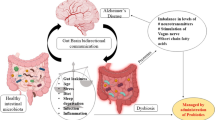
Abstract
Through modulating effects on the gut-brain axis, probiotics are an effective adjuvant treatment for Alzheimer’s disease (AD), one of our century’s most important medical care challenges (Agahi et al. Front Neurol 9:662, 2018). This trial aimed to examine the effects of two different single-strain probiotics on oxidative stress and inflammation in patients with mild and moderate AD. This was a 12-week placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized clinical trial performed on 90 patients with AD. Eligible patients were randomly assigned to two different interventions (Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus HA-114 (7.5 × 109) or Bifidobacterium longum R0175 (7.5 × 109)) and a placebo group, supplemented twice daily. We used mixed-effect models to examine the probiotic’s independent effects on clinical results. Significant improvements in serum inflammatory and oxidative stress markers were observed at the end of the trial (P < 0.05). Probiotic supplementation for 12 weeks had beneficial effects on oxidative stress, inflammation, quality of life, and physical activity in patients with mild and moderate AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data produced or examined during the research are included in this article. For additional information, please contact the corresponding author.
References
Agahi A, Hamidi GA, Daneshvar R, Hamdieh M, Soheili M, Alinaghipour A et al (2018) Does severity of Alzheimer’s disease contribute to its responsiveness to modifying gut microbiota? A double blind clinical trial. Front Neurol 9:662
Akbari E, Asemi Z, Daneshvar Kakhaki R, Bahmani F, Kouchaki E, Tamtaji OR et al (2016) Effect of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function and metabolic status in Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized, double-blind and controlled trial. Front Aging Neurosci 8:256
Akhgarjand C, Vahabi Z, Shab-Bidar S, Etesam F, Djafarian K (2022) Effects of probiotic supplements on cognition, anxiety, and physical activity in subjects with mild and moderate Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled study. Front Aging Neurosci 14:1032494
Arora K, Green M, Prakash S (2020) The microbiome and Alzheimer’s disease: potential and limitations of prebiotic, synbiotic, and probiotic formulations. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:537847
Athari Nik Azm S, Djazayeri A, Safa M, Azami K, Djalali M, Sharifzadeh M et al (2017) Probiotics improve insulin resistance status in an experimental model of Alzheimer’s disease. Med J Islam Repub Iran 31:103
Athari Nik Azm S, Djazayeri A, Safa M, Azami K, Ahmadvand B, Sabbaghziarani F et al (2018) Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria ameliorate memory and learning deficits and oxidative stress in β-amyloid (1–42) injected rats. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 43(7):718–726
Bolengo F (2023) The intersecting worlds of Alzheimer's disease and Gut Microbiota: a narrative review
Bonfili L, Cecarini V, Cuccioloni M, Angeletti M, Berardi S, Scarpona S et al (2018) SLAB51 probiotic formulation activates SIRT1 pathway promoting antioxidant and neuroprotective effects in an AD mouse model. Mol Neurobiol 55(10):7987–8000
Cammann D, Lu Y, Cummings MJ, Zhang ML, Cue JM, Do J et al (2023) Genetic correlations between Alzheimer’s disease and gut microbiome genera. Sci Rep 13(1):5258
Chen X-X, Zeng M-X, Cai D, Zhou H-H, Wang Y-J, Liu Z (2023) Correlation between APOE4 gene and gut microbiota in Alzheimer’s disease. Benef Microbes 14(4):349–360
Chudzik A, Orzyłowska A, Rola R, Stanisz GJ (2021) Probiotics, prebiotics and postbiotics on mitigation of depression symptoms: modulation of the brain–gut–microbiome axis. Biomolecules 11(7):1000
D’Argenio V, Sarnataro D (2021) Probiotics, prebiotics and their role in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res 16(9):1768–1769
Den H, Dong X, Chen M, Zou Z (2020) Efficacy of probiotics on cognition, and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in adults with Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment—a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Aging (albany, NY) 12(4):4010
Dinan TG, Stanton C, Cryan JF (2013) Psychobiotics: a novel class of psychotropic. Biol Psychiat 74(10):720–726
Distrutti E, O’Reilly J-A, McDonald C, Cipriani S, Renga B, Lynch MA et al (2014) Modulation of intestinal microbiota by the probiotic VSL# 3 resets brain gene expression and ameliorates the age-related deficit in LTP. PLoS ONE 9(9):e106503
Erny D, Hrabě de Angelis AL, Jaitin D, Wieghofer P, Staszewski O, David E et al (2015) Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat Neurosci 18(7):965–977
Feldman H, Scheltens P, Scarpini E, Hermann N, Mesenbrink P, Mancione L et al (2004) Behavioral symptoms in mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 62(7):1199–1201
Fredua-Agyeman M, Stapleton P, Basit AW, Gaisford S (2017) Microcalorimetric evaluation of a multi-strain probiotic: interspecies inhibition between probiotic strains. J Funct Foods 36:357–361
