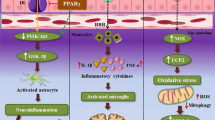
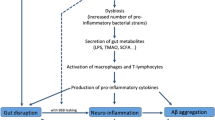
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by dementia and the accumulation of amyloid beta in the brain. Recently, microbial dysbiosis has been identified as one of the major factors involved in the onset and progression of AD. Imbalance in gut microbiota is known to affect central nervous system (CNS) functions through the gut-brain axis and involves inflammatory, immune, neuroendocrine and metabolic pathways. An altered gut microbiome is known to affect the gut and BBB permeability, resulting in imbalance in levels of neurotransmitters and neuroactive peptides/factors. Restoration of levels of beneficial microorganisms in the gut has demonstrated promising effects in AD in pre-clinical and clinical studies. The current review enlists the important beneficial microbial species present in the gut, the effect of their metabolites on CNS, mechanisms involved in dysbiosis related to AD and the beneficial effects of probiotics on AD. It also highlights challenges involved in large-scale manufacturing and quality control of probiotic formulations.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analysed in this study.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- GABA:
-
gamma amino butyric acid
- SCFA:
-
short-chain fatty acids
- COX-2:
-
cyclooxygenase-2
- FMT:
-
faecal microbiota transplantation
- Aβ:
-
β-amyloid
- TLR2:
-
toll-like receptor-2
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase activator protein-1
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- NMDAR:
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
- BDNF:
-
brain-derived neurotropic factor
- BBB:
-
blood-brain barrier
- TGF β:
-
transforming growth factor beta
- TNF-α:
-
tumour necrosis factor alpha
- IL:
-
interleukin
- HPA:
-
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal
- DALYs:
-
disability-adjusted life years
References
2021 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures (2021) Alzheimers Dement 17:327–406
Aeron G, Morya S (2017) Probiotics as therapeutics. J Adv Res Biotechnol 2:1–6
Ahmad W, Ijaz B, Shabbiri K et al (2017) Oxidative toxicity in diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease: mechanisms behind ROS/ RNS generation. J Biomed Sci 24:1–10
Ait-Belgnaoui A, Durand H, Cartier C et al (2012) Prevention of gut leakiness by a probiotic treatment leads to attenuated HPA response to an acute psychological stress in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 37:1885–1895
Altaib H, Badr Y, Suzuki T (2021) Bifidobacteria and psychobiotic therapy: current evidence and future prospects. Rev Agricult Sci 9:74–91
Amorim Neto DP, Bosque BP, de Pereira Godoy JV et al (2022) Akkermansia muciniphila induces mitochondrial calcium overload and α -synuclein aggregation in an enteroendocrine cell line. iScience; 25. Epub ahead of print 3 March. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ISCI.2022.103908
Armstrong RA (2019) Risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. Folia Neuropathol 57:87–105
Arora K, Green M, Prakash S (2020) The microbiome and Alzheimer’s disease: potential and limitations of prebiotic, synbiotic, and probiotic formulations. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:1411
Arumugam M, Raes J, Pelletier E et al (2011) Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 473:174
Asaoka D, Xiao J, Takeda T et al (2022) Effect of probiotic Bifidobacterium breve in improving cognitive function and preventing brain atrophy in older patients with suspected mild cognitive impairment: results of a 24-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Alzheimers Dis 88:1–21
Azam S, Jakaria M, Kim IS et al (2019) Regulation of toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway by polyphenols in the treatment of age-linked neurodegenerative diseases: focus on TLR4 signaling. Front Immunol 10:1000
Bäuerl C, Collado MC, Diaz Cuevas A et al (2018) Shifts in gut microbiota composition in an APP/PSS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease during lifespan. Lett Appl Microbiol 66:464–471
Bedu-Ferrari C, Biscarrat P, Langella P et al (2022) Prebiotics and the human gut microbiota: from breakdown mechanisms to the impact on metabolic health. Nutrients 14:2096
Bello-Medina PC, Hernández-Quiroz F, Pérez-Morales M et al (2021) Spatial memory and gut microbiota alterations are already present in early adulthood in a pre-clinical transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci; 15. Epub ahead of print 29 April. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.595583
