Abstract
Background
To compare the efficacy of Adalimumab (ADA) in noninfectious anterior uveitis (AU) and posterior segment (PS) involvement, associated with different conditions, with a focus on Behçet’s syndrome (BS).
Methods
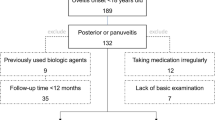
In this retrospective, multicenter post-hoc study, we evaluated the efficacy of ADA in terms of ocular control and relapses in 96 patients with AU and PS uveitis, either idiopathic (IU) or associated with BS or with other systemic disorders (OSD) (Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada, Inflammatory Bowel Disease), followed in three tertiary referral centers.
Results
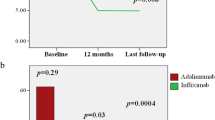
Ninety-six patients (45 AU; 51 PS uveitis) were included. Eleven had IU, 58 BS, and 27 OSD. All patients with AU achieved complete long-term ocular control. In PS uveitis, 89%, 67% and 100% of patients with BS, IU and OSD achieved ocular control at the last follow-up (> 12 months), respectively. The lowest ocular relapse rate occurred in patients with AU with BS (1/13) or IU (0/2). ADA accounted for long-term disease control, and no predictors of ocular control and relapse were identified; particularly, ocular relapses seemed not related to systemic ones. Macular edema resolved in 75% and 67% of PS uveitis with BS and IU, respectively.
Conclusions
ADA controls both anterior and posterior uveitis, with an efficacy similar in IU, BS and OSD patients. In BS, the efficacy of ADA seems to be independent of demographic and clinical characteristics, and ocular relapses mostly occurred independently from systemic ones. Based on our results, ADA may represent a valid alternative in anterior refractory uveitis.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Bitossi A, Bettiol A, Silvestri E et al (2019) Adalimumab accounts for long-term control of noninfectious uveitis also in the absence of concomitant DMARD treatment: a multicenter retrospective study. Mediators Inflamm 2019:1623847. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1623847
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Listing J, Sieper J (2005) Decreased incidence of anterior uveitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with the anti-tumor necrosis factor agents infliximab and etanercept. Arthritis Rheum 52:2447–2451. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21197
Chen G, Goeddel DV (2002) TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science 296:1634–1635. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1071924
Cunningham ET, Stalder A, Sanna PP et al (1997) Localization of tumor necrosis factor receptor messenger RNA in normal and herpes simplex virus-infected mouse eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 38:9–15
Díaz-Llopis M, Salom D, Garcia-de-Vicuña C et al (2012) Treatment of refractory uveitis with adalimumab: a prospective multicenter study of 131 patients. Ophthalmology 119:1575–1581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.02.018
Dobner BC, Max R, Becker MD et al (2013) A three-centre experience with adalimumab for the treatment of non-infectious uveitis. Br J Ophthalmol 97:134–138. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2011-301401
Durrani K, Kempen JH, Ying G-S et al (2017) Adalimumab for ocular inflammation. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 25:405–412. https://doi.org/10.3109/09273948.2015.1134581
Emmi G, Prisco D (2019) Behçet’s syndrome: focus on pathogenetic background, clinical phenotypes and specific treatments. Intern Emerg Med 14:639–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-019-02154-9
European Medicine Agency. Adalimumab—summary of product characteristics
Fabiani C, Vitale A, Emmi G et al (2017) Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in Behçet’s disease-related uveitis: a multicenter retrospective observational study. Clin Rheumatol 36:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3480-x
Fabiani C, Vitale A, Lopalco G et al (2016) Different roles of TNF inhibitors in acute anterior uveitis associated with ankylosing spondylitis: state of the art. Clin Rheumatol 35:2631–2638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3426-3
Fabiani C, Vitale A, Rigante D et al (2019) Efficacy of anti-tumour necrosis factor-α monoclonal antibodies in patients with non-infectious anterior uveitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 37:301–305
Fabiani C, Vitale A, Rigante D et al (2018) Predictors of sustained clinical response in patients with Behçet’s disease-related uveitis treated with infliximab and adalimumab. Clin Rheumatol 37:1715–1720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4092-4
Gueudry J, Muraine M (2018) Anterior uveitis J Fr Ophtalmol 41:e11–e21
Hernández Garfella ML, Palomares Fort P, Román Ivorra JA, Cervera Taulet E (2015) Aqueous humor levels of different interleukins 1-β, 2, 6 and 10, tumor necrosis factor-α and vascular endothelial growth factor in uveitis treated with adalimumab. J Ophthalmic Vis Res 10:49–54. https://doi.org/10.4103/2008-322X.156110
Jaffe GJ, Dick AD, Brézin AP et al (2016) Adalimumab in patients with active noninfectious uveitis. N Engl J Med 375:932–943. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1509852
Lee JT, Yates WB, Rogers S et al (2018) Adalimumab for the treatment of refractory active and inactive non-infectious uveitis. Br J Ophthalmol 102(12):1672–1678. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2017-311234
Nguyen QD, Merrill PT, Jaffe GJ et al (2016) Adalimumab for prevention of uveitic flare in patients with inactive non-infectious uveitis controlled by corticosteroids (VISUAL II): a multicentre, double-masked, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet (Lond, Engl) 388:1183–1192. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31339-3
Sheppard J, Joshi A, Betts KA et al (2017) Effect of adalimumab on visual functioning in patients with noninfectious intermediate uveitis, posterior uveitis, and panuveitis in the VISUAL-1 and VISUAL-2 Trials. JAMA Ophthalmol 135:511–518. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.0603
Sippy BD, Hofman FM, Wright AD et al (1996) Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors are present in human vitreous and shed by retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res 63:311–317. https://doi.org/10.1006/exer.1996.0120
Suhler EB, Adán A, Brézin AP et al (2018) Safety and Efficacy of Adalimumab in Patients with Noninfectious Uveitis in an Ongoing Open-Label Study: VISUAL III. Ophthalmology 125:1075–1087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2017.12.039
Suhler EB, Lowder CY, Goldstein DA et al (2013) Adalimumab therapy for refractory uveitis: results of a multicentre, open-label, prospective trial. Br J Ophthalmol 97:481–486. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2012-302292
Suhler EB, Thorne JE, Mittal M et al (2017) Corticosteroid-related adverse events systematically increase with corticosteroid dose in noninfectious intermediate, posterior, or panuveitis. Ophthalmology 124:1799–1807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2017.06.017
Vallet H, Riviere S, Sanna A et al (2015) Efficacy of anti-TNF alpha in severe and/or refractory Behçet’s disease: multicenter study of 124 patients. J Autoimmun 62:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2015.06.005
Vitale A, Rigante D, Lopalco G et al (2016) New therapeutic solutions for Behçet’s syndrome. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 25(7):827–840
Wajant H, Henkler F, Scheurich P (2001) The TNF-receptor-associated factor family: scaffold molecules for cytokine receptors, kinases and their regulators. Cell Signal 13:389–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0898-6568(01)00160-7
Funding
This study was not funded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All people that contributed to this work are listed as co-authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval was waived by the ethics committee of Careggi University Hospital (CEAVC Reference number: 13366). The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. In view of the retrospective nature of the study and all the procedures being performed were part of the routine care.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Lorenzo Vannozzi and Domenico Prisco share senior authorship.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silvestri, E., Bitossi, A., Bettiol, A. et al. Adalimumab effectively controls both anterior and posterior noninfectious uveitis associated with systemic inflammatory diseases: focus on Behçet’s syndrome. Inflammopharmacol 28, 711–718 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00697-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00697-4