0.05). Even after > 5 years of the treatment, both the number of ocular attacks and the BOS24 score kept decreasing. The visual acuity in 42 of 48 eyes (24 patients) was improved or maintained.
Conclusions
IFX was effective for controlling ocular inflammatory attacks and diminishing ocular disease activities in patients with BD-associated uveitis, and it maintained the patients' visual acuity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okada AA, Goto H, Ohno S, Mochizuki M (2012) Multicenter study of infliximab for refractory uveoretinitis in Behçet disease. Arch Ophthalmol 130(5):592–598
Tugal-Tutkun I, Onal S, Altan-Yaycioglu R, Huseyin Altunbas H, Urgancioglu M (2004) Uveitis in Behçet disease: an analysis of 880 patients. Am J Ophthalmol 138(3):373–380
Sfikakis PP, Theodossiadis PG, Katsiari CG, Kaklamanis P, Markomichelakis NN (2001) Effect of infliximab on sight-threatening panuveitis in Behçet’s disease. Lancet 358:295–296
Katsuyama A, Kusuhara S, Nishisho R, Matsumiya W, Azumi A, Nakamura M (2019) Long-term efficacy and safety of infliximab and cyclosporine combination therapy for refractory uveoretinitis in Behçet’s disease. Clin Ophthalmol 13:521–527
Ueda S, Akahoshi M, Takeda A et al (2018) Long-term efficacy of infliximab treatment and the predictors of treatment outcomes in patients with refractory uveitis associated with Behçet’s disease. Eur J Rheumatol 5(1):9–15
Fabiani C, Vitale A, Rigante D et al (2018) Predictors of sustained clinical response in patients with Behçet’s disease-related uveitis treated with infliximab and adalimumab. Clin Rheumatol 37(6):1715–1720
Takeuchi M, Kezuka T, Sugita S et al (2014) Evaluation of the long-term efficacy and safety of infliximab treatment for uveitis in Behçet’s disease: a multicenter study. Ophthalmology 121(10):1877–1884
Al Rashidi S, Al Fawaz A, Kangave D, Abu El-Asrar AM (2013) Long-term clinical outcomes in patients with refractory uveitis associated with Behçet disease treated with infliximab. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 21(6):468–474
Fabiani C, Sota J, Vitale A et al (2019) Ten-year retention rate of infliximab in patients with Behçet’s disease-related uveitis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 27(1):34–39
Abu El-Asrar AM, Abboud EB, Aldibhi H, Al-Arfaj A (2005) Long-term safety and efficacy of infliximab therapy in refractory uveitis due to Behçet’s disease. Int Ophthalmol 26(3):83–92
Accorinti M, Pirraglia MP, Paroli MP, Priori R, Conti F, Pivetti-Pezzi P (2007) Infliximab treatment for ocular and extraocular manifestations of Behçet’s disease. Jpn J Ophthalmol 51(3):191–196
Niccoli L, Nannini C, Benucci M et al (2007) Long-term efficacy of infliximab in refractory posterior uveitis of Behcet’s disease: a 24-month follow-up study. Rheumatology 46(7):1161–1164
Capella MJ, Foster CS (2012) Long-term efficacy and safety of infliximab in the treatment of Behçet’s disease. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 20(3):198–202
Ohno S, Nakamura S, Hori S, Shimakawa M, Kawashima H, Mochizuki M et al (2004) Efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of multiple administration of infliximab in Behçet’s disease with refractory uveoretinitis. J Rheumatol 31(7):1362–1368
Horiguchi N, Kamoi K, Horie S et al (2020) A 10-year follow-up of Infliximab monotherapy for refractory uveitis in Behçet’s syndrome. Sci Rep 10(1):22227
Mizushima Y (1988) Revised diagnostic criteria for Behçet’s disease in 1987. Ryumachi 28(1):66–70
Tanaka R, Murata H, Takamoto M et al (2016) Behçet’s disease ocular attack score 24 and visual outcome in patients with Behçet’s disease. Br J Ophthalmol 100(7):990–994
Kaburaki T, Namba K, Sonoda KH et al (2014) Behçet’s disease ocular attack score 24: evaluation of ocular disease activity before and after initiation of infliximab. Jpn J Ophthalmol 58(2):120–130
Kaburaki T, Araki F, Takamoto M et al (2010) Best-corrected visual acuity and frequency of ocular attacks during the initial 10 years in patients with Behçet’s disease. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 248(5):709–714
Dervieux T, Weinblatt ME, Kivitz A, Kremer JM (2013) Methotrexate polyglutamation in relation to infliximab pharmacokinetics in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 72(6):908–910
Lin J, Ziring D, Desai S et al (2008) TNFalpha blockade in human diseases: an overview of efficacy and safety. Clin Immunol 126(1):13–30
Lopez-Olivo MA, Tayar JH, Martinez-Lopez JA et al (2012) Risk of malignancies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologic therapy: a meta-analysis. JAMA 308(9):898–908
Wadström H, Frisell T, Askling J (2017) Malignant neoplasms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, tocilizumab, abatacept, or rituximab in clinical practice: a nationwide cohort study from Sweden. JAMA Intern Med 177(11):1605–1612
Tanaka Y, Takeuchi T, Mimori T et al (2010) Discontinuation of infliximab after attaining low disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: RRR (remission induction by Remicade in RA) study. Ann Rheum Dis 69(7):1286–1291
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of Kyushu University. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Nonapplicable due to the retrospective design.
Informed consent
Nonapplicable due to the retrospective design.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamana, S., Hasegawa, E., Takeda, A. et al. Long-term outcomes of infliximab in patients with Behçet's disease-associated uveitis. Int Ophthalmol 43, 937–944 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-022-02495-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-022-02495-z