Bercik P, Denou E, Collins J et al (2011) The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology; 141. Epub ahead of print. https://doi.org/10.1053/J.GASTRO.2011.04.052
Blennow K, de Leon MJ, Zetterberg H (2006) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 368:387–403
Bonfili L, Cecarini V, Gogoi O et al (2020) Gut microbiota manipulation through probiotics oral administration restores glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 87:35–43
Bravo JA, Forsythe P, Chew MV et al (2011) Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:16050–16055
Bull MJ, Plummer NT (2014) Part 1: The human gut microbiome in health and disease. Integ Med: Clinician’s J 13:17
Chen Y, Xu J, Chen Y (2021) Regulation of neurotransmitters by the gut microbiota and effects on cognition in neurological disorders. Nutrients; 13. Epub ahead of print 1 June 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU13062099
Coman V, Vodnar DC (2020) Gut microbiota and old age: modulating factors and interventions for healthy longevity. Exp Gerontol; 141. Epub ahead of print 1 November. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EXGER.2020.111095
Dando SJ, Mackay-Sim A, Norton R et al (2014) Pathogens penetrating the central nervous system: infection pathways and the cellular and molecular mechanisms of invasion. Clin Microbiol Rev 27:691–726
Davani-Davari D, Negahdaripour M, Karimzadeh I, et al. (2019) Prebiotics: definition, types, sources, mechanisms, and clinical applications. Foods; 8. Epub ahead of print 1 March 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/FOODS8030092
Dementia statistics | Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI), https://www.alzint.org/about/dementia-facts-figures/dementia-statistics/
Deng H, Dong X, Chen M et al (2020) Efficacy of probiotics on cognition, and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in adults with Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment — a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Aging (Albany NY) 12:4010
Du X, Wang X, Geng M (2018) Alzheimer’s disease hypothesis and related therapies. Transl Neurodegener; 7. Epub ahead of print 30 January. https://doi.org/10.1186/S40035-018-0107-Y
Durack J, Lynch SV (2019) The gut microbiome: relationships with disease and opportunities for therapy. J Exp Med 216:20
Feigin VL, Nichols E, Alam T et al (2019) Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol 18:459
Ferro A, Auguste YSS, Cheadle L (2021) Microglia, cytokines, and neural activity: unexpected interactions in brain development and function. Front Immunol 12:2546
Galland L (2014) The gut microbiome and the brain. J Med Food 17:1261
Geng S, Yang L, Cheng F et al (2020) Gut microbiota are associated with psychological stress-induced defections in intestinal and blood–brain barriers. Front Microbiol 10:3067
Gomaa EZ (2020) Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: a review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 113:2019–2040
Guerreiro CS, Calado Â, Sousa J et al (2018) Diet, microbiota, and gut permeability-the unknown triad in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Med (Lausanne) 5:349
Guinane CM, Cotter PD (2013) Role of the gut microbiota in health and chronic gastrointestinal disease: understanding a hidden metabolic organ. Ther Adv Gastroenterol 6:295
Gupta V, Garg R (2009) Probiotics. Indian J Med Microbiol 27:202–209
Hakansson A, Molin G (2011) Gut microbiota and inflammation. Nutrients 3:637
Hasan N, Yang H (2019) Factors affecting the composition of the gut microbiota, and its modulation. Peer J; 7. Epub ahead of print. https://doi.org/10.7717/PEERJ.7502
Hassel B, Dahlberg D, Mariussen E et al (2014) Brain infection with Staphylococcus aureus leads to high extracellular levels of glutamate, aspartate, γ-aminobutyric acid, and zinc. J Neurosci Res 92:1792–1800
Ho L, Ono K, Tsuji M et al (2018) Protective roles of intestinal microbiota derived short chain fatty acids in Alzheimer’s disease-type beta-amyloid neuropathological mechanisms. Expert Rev Neurother 18:83–90
Holzer P, Farzi A (2014) Neuropeptides and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Adv Exp Med Biol 817:196–219
Houser MC, Tansey MG (2017) The gut-brain axis: is intestinal inflammation a silent driver of Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis? npj Parkinson’s Disease 3:1 2017; 3: 1–9
Islam SU (2016) Clinical uses of probiotics. Medicine 95:e2658
