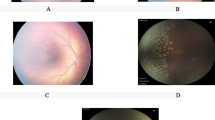
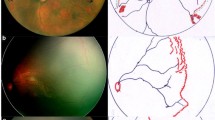
Abstract
Purpose
To study treatment outcomes of combination treatment of intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) injection and laser photocoagulation in Type 1 Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP) and Aggressive Posterior ROP (APROP).
Methods
This is a retrospective observational study of 87 eyes of 48 premature babies who presented with Type I ROP or APROP and were treated with combination of laser and anti-VEGF therapy. Retrospective evaluation of case records was done to collect data on gestational age, birth weight, age at intervention, anterior segment and fundus findings, intervention with laser and anti-VEGF and response to treatment. Outcome measure was defined as attached retina at posterior pole at last follow-up.
Results
Mean gestational age was 29.1 weeks, and mean birth weight was 1226.9 gms. Sixty-six (75.8%) eyes had Type I ROP and 21 (24.1%) eyes had APROP at presentation. Five eyes (3 patients) were lost to follow-up after treatment. Of 82 eyes, 80.5% (66 eyes) showed regression of ROP following combination treatment and 19.5% (16 eyes) needed surgery. Of these, 15 underwent surgery and 12 had successful outcome. Mean follow-up duration of patients was 52 weeks. Finally, 95.1% (78 eyes) had attached retina at posterior pole and 4.9% (4 eyes) had detached retina.
Conclusion
We conclude that combination therapy is an effective and safe treatment strategy for Type I ROP and APROP.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steinkuller PG, Du L, Gilbert C, Foster A, Collins ML, Coats DK (1999) Childhood blindness. J AAPOS 3(1):26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1091-8531(99)70091-1
Mintz-Hittner HA, Kennedy KA, Chuang AZ (2011) BEAT-ROP Cooperative group. Efficacy of intravitreal bevacizumab for stage 3+ retinopathy of prematurity. N Engl J Med 364(7):603–615. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1007374
Kychenthal A, Dorta P, Katz X (2006) Zone I retinopathy of prematurity: clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes. Retina 26(7):S11–S15. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.iae.0000244285.79004.e6
Hård AL, Hellström A (2011) On safety, pharmacokinetics and dosage of bevacizumab in ROP treatment: a review. Acta Paediatr 100(12):1523–1527. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2011.02445.x
Avery RL (2012) Bevacizumab (Avastin) for retinopathy of prematurity: wrong dose, wrong drug, or both? J AAPOS 16(1):2–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2011.11.002
Yang CH (2012) Anti-vascular endothelium growth factor therapy for retinopathy of prematurity: a continuing debate. Taiwan J Ophthalmol 2(4):115–116
Hu J, Blair MP, Shapiro MJ, Lichtenstein SJ, Galasso JM, Kapur R (2012) Reactivation of retinopathy of prematurity after bevacizumab injection. Arch Ophthalmol 130(8):1000–1006. https://doi.org/10.1001/archophthalmol.2012.592
Chung EJ, Kim JH, Ahn HS, Koh HJ (2007) Combination of laser photocoagulation and intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) for aggressive zone I retinopathy of prematurity. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245(11):1727–1730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-007-0661-y
Lee JY, Chae JB, Yang SJ, Yoon YH, Kim JG (2010) Effects of intravitreal bevacizumab and laser in retinopathy of prematurity therapy on the development of peripheral retinal vessels. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 248(9):1257–1262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-010-1375-0
Sonmez K, Drenser KA, Capone A Jr, Trese MT (2008) Vitreous levels of stromal cell-derived factor 1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with retinopathy of prematurity. Ophthalmology 115(6):1065–1070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2007.08.050
Early Treatment For Retinopathy Of Prematurity Cooperative Group (2003) Revised indications for the treatment of retinopathy of prematurity: results of the early treatment for retinopathy of prematurity randomized trial. Arch Ophthalmol 121(12):1684–1694. https://doi.org/10.1001/archopht.121.12.1684
O’Keefe M, Lanigan B, Long VW (2003) Outcome of zone 1 retinopathy of prematurity. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 81(6):614–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1395-3907.2003.00171.x
Bakri SJ, Snyder MR, Reid JM, Pulido JS, Singh RJ (2007) Pharmacokinetics of intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin). Ophthalmology 114(5):855–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2007.01.017
Shah PK, Narendran V, Tawansy KA, Raghuram A, Narendran K (2007) Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) for post laser anterior segment ischemia in aggressive posterior retinopathy of prematurity. Indian J Ophthalmol 55(1):75. https://doi.org/10.4103/0301-4738.29505
Travassos A, Teixeira S, Ferreira P, Regadas I, Travassos AS, Esperancinha FE, Prieto I, Pires G, van Velze R, Valido A, Machado Mdo C (2007) Intravitreal bevacizumab in aggressive posterior retinopathy of prematurity. Ophthal Surg Lasers Imag 38(3):233–7. https://doi.org/10.3928/15428877-20070501-09