Ibrahim A, Ali RAR, Manaf MRA, Ahmad N, Tajurruddin FW, Qin WZ et al (2020) Multi-strain probiotics (Hexbio) containing MCP BCMC strains improved constipation and gut motility in Parkinson’s disease: a randomised controlled trial. PLoS ONE 15(12):e0244680
Karttunen K, Karppi P, Hiltunen A, Vanhanen M, Välimäki T, Martikainen J et al (2011) Neuropsychiatric symptoms and quality of life in patients with very mild and mild Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 26(5):473–482
Kazemi A, Noorbala AA, Azam K, Eskandari MH, Djafarian K (2019) Effect of probiotic and prebiotic vs placebo on psychological outcomes in patients with major depressive disorder: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr 38(2):522–528
Kim G, Kim J, Rhie S, Yoon S (2015) The role of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Neurobiol 24:325
Li X, Hu D, Tian Y, Song Y, Hou Y, Sun L et al (2020) Protective effects of a novel Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain with probiotic characteristics against lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct 11(7):5799–5814
McFarland LV (2021) Efficacy of single-strain probiotics versus multi-strain mixtures: systematic review of strain and disease specificity. Dig Dis Sci 66(3):694–704
Missotten P, Squelard G, Ylieff M, Di Notte D, Paquay L, De Lepeleire J et al (2008) Relationship between quality of life and cognitive decline in dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 25(6):564–572
Mohammadi G, Dargahi L, Peymani A, Mirzanejad Y, Alizadeh SA, Naserpour T et al (2019) The effects of probiotic formulation pretreatment (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) on a lipopolysaccharide rat model. J Am Coll Nutr 38(3):209–217
Musa NH, Mani V, Lim SM, Vidyadaran S, Majeed ABA, Ramasamy K (2017) Lactobacilli-fermented cow’s milk attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and memory impairment in vitro and in vivo. J Dairy Res 84(4):488–495
Nandi A, Counts N, Chen S, Seligman B, Tortorice D, Vigo D et al (2022) Global and regional projections of the economic burden of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias from 2019 to 2050: a value of statistical life approach. EClinicalMedicine 51:101580
Oelschlaeger TA (2010) Mechanisms of probiotic actions—a review. Int J Med Microbiol 300(1):57–62
Peters K, Rockwood K, Black S, Bouchard R, Gauthier S, Hogan D et al (2006) Characterizing neuropsychiatric symptoms in subjects referred to dementia clinics. Neurology 66(4):523–528
Rodes L, Khan A, Paul A, Coussa-Charley M, Marinescu D, Tomaro-Duchesneau C et al (2013) Effect of probiotics Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium on gut-derived lipopolysaccharides and inflammatory cytokines: an in vitro study using a human colonic microbiota model. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(4):518–526
Scheltens P, Blennow K, Breteler MM, de Strooper B, Frisoni GB, Salloway S et al (2016) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet (london, England) 388(10043):505–517
Scheltens P, De Strooper B, Kivipelto M, Holstege H, Chételat G, Teunissen CE et al (2021) Alzheimer’s disease. The Lancet 397(10284):1577–1590
Selvarajah D, Wilkinson ID, Davies J, Gandhi R, Tesfaye S (2011) Central nervous system involvement in diabetic neuropathy. Curr DiabRep 11(4):310–322
Tekin S, Fairbanks LA, O’Connor S, Rosenberg S, Cummings JL (2001) Activities of daily living in Alzheimer’s disease: neuropsychiatric, cognitive, and medical illness influences. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 9(1):81–86
Zhan X, Stamova B, Sharp FR (2018) Lipopolysaccharide associates with amyloid plaques, neurons and oligodendrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease brain: a review. Front Aging Neurosci 10:42
Zhan Y, Al-Nusaif M, Ding C, Zhao L, Dong C (2023) The potential of the gut microbiome for identifying Alzheimer’s disease diagnostic biomarkers and future therapies. Front Neurosci 17:1130730
Zhang R, Miller RG, Gascon R, Champion S, Katz J, Lancero M et al (2009) Circulating endotoxin and systemic immune activation in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (sALS). J Neuroimmunol 206(1–2):121–124
Zhang X-X, Tian Y, Wang Z-T, Ma Y-H, Tan L, Yu J-T (2021) The epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease modifiable risk factors and prevention. J Prev Alzheimer’s Dis 8:313–321
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from Tehran University of Medical Science. The authors appreciate all participants and the staff of Ziaeeian, Roozbeh and Shariati Hospital.
Funding
This study did not receive any funding from public, commercial, or not-for-profit entities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KD takes responsibility for the accuracy and integrity of the research. CA and ZV were responsible for composing the manuscript, while SSB and CA gathered the data. SSB reviewed and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akhgarjand, C., Vahabi, Z., Shab-Bidar, S. et al. The effects of probiotic supplements on oxidative stress and inflammation in subjects with mild and moderate Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Inflammopharmacol 32, 1413–1420 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01427-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01427-2