Jiang C, Li G, Huang P et al (2017) The gut microbiota and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 58:1–15
Kar F, Hacioglu C, Kar E et al (2022) Probiotics ameliorates LPS induced neuroinflammation injury on Aβ 1-42, APP, γ-β secretase and BDNF levels in maternal gut microbiota and fetal neurodevelopment processes. Metab Brain Dis. Epub ahead of print. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11011-022-00964-Z
Kaur H, Bose C, Mande SS (2019) Tryptophan metabolism by gut microbiome and gut-brain-axis: an in silico analysis. Front Neurosci 13:1365
Kaur H, Nagamoto-Combs K, Golovko S et al (2020) Probiotics ameliorate intestinal pathophysiology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 92:114–134
Kelly JR, Kennedy PJ, Cryan JF et al (2015) Breaking down the barriers: the gut microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric disorders. Front Cell Neurosci 9:392
Khalifeh M, Read MI, Barreto GE et al (2020) Trehalose against Alzheimer’s disease: insights into a potential therapy. Bioessays; 42. Epub ahead of print 1 August. https://doi.org/10.1002/BIES.201900195
Kho ZY, Lal SK (2018) The human gut microbiome - a potential controller of wellness and disease. Front Microbiol 9:1835
Kim CS, Cha L, Sim M et al (2021b) Probiotic supplementation improves cognitive function and mood with changes in gut microbiota in community-dwelling older adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 76:32–40
Kim H, Kim S, Park SJ et al (2021a) Administration of Bifidobacterium bifidum BGN4 and Bifidobacterium longum BORI improves cognitive and memory function in the mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci; 13. Epub ahead of print 6 August. https://doi.org/10.3389/FNAGI.2021.709091
Kim MS, Kim Y, Choi H et al (2020) Transfer of a healthy microbiota reduces amyloid and tau pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease animal model. Gut 69:283–294
Kobayashi Y, Kinoshita T, Matsumoto A et al (2019b) Bifidobacterium Breve A1 supplementation improved cognitive decline in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: an open-label, single-arm study. J Prev Alzheimers Dis 6:70–75
Kobayashi Y, Kuhara T, Oki M et al (2019a) Effects of Bifidobacterium breve A1 on the cognitive function of older adults with memory complaints: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Benefic Microbes 10:511–520
Kobayashi Y, Sugahara H, Shimada K et al (2017) Therapeutic potential of Bifidobacterium breve strain A1 for preventing cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Scientific Reports; 7: 1–10
Krüger JF, Hillesheim E, Pereira ACSN et al (2021) Probiotics for dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Rev 79:160–170
Lee DY, Shin YJ, Kim JK et al (2021) Alleviation of cognitive impairment by gut microbiota lipopolysaccharide production-suppressing Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium longum in mice. Food Funct 12:10750–10763
Li Z, Zhu H, Guo Y et al (2020) Gut microbiota regulate cognitive deficits and amyloid deposition in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 155:448–461
Limon A, Reyes-Ruiz JM, Miledi R (2012) Loss of functional GABA A receptors in the Alzheimer diseased brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:10071–10076
Liu J, Chang L, Song Y et al (2019) The role of NMDA receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci 13:43
Liu S, Gao J, Zhu M et al (2020) Gut microbiota and dysbiosis in Alzheimer’s disease: implications for pathogenesis and treatment. Mol Neurobiol 57:5026
Lupien SJ, McEwen BS, Gunnar MR et al (2009) Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:434–445
Madison A, Kiecolt-Glaser JK (2019) Stress, depression, diet, and the gut microbiota: human–bacteria interactions at the core of psychoneuroimmunology and nutrition. Curr Opin Behav Sci 28:105
Marizzoni M, Cattaneo A, Mirabelli P et al (2020) Short-chain fatty acids and lipopolysaccharide as mediators between gut dysbiosis and amyloid pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 78:683–697
Markowiak-Kopeć P, Śliżewska K (2020) The effect of probiotics on the production of short-chain fatty acids by human intestinal microbiome. Nutrients; 12. Epub ahead of print 1 April. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU12041107
Mazzoli R, Pessione E (2016) The neuro-endocrinological role of microbial glutamate and GABA signaling. Front Microbiol; 7. Epub ahead of print 30 November 2016. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2016.01934
