Abstract
Background
Myocardial infarction (MI), commonly referred to as a heart attack, occurs when the blood flow to a portion of the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. In this study, we scrutinized the cardioprotective effect of gypenoside against the isoproterenol (ISO)-induced myocardial injury (MI) in the rats.
Methods
Wistar rats were divided into four groups as follow: normal, gypenoside (10 mg/kg), ISO control, and ISO control treated with the gypenoside (2.5, 5, and 10 mg/kg). Various parameters were estimated such as infract size, hemodynamic, inflammatory, antioxidant, cardiac, cytokines, and apoptotic markers. We also estimated the gut microbiota in the faces of the experimental rats. Finally, heart tissue histopathology performed.
Result
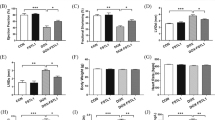
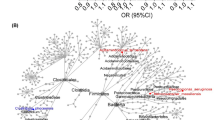
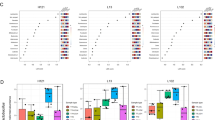
Dose-dependent treatment of gypenoside significantly (P < 0.001) reduced the infracted size along with suppression of the heart weight and heart ratio along with enhance the body weight. Gypenoside treatment considerably altered the level of cardiac parameters, cardiac membrane stabilizing enzyme, hemodynamic parameters, antioxidant, lipid parameters, hepatic parameters, renal parameters, inflammatory cytokines, and mediators. Gypenoside significantly (P < 0.001) suppressed the level of apoptotic markers such as caspase-3, caspase-6, and caspase-9. Gypenoside significantly (P < 0.001) altered the relative abundance of unclassified bacteria, Tenericutes, Candidatus_Saccharibacteria, Verrucomicrobia, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes and suppressed the ratio of F/B.
Conclusion
Gypenoside acts as a protective phytoconstituents against the ISO-induced myocardial infraction in the rats via alteration of gut microbiota, inflammatory, and oxidative stress.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data available can be provided upon a request to corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abukhalil MH, Hussein OE, Aladaileh SH et al (2021) Visnagin prevents isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation and upregulating Nrf2 signaling in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22906
Alabi BA, Omobowale TO, Oyagbemi A et al (2020) Corchorus olitorius extract attenuate isoproterenol-induced cardiac injury via inhibition of oxidative stress, arrhythmia and pro-apoptotic protein bax expression. J Complement Altern Med Res. https://doi.org/10.9734/jocamr/2020/v10i230159
Anwar F, Alhayyani S, Al-Abbasi FA et al (2022) Pharmacological role of Vitamin C in stress-induced cardiac dysfunction via alteration in Gut microbiota. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22986
Bhattacharjee S, Elancheran R, Dutta K et al (2022) Cardioprotective potential of the antioxidant-rich bioactive fraction of Garcinia pedunculata Roxb. ex Buch.-Ham. against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in Wistar rats. Front Pharmacol 13:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1009023
Biswas L, Zeng Z, Graham A, Shu X (2020) Gypenosides mediate cholesterol efflux and suppress oxidized LDL induced inflammation in retinal pigment epithelium cells. Exp Eye Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2020.107931
Çetin E (2019) Pretreatment with β-glucan attenuates isoprenaline-induced myocardial injury in rats. Exp Physiol 104:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1113/EP086739
Chen Y, Peng L, Shi S et al (2021) Boeravinone B alleviates gut dysbiosis during myocardial infarction-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. J Cell Mol Med 25:6403–6416. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.16620
Cheng G, Zhang J, Jia S et al (2022) Cardioprotective effect of gossypin against myocardial ischemic/reperfusion in rats via alteration of oxidative stress, inflammation and gut microbiota. J Inflamm Res 15:1637–1651. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S348883
Cinar I, Yayla M, Tavaci T et al (2022) In Vivo and in vitro cardioprotective effect of gossypin against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction injury. Cardiovasc Toxicol 22:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-021-09698-3
Circosta C, De Pasquale R, Occhiuto F (2005) Cardiovascular effects of the aqueous extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino. Phytomedicine 12:638–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2004.06.023
D’Oria R, Schipani R, Leonardini A, et al (2020) The role of oxidative stress in cardiac disease: from physiological response to injury factor. Oxid Med. Cell Longev
Du H, Bai J, Wang J et al (2019) Assessment of the hepatocyte protective effects of gypenoside and its phosphorylated derivative against DHAV-1 infection on duck embryonic hepatocytes. BMC Vet Res. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-019-1891-z
Fathiazad F, Tamarzadeh N, Alsos D et al (2019) The effect of astragaloside IV on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Pharm Sci 25:100–110. https://doi.org/10.15171/PS.2019.16
Forkosh E, Ilan Y (2019) The heart-gut axis: New target for atherosclerosis and congestive heart failure therapy. Open Heart. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2018-000993
Gao Y, Song G, Cao YJ et al (2019) The Guizhi Gancao decoction attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing inflammation and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1947465
Ghartavol MM, Gholizadeh-Ghaleh Aziz S, Babaei G et al (2019) The protective impact of betaine on the tissue structure and renal function in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rat. Mol Genet Genomic Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.579
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J et al (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-X
Han Y, Gong Z, Sun G et al (2021) Dysbiosis of gut microbiota in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.680101
Huang H, Geng Q, Yao H et al (2018) Protective effect of scutellarin on myocardial infarction induced by isoprenaline in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 21:267–276. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2018.26110.6415
Ibrahim MA, Geddawy A, Abdel-Wahab S (2018) Sitagliptin prevents isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats by modulating nitric oxide synthase enzymes. Eur J Pharmacol 829:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.04.005
Islam D, Banerjee Shanta M, Akhter S et al (2020) Cardioprotective effect of garlic extract in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in a rat model: assessment of pro-apoptotic caspase-3 gene expression. Clin Phytosci. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-020-00199-4