Mintz-Hittner HA, Kuffel RR Jr (2008) Intravitreal injection of bevacizumab (avastin) for treatment of stage 3 retinopathy of prematurity in zone I or posterior zone II. Retina 28(6):831–838. https://doi.org/10.1097/IAE.0b013e318177f934
Quiroz-Mercado H, Martinez-Castellanos MA, Hernandez-Rojas ML, Salazar-Teran N, Chan RV (2008) Antiangiogenic therapy with intravitreal bevacizumab for retinopathy of prematurity. Retina 28(3 Suppl):S19-25. https://doi.org/10.1097/IAE.0b013e318159ec6b
Lalwani GA, Berrocal AM, Murray TG, Buch M, Cardone S, Hess D, Johnson RA, Puliafito CA (2008) Off-label use of intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) for salvage treatment in progressive threshold retinopathy of prematurity. Retina 28(3 Suppl):S13–S18. https://doi.org/10.1097/IAE.0b013e3181644ad2
Stahl A, Lepore D, Fielder A, Fleck B, Reynolds JD, Chiang MF, Li J, Liew M, Maier R, Zhu Q, Marlow N (2019) Ranibizumab versus laser therapy for the treatment of very low birthweight infants with retinopathy of prematurity (RAINBOW): an open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet 394(10208):1551–1559. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31344-3
Naug HL, Browning J, Gole GA, Gobé G (2000) Vitreal macrophages express vascular endothelial growth factor in oxygen-induced retinopathy. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 28(1):48–52. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1442-9071.2000.00226.x
Flynn JT, Chan-Ling T (2006) Retinopathy of prematurity: two distinct mechanisms that underlie zone 1 and zone 2 disease. Am J Ophthalmol 142(1):46–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2006.02.018
Mintz-Hittner HA (2012) Intravitreal pegaptanib as adjunctive treatment for stage 3+ ROP shown to be effective in a prospective, randomized, controlled multicenter clinical trial. Eur J Ophthalmol 22(5):685–6. https://doi.org/10.5301/ejo.5000176
Autrata R, Senková K, Holousová M, Krejcírová I, Dolezel Z, Borek I (2012) Effects of intravitreal pegaptanib or bevacizumab and laser in treatment of threshold retinopathy of prematurity in zone I and posterior zone II–four years results. Cesk Slov Oftalmol 68(1):29–36
Sen P, Abraham S, Jain S, Gopal L, Bhende P (2019) Treatment outcomes of zone 1 retinopathy of prematurity: a study from a tertiary eye care center in South India. Taiwan J Ophthalmol 9(4):255–261. https://doi.org/10.4103/tjo.tjo_62_18
Kim MJ, Kim SJ, Yu YS (2008) The risk for retinal detachment associated with hemorrhages pre- and postlaser treatment in retinopathy of prematurity. Retina 28(10):1451–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/iae.0b013e31817f2f15
Azuma N, Ishikawa K, Hama Y, Hiraoka M, Suzuki Y, Nishina S (2006) Early vitreous surgery for aggressive posterior retinopathy of prematurity. Am J Ophthalmol 142(4):636–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2006.05.048
Micelli Ferrari T, Furino C, Lorusso VV, Dammacco R, Sborgia G, Sborgia L, Besozzi G (2007) Three-port lens-sparing vitrectomy for aggressive posterior retinopathy of prematurity: early surgery before tractional retinal detachment appearance. Eur J Ophthalmol 17(5):785–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/112067210701700516
Hutcheson KA, Nguyen AT, Preslan MW, Ellish NJ, Steidl SM (2003) Vitreous hemorrhage in patients with high-risk retinopathy of prematurity. Am J Ophthalmol 136(2):258–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9394(03)00190-9
Dani C, Frosini S, Fortunato P, Bertini G, Pratesi S, Pollazzi L, Caputo R, La Torre A (2012) Intravitreal bevacizumab for retinopathy of prematurity as first line or rescue therapy with focal laser treatment. A case series. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 25(11):2194–7. https://doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2012.684109
Nicoară SD, Stefănuţ AC, Nascutzy C, Zaharie GC, Toader LE, Drugan TC (2016) Regression rates following the treatment of aggressive posterior retinopathy of prematurity with bevacizumab versus laser: 8-year retrospective analysis. Med Sci Monit 10(22):1192–1209. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.897095
Sanghi G, Dogra MR, Katoch D, Gupta A (2014) Aggressive posterior retinopathy of prematurity in infants ≥ 1500 g birth weight. Indian J Ophthalmol 62(2):254–257. https://doi.org/10.4103/0301-4738.128639
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PS, AA, PB, and SG contributed to concept and design; PS, AA, PB, and SG contributed to data collection; PS, AA, PB, and SG contributed to analysis and interpretation; PS, AA, PB, and SG contributed to overall responsibility; Data Availability: authors have access to data and can be shared if needed.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was waived by the local Ethics Committee of the Medical Research Foundation, Chennai, in view of the retrospective nature of the study.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the parents.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, P., Agarwal, A.A.K., Bhende, P. et al. Treatment outcomes of combination of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor injection and laser photocoagulation in Type 1 ROP and APROP. Int Ophthalmol 42, 95–101 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-021-02004-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-021-02004-8