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (2002) Local neuroinflammation and the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. J NeuroVirolog 8:529–538
Miranda M, Morici JF, Zanoni MB et al (2019) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a key molecule for memory in the healthy and the pathological brain. Front Cell Neurosci 13:363
Misiak B, Łoniewski I, Marlicz W et al (2020) The HPA axis dysregulation in severe mental illness: can we shift the blame to gut microbiota? Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 102:109951
Morais LH, Schreiber HL, Mazmanian SK (2020) The gut microbiota–brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat Rev Microbiol 19:241–255
Morgan MJ, Liu ZG (2011) Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res 21:103
Mufson EJ, Counts SE, Perez SE et al (2014) Cholinergic system during the progression of Alzheimer’s disease: therapeutic implications 8: 1703–1718. https://doi.org/10.1586/147371758111703
Naomi R, Embong H, Othman F et al (2021) Probiotics for Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Nutrients; 14. Epub ahead of print 1 January. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU14010020
Ng TKS, Ho CSH, Tam WWS et al (2019) Decreased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci; 20. Epub ahead of print. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS20020257
Nishimori JH, Newman TN, Oppong GO et al (2012) Microbial amyloids induce interleukin 17A (IL-17A) and IL-22 responses via toll-like receptor 2 activation in the intestinal mucosa. Infect Immun 80:4398
Ohsawa K, Nakamura F, Uchida N et al (2018) Lactobacillus helveticus-fermented milk containing lactononadecapeptide (NIPPLTQTPVVVPPFLQPE) improves cognitive function in healthy middle-aged adults: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int J Food Sci Nutr 69:369–376
Padgett LE, Broniowska KA, Hansen PA et al (2013) The role of reactive oxygen species and proinflammatory cytokines in type 1 diabetes pathogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1281:16
Papadopoulos G, Weinberg EO, Massari P et al (2013) Macrophage-specific TLR2 signaling mediates pathogen-induced TNF-dependent inflammatory oral bone loss. J Immunol Auth Choi 190:1148
Park SJ, Kim DH, Kang HJ et al. (2021) Enhanced production of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) using Lactobacillus plantarum EJ2014 with simple medium composition. LWT; 137. Epub ahead of print 1 February 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LWT.2020.110443
Picciotto MR, Higley MJ, Mineur YS (2012) Acetylcholine as a neuromodulator: cholinergic signaling shapes nervous system function and behavior. Neuron 76:116
Quigley EMM (2017) Microbiota-brain-gut axis and neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep; 17. Epub ahead of print 1 December. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11910-017-0802-6
Quigley EMM (2019) Prebiotics and probiotics in digestive health. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:333–344
Rai SN, Tiwari N, Singh P et al (2021) Therapeutic potential of vital transcription factors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease with particular emphasis on transcription factor EB mediated autophagy. Front Neurosci 15:1703
Rinninella E, Raoul P, Cintoni M et al (2019) What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 7:14
Rodríguez JJ, Olabarria M, Chvatal A et al (2009) Astroglia in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death & Differentiation 16:3 2008; 16: 378–385
Ronald de Kloet E, Schmidt M, Meijer OC (2005) Corticosteroid receptors and HPA-axis regulation. Techniq Behav Neural Sci 15:265–294
Ruiz L, Delgado S, Ruas-Madiedo P et al (2017) Bifidobacteria and their molecular communication with the immune system. Front Microbiol 8:2345
Russell WR, Hoyles L, Flint HJ et al (2013) Colonic bacterial metabolites and human health. Curr Opin Microbiol 16:246–254
Rutsch A, Kantsjö JB, Ronchi F (2020) The gut-brain axis: how microbiota and host inflammasome influence brain physiology and pathology. Front Immunol 11:3237
Saeedi M, Rashidy-Pour A (2021) Association between chronic stress and Alzheimer’s disease: therapeutic effects of Saffron. Biomed Pharmacother 133:110995
Saify ZS, Sultana N (2014) Role of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and Alzheimer disease. Drug Design Discov Alzheimer’s Dis:387–425