Jia G, Zao M, Liu X (2017) Protective effect of diethylcarbamazine inhibits NF-κB activation in isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial infarction rat model through the PARP pathway. Mol Med Rep 16:1596–1602. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6695
Kocak C, Kocak FE, Akcilar R et al (2016) Molecular and biochemical evidence on the protective effects of embelin and carnosic acid in isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial injury in rats. Life Sci 147:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.01.038
Kumar M, Kasala ER, Bodduluru LN et al (2016) Baicalein protects isoproterenol induced myocardial ischemic injury in male Wistar rats by mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation. Inflamm Res 65:613–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-0944-z
Liang WL, Cai MR, Zhang MQ, et al (2021) Chinese herbal medicine alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Evidence-based complement. Altern Med
Mastinu A, Bonini SA, Premoli M et al (2021) Protective effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Var. ginpent) against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and motor alteration in mice. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030570
Mnafgui K, Hajji R, Derbali F et al (2016) Protective effect of hydroxytyrosol against cardiac remodeling after isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rat. Cardiovasc Toxicol 16:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-015-9323-1
Mohamed D, Mabrok H, Abdelgayed S, Elbakry H (2021a) Cardioprotective potency of anthocyanin-rich extract of red cabbage against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in experimental animals. J Appl Pharm Sci 11:22–30. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2021.110804
Mohamed ME, Abduldaium MS, Younis NS (2021b) Cardioprotective effect of linalool against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction. Life 11:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11020120
Naqvi S, Asar TO, Kumar V et al (2021) A cross-talk between gut microbiome, salt and hypertension. Biomed Pharmacother 134:111156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111156
Neto JC, Paulino ET, Rodrigues AKBF et al (2022) Cardioprotective effect of hydroalcoholic extract of Brazilian red propolis against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Phytomed plus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phyplu.2021.100190
Qiao S, Liu X, Chen L (2018) Gypenosides protect against cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Trop J Pharm Res 17:1591–1597. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v17i8.18
Sithuraj S, Viswanadha VP (2018) Berbamine protects the heart from isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction by modulating eNOS and iNOS expressions in rats. J Appl Biomed 16:301–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jab.2018.06.001
Stafford N, Assrafally F, Prehar S et al (2020) Signaling via the Interleukin-10 receptor attenuates cardiac hypertrophy in mice during pressure overload, but not isoproterenol infusion. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.559220
Sun W, Pan R, Song J, Sun H (2019) The effects of simvastatin preconditioning on the expression of caspase-3 after myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Exp Ther Med. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7164
Tamburini S, Shen N, Wu HC, Clemente JC (2016) The microbiome in early life: implications for health outcomes. Nat Med 22:713–722
Wong ZW, Thanikachalam PV, Ramamurthy S (2017) Molecular understanding of the protective role of natural products on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 94:1145–1166
Wu M, Lu S, Zhong J et al (2017) Protective effects of pterostilbene against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Inflammation 40:578–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0504-2
Young DS, Thomas DW, Friedman RB, Pestaner LC (1972) Effects of drugs on clinical laboratory tests. Clin Chem 18:1041–1303. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/18.10.1041
Yu H, Guan Q, Guo L et al (2016) Gypenosides alleviate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via attenuation of oxidative stress and preservation of mitochondrial function in rat heart. Cell Stress Chaperones 21:429–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-016-0669-5
Yuan Q, Chen R, Zheng X et al (2017a) Chinese herbal medicine Xinji pill protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Mol Med Rep 16:1551–1558. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6732
Yuan X, Xiang Y, Zhu N et al (2017b) Salvianolic acid a protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing platelet activation and inflammation. Exp Ther Med 14:961–966. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4619
Zaafan MA, Zaki HF, El-Brairy AI, Kenawy SA (2013) Protective effects of atorvastatin and quercetin on isoprenaline-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Bull Fac Pharm Cairo Univ 51:35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bfopcu.2013.03.001
Zhai XF, Zu ML, Wang YR et al (2021) Protective effects of four new saponins from Gynostemma pentaphyllum against hydrogen peroxide-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Bioorg Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104470
Zhang G, Zhao Z, Gao L et al (2011) Gypenoside attenuates white matter lesions induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 99:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2011.03.019
Zhang B, Wang H, Yang Z et al (2020) Protective effect of alpha-pinene against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction through NF-κB signaling pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol 39:1596–1606. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327120934537
Funding
The research was self-funded and has no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ conceptualized and performed the study, YZ, XZ, JZ, JD, SJ, PF, and PX analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. GC conceptualized the research, analyzed the data and critically reviewed the whole manuscript. All the authors read the draft and approved the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This research was approved by Shaanxi Provincial People's Hospital animal ethical committee, Approved No. Ethical no. XJTUAE2023-138.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhao, Y., Zhao, X. et al. Anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective effect of gypenoside against isoproterenol-induced cardiac remodeling in rats via alteration of inflammation and gut microbiota. Inflammopharmacol 31, 2731–2750 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01307-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01307-9