Salleh RM, Kuan G, Aziz MNA et al (2021) Effects of probiotics on anxiety, stress, mood and fitness of badminton players. Nutrients; 13. Epub ahead of print 1 June. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU13061783
Savignac HM, Corona G, Mills H et al (2013) Prebiotic feeding elevates central brain derived neurotrophic factor, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits and d-serine. Neurochem Int 63:756
Saxelin M (2008) Probiotic formulations and applications, the current probiotics market, and changes in the marketplace: a European perspective. Clin Infect Dis; 46 Suppl 2. Epub ahead of print 1 February. https://doi.org/10.1086/523337
Schindowski K, Belarbi K, Buée L (2008) Neurotrophic factors in Alzheimer’s disease: role of axonal transport. Genes Brain Behav 7:43
Shamsipour S, Sharifi G, Taghian F (2021) Impact of interval training with probiotic (L. plantarum / Bifidobacterium bifidum) on passive avoidance test, ChAT and BDNF in the hippocampus of rats with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett; 756. Epub ahead of print 21 June. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEULET.2021.135949
Sheffler ZM, Reddy V, Pillarisetty LS (2022) Physiology, neurotransmitters. StatPearls, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539894/ (2022, accessed 15 July 2022)
Shen L, Ji HF (2019) Associations between gut microbiota and Alzheimer’s disease: current evidences and future therapeutic and diagnostic perspectives. J Alzheimers Dis 68:25–31
Sheng JA, Bales NJ, Myers SA et al (2021) The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: development, programming actions of hormones, and maternal-fetal interactions. Front Behav Neurosci 14:256
Silva YP, Bernardi A, Frozza RL (2020) The role of short-chain fatty acids from gut microbiota in gut-brain communication. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11:25
Singh AK, Rai SN, Maurya A, et al (2021a) Therapeutic potential of phytoconstituents in management of Alzheimer’s disease. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine; 2021. Epub ahead of print. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5578574
Singh AK, Sen SS, Rathore AS et al (2021b) Lipid-coated MCM-41 mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with berberine improved inhibition of acetylcholine esterase and amyloid formation. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 7:3737–3753
Stephens MAC, Wand G (2012) Stress and the HPA axis: role of glucocorticoids in alcohol dependence. Alcohol Res 34:468
Stoeva MK, Garcia-So J, Justice N et al (2021) Butyrate-producing human gut symbiont, Clostridium butyricum, and its role in health and disease. Gut Microbes 13:1–28
Sultana R, Butterfield DA (2010) Role of oxidative stress in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 19:341–353
Sun J, Xu J, Ling Y, et al (2019) Fecal microbiota transplantation alleviated Alzheimer’s disease-like pathogenesis in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Translational Psychiatry 9:1 2019; 9: 1–13
Sun J, Xu J, Yang B, et al (2020) Effect of Clostridium butyricum against microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease via regulating gut microbiota and metabolites butyrate. Mol Nutr Food Res; 64. Epub ahead of print 1 January. https://doi.org/10.1002/MNFR.201900636
Tamtaji OR, Heidari-soureshjani R, Mirhosseini N et al (2019) Probiotic and selenium co-supplementation, and the effects on clinical, metabolic and genetic status in Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Clin Nutr 38:2569–2575
Tarawneh R, Penhos E (2022) The gut microbiome and Alzheimer’s disease: complex and bidirectional interactions. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 141:104814
Thursby E, Juge N (2017) Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem J 474:1823
Ton AMM, Campagnaro BP, Alves GA, et al (2020) Oxidative stress and dementia in Alzheimer’s patients: effects of synbiotic supplementation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. Epub ahead of print 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2638703
Tyszkowski R, Mehrzad R (2023) Inflammation: a multifaceted and omnipresent phenomenon. Inflammation and Obesity: A New and Novel Approach to Manage Obesity and its Consequences; 19–30
Umeno A, Biju V, Yoshida Y (2017) In vivo ROS production and use of oxidative stress-derived biomarkers to detect the onset of diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and diabetes. Free Radic Res 51:413–427. https://doi.org/10.1080/1071576220171315114
Vagnerová K, Vodička M, Hermanová P et al (2019) Interactions between gut microbiota and acute restraint stress in peripheral structures of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis and the intestine of male mice. Front Immunol 10:2655
Varatharaj A, Galea I (2017) The blood-brain barrier in systemic inflammation. Brain Behav Immun 60:1–12
Wang H, Lee IS, Braun C et al (2016) Effect of probiotics on central nervous system functions in animals and humans: a systematic review. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 22:589
Wang R, Reddy PH (2017) Role of glutamate and NMDA receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 57:1041
Wang WY, Tan MS, Yu JT et al (2015) Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Transl Med 3:136
Wang X, Zhang P, Zhang X (2021) Probiotics regulate gut microbiota: an effective method to improve immunity. Molecules; 26. Epub ahead of print 1 October . https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES26196076
Wieërs G, Belkhir L, Enaud R et al (2019) How probiotics affect the microbiota. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 9:454
Won E, Kim Y-K (2016) Stress, the autonomic nervous system, and the immune-kynurenine pathway in the etiology of depression. Curr Neuropharmacol 14:665
Xiao J, Katsumata N, Bernier F et al (2020) Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve in improving cognitive functions of older adults with suspected mild cognitive impairment: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Alzheimers Dis 77:139
Xu Q, Wen L, Wei G, et al (2022) Marked response of rat ileal and colonic microbiota after the establishment of Alzheimer’s disease model with bilateral intraventricular injection of Aβ (1-42). Front Microbiol; 13. Epub ahead of print 11 February. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2022.819523
Yaghoubfar R, Behrouzi A, Ashrafian F, et al (2020) Modulation of serotonin signaling/metabolism by Akkermansia muciniphila and its extracellular vesicles through the gut-brain axis in mice. Scientific Reports 10:1 2020; 10: 1–12
Zecca C, Pasculli G, Tortelli R et al (2021) The role of age on beta-amyloid1–42 plasma levels in healthy subjects. Front Aging Neurosci 13:563
Zhai S, Zhu L, Qin S, et al (2018) Effect of lactulose intervention on gut microbiota and short chain fatty acid composition of C57BL/6J mice. Microbiologyopen; 7. Epub ahead of print 1 December. https://doi.org/10.1002/MBO3.612
Zhang N, Zhang Y, Li M, et al (2020) Efficacy of probiotics on stress in healthy volunteers: a systematic review and meta-analysis based on randomized controlled trials. Brain Behav; 10. Epub ahead of print 1 September. https://doi.org/10.1002/BRB3.1699
Zhao Y, Dua P, Lukiw WJ (2015) Microbial sources of amyloid and relevance to amyloidogenesis and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism 5:177
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Quan M et al (2021) Gut microbiota changes and their correlation with cognitive and neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 81:583–595
Zhu G, Zhao J, Zhang H, et al. (2021) Administration of Bifidobacterium breve improves the brain function of Aβ 1-42-treated mice via the modulation of the gut microbiome. Nutrients; 13. Epub ahead of print 1 May 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU13051602
Zhu X, Han Y, Du J et al (2017) Microbiota-gut-brain axis and the central nervous system. Oncotarget 8:53829
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Shobhaben Pratapbhai Patel School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM’s NMIMS for providing the infrastructural facilities.
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Central Council for Research in Unani Medicine, Ministry of AYUSH (3-18/2021-CCRUM/Tech).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Amisha Vora and Ginpreet Kaur made the draft of the review. Ami Thakkar and Amisha Vora contributed by doing literature searches and preparing a manuscript draft. Amisha Vora, Jamal Akhtar and Ginpreet Kaur revised and approved the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version. The authors confirm that no paper mill and artificial intelligence was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thakkar, A., Vora, A., Kaur, G. et al. Dysbiosis and Alzheimer’s disease: role of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396, 2911–2923 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02554-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